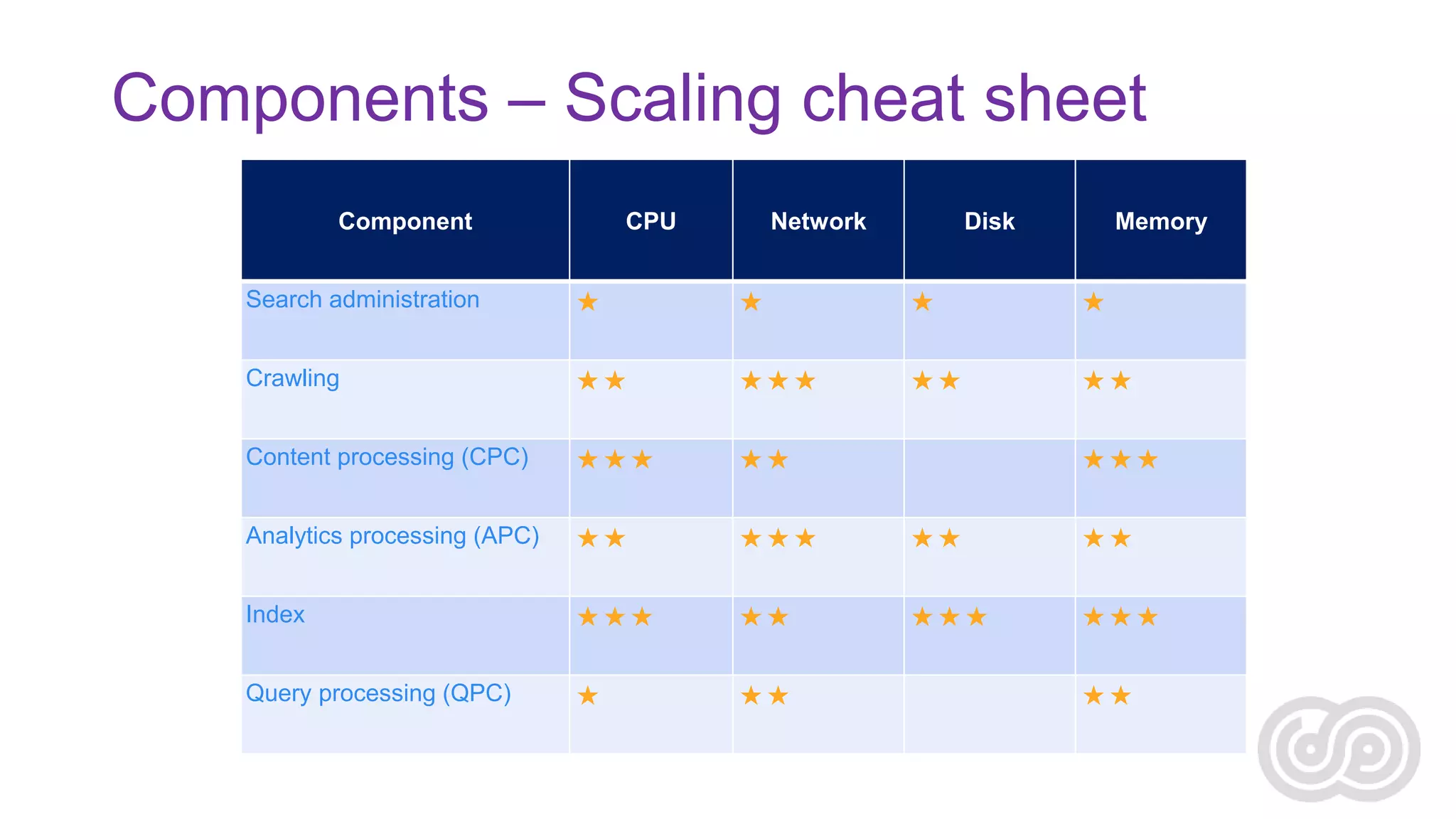
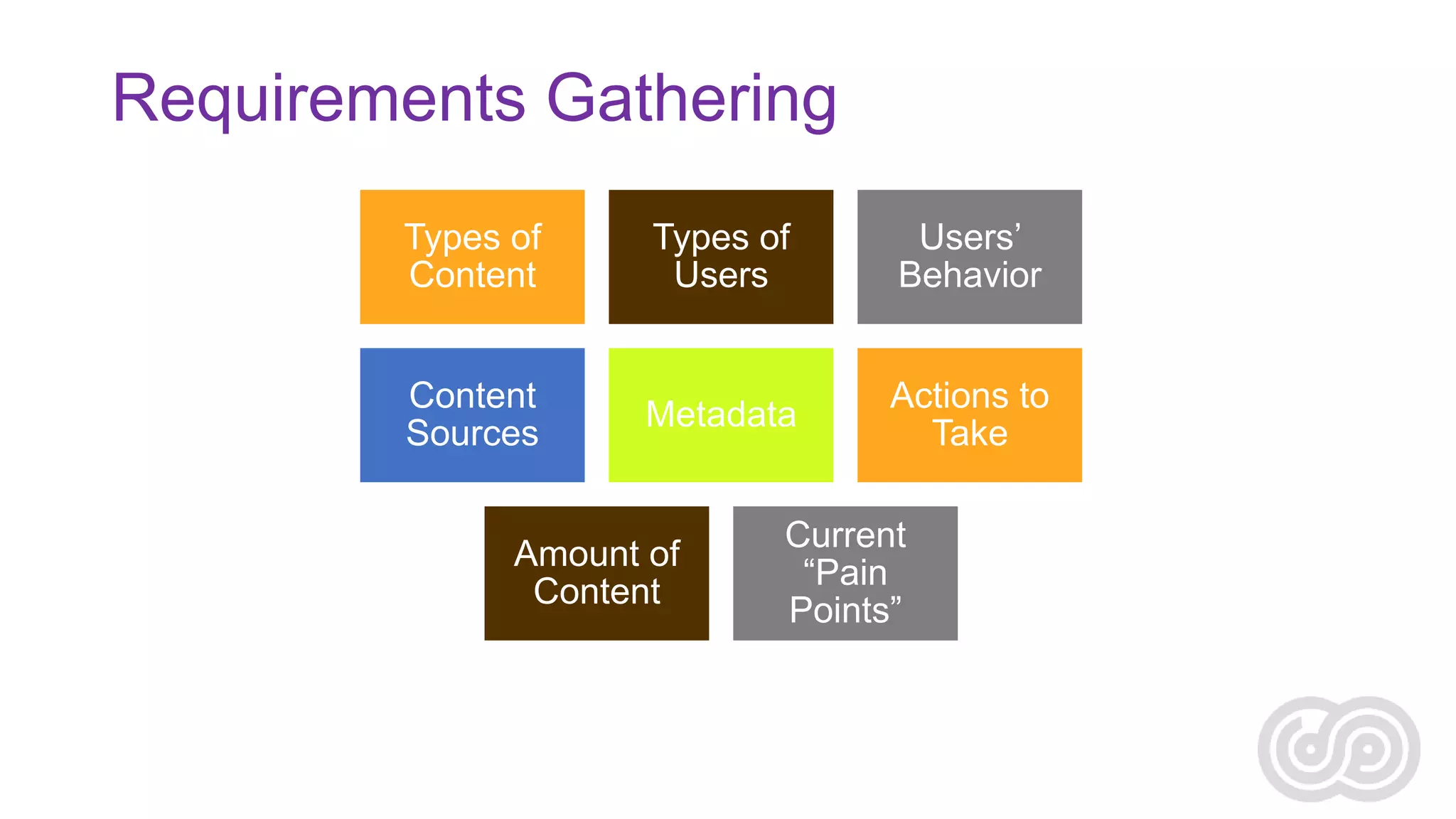
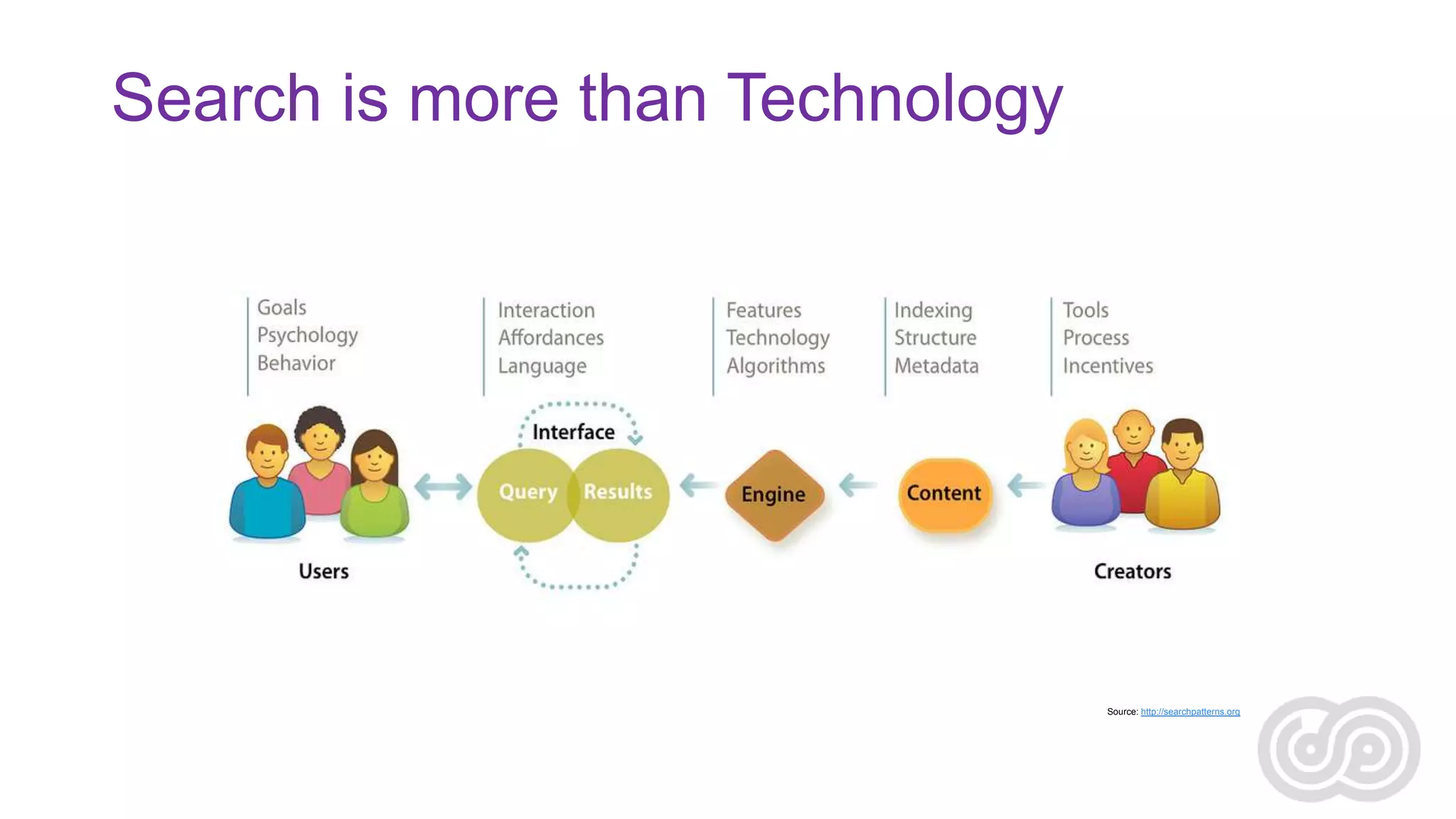
