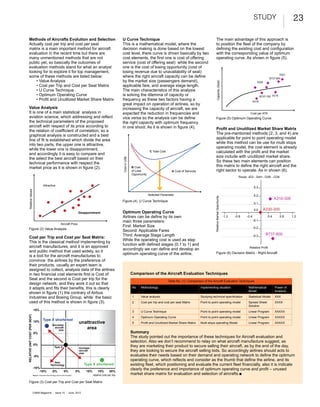
This document discusses various techniques for evaluating and selecting aircraft, including cost per trip and cost per seat matrices, the U curve technique, optimum operating curves, and profit and unutilized market share matrices. It notes that while manufacturers like Airbus and Boeing use cost matrices to promote their own aircraft, airlines should evaluate their own needs based on factors like demand and network to define the optimum aircraft using techniques like the optimum operating curve. The document compares the power of different evaluation techniques and notes the importance of these methods for aircraft selection.