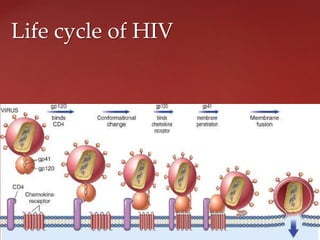
This document summarizes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) and HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). It discusses that AIDS is caused by HIV, which belongs to the lentivirus family (HIV-1 and HIV-2) and targets CD4 T-cells. HIV transmission occurs through sexual contact, blood exposure, and from mother to infant. The life cycle and structure of HIV is also outlined. The clinical features of AIDS are described in three stages: acute, chronic, and crisis phases. Treatment options like antiretroviral therapy and acupuncture are also mentioned.