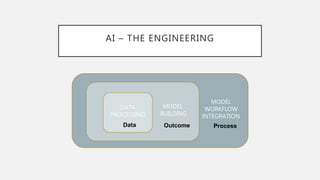
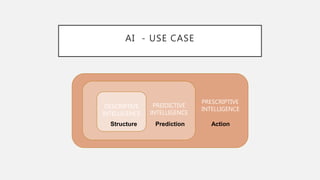
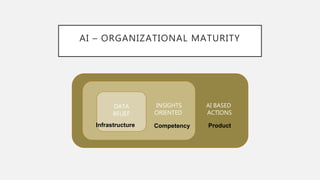
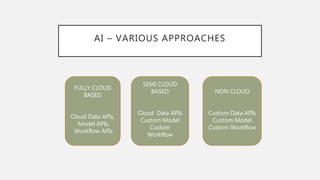
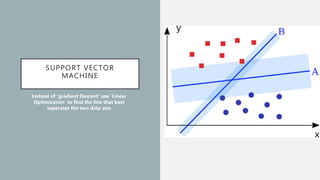
The document discusses the intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and security, exploring fundamental philosophical questions about machine intelligence and consciousness. It outlines the potential business impacts of AI, various approaches to machine learning, and specific use cases in security such as malicious URL detection and malware identification. The document emphasizes how AI can enhance security measures while also enforcing integrity and privacy.








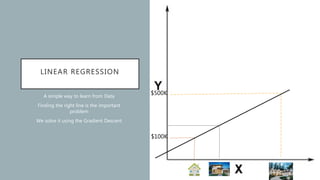
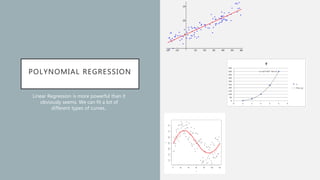


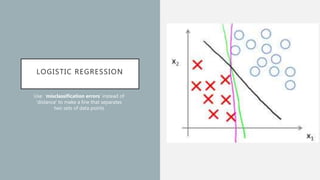
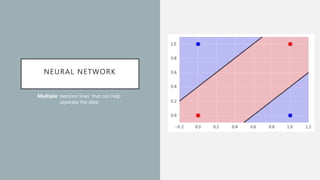



![MALICIOUS URLS
Given a website ‘W’ and a list of
malicious/benign websites , identify
whether ‘W’ is malicious or not
Training Data = URLs of
benign/malicious sites
Use Whitelisted/Blacklisted Websites
URLs from well known sources
http://www.bfuduuioo1fp.mobi/ws/ebayisapi.dll
WHOIS registration 3/25/2008
Hosted from 208.76.89.91/22
IP hosted in Jaipur
Connection Speed T1
Has DNS PTR Record ? Yes
Registrant ”Anurag”
[ 0.56, 9.45, ……. 0 0 1 1 1 …. 1 0 .. 1 0 ]Feature
Building
Real
Valued
Host Based NLP Based
+
Feature Extraction from Website
Website DOM Structure
Advertising Categories
In/Out Links Type
Images on the Website
Now apply, one of the algorithms that we talked abo
and given a new website ‘W’ one can identify whethe
its malicious or not..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mlsecurity0-171213085349/85/AI-and-Security-27-320.jpg)