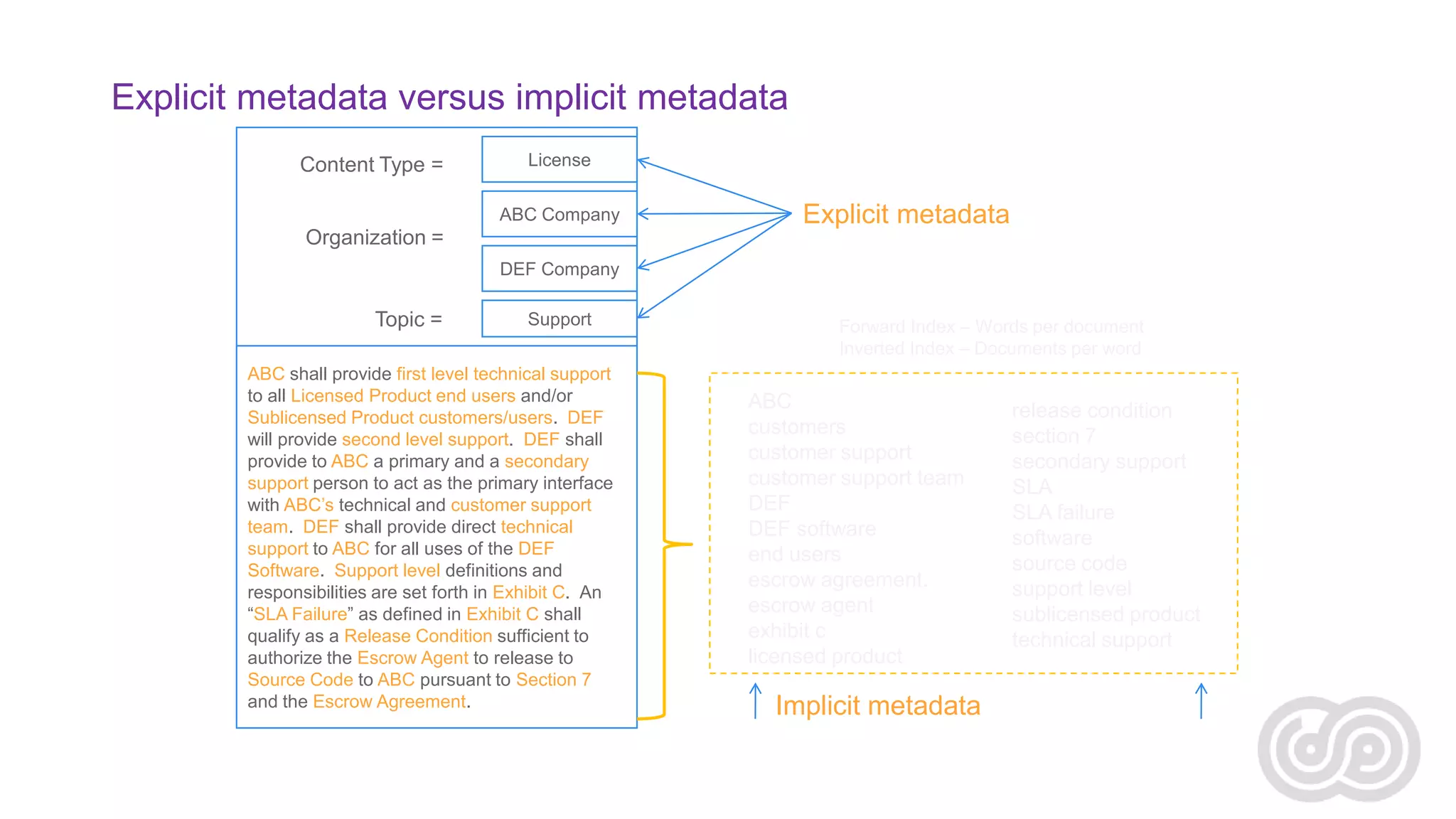
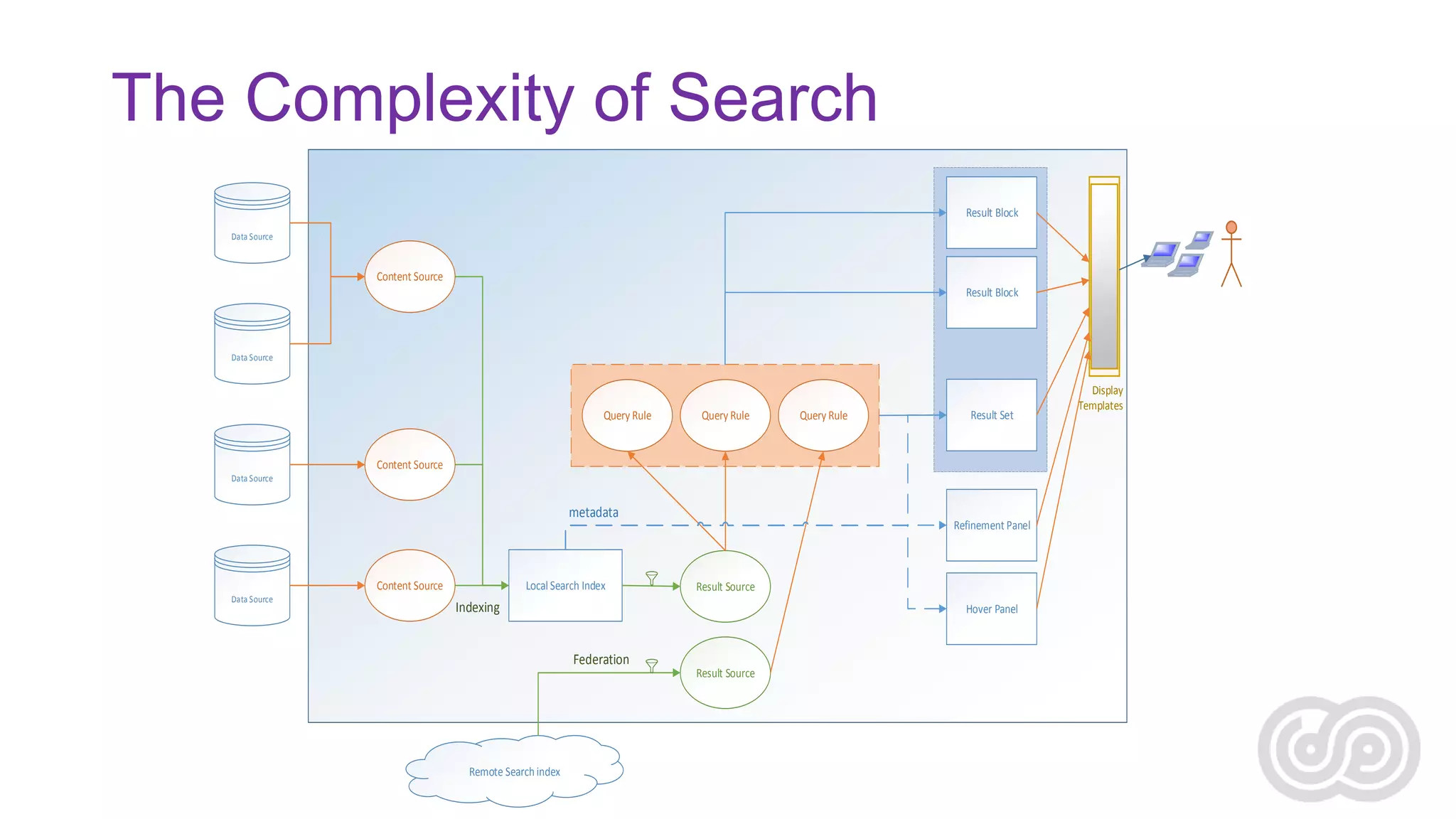
Agnes Molnar is an international SharePoint consultant and Microsoft MVP who has over 10 years of experience with SharePoint. In her presentation, she discusses some of the real world challenges organizations face with enterprise search, including information overload, the complexity of content and metadata, security, scaling, and relevance ranking. She emphasizes that search is an application that requires understanding user needs and behaviors as well as content sources in order to be successful.






