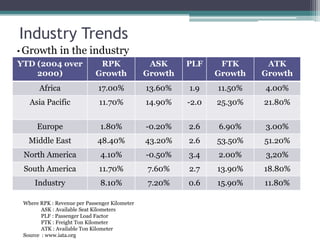
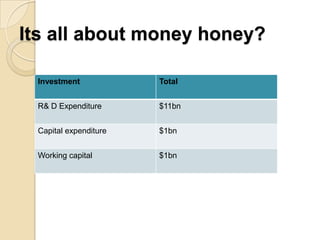
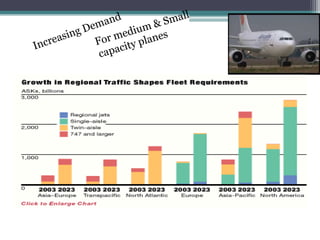
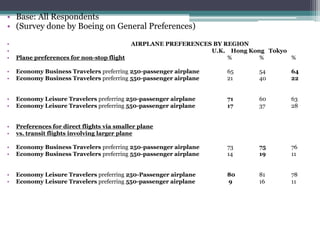
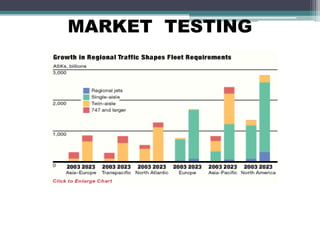
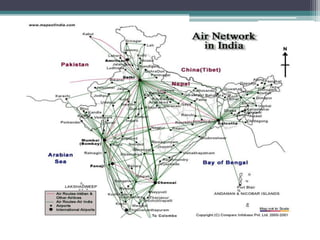
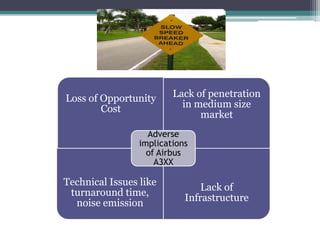
The document discusses Airbus's plans to develop the A3XX, which would be the world's largest commercial jet. It provides background on industry trends favoring larger aircraft, as well as Airbus and Boeing's business models. While a very large aircraft could offer economies of scale, surveys show customer preference for smaller craft. Financial projections estimate an $13 billion cost, with government support contributing. The viability of the A3XX is questioned given capacity challenges and customer preferences.