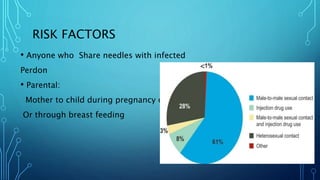
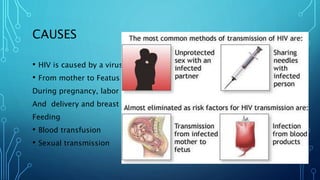
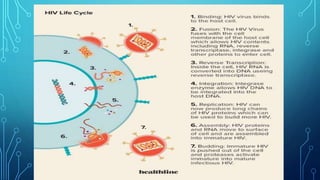
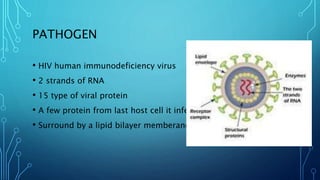
This document discusses AIDS (HIV). It covers the epidemiology of HIV/AIDS, including statistics on people living with HIV and receiving treatment. It also outlines risk factors for transmission such as sharing needles or mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy/birth. The document discusses diagnosing HIV through antibody tests, as well as the causes, symptoms, life cycle, and treatment and prevention of HIV/AIDS.