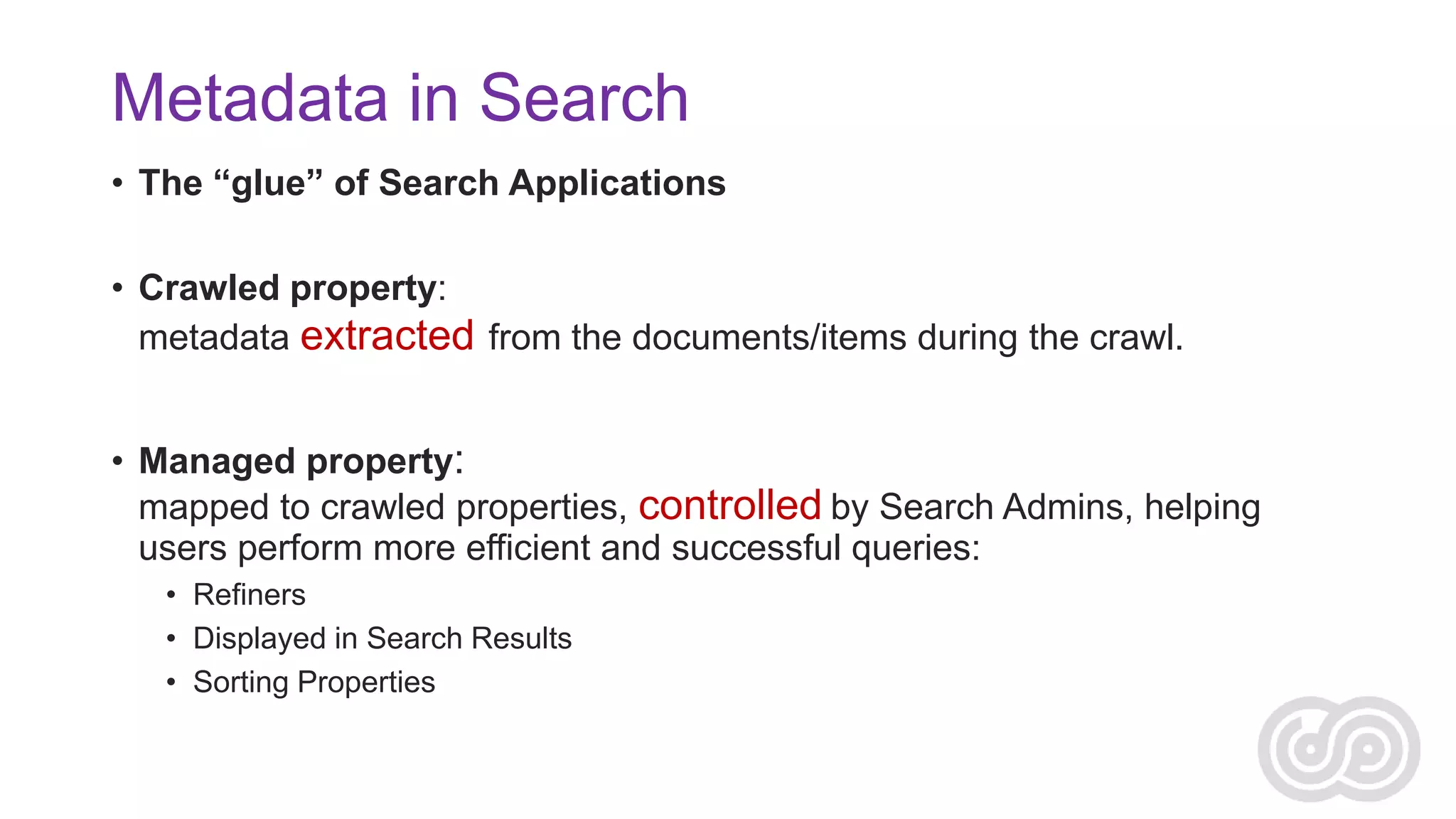
![User – Context – Content
• Context:
Business models & goals,
corporate culture, resources
• [Where information is used]
• Content:
Document types Objects,
structure, attributes, Metainformation
Context
• [How to describe the information]
• Users:
Information needs, audience
types, expertise, tasks
• [How to Use the Information]
Content
Users](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agnesmolnar-realworldchallenges-131129090713-phpapp01/75/Solving-Real-World-Challenges-with-Enterprise-Search-10-2048.jpg)



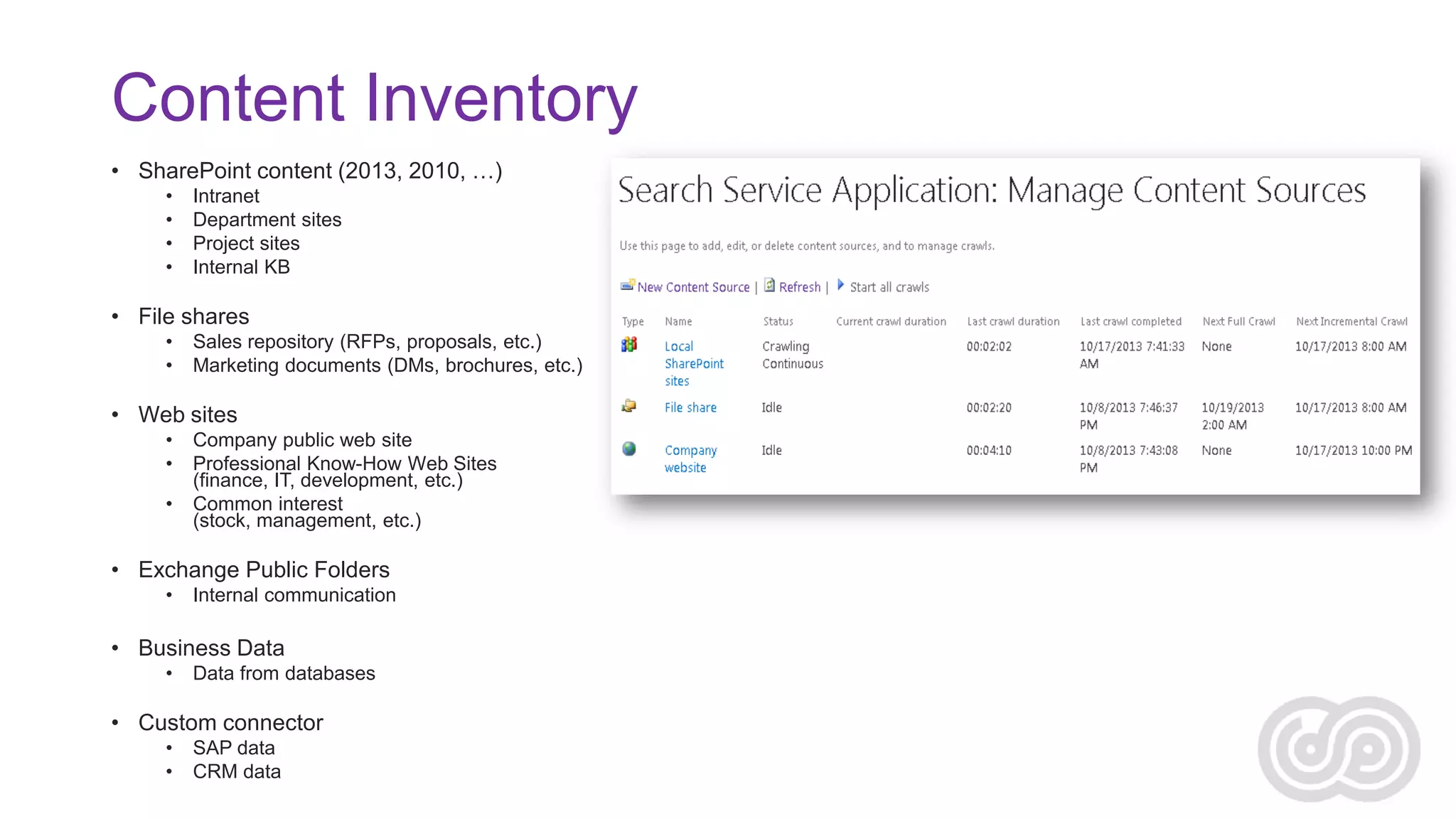

![Content Source Inventory
Name
Type
Location
Owner
Volume of
Content
Frequency of
Updates
Intranet
SharePoint
http://intranet
Intranet Team
200K items
100-300/hr
Project Sites
SharePoint
http://projects
Delivery
200K items
100-200/hr
Sales share
File share
X:Sales
Sales
500K docs
300-500/hr
Marketing share
File share
X:Marketing
Marketing
200K docs
300-500/hr
Company web
site
Web site
http://mycompany.com
Marketing/
Publishing Team
<100K pages
1-10/day
Competitor’s web
site
Web site
http://competitor.com
[external]
<100K pages
1-10/day
Professional
Know-How
Web site
http://www.mykb.com
[external]
<100K pages
5-10/week
Company
Announcements
Exchange
Public
Folder
Exchange/Public
Folders/Announcements
Marketing/
Internal Comm.
Team
<100K items
5-10/day
HR data
Business
Data (SQL)
SQL database
HR
<100K items
10-100/day
CRM data
Custom
Connector
CRM system
Sales
500K entries
500-1000/hr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agnesmolnar-realworldchallenges-131129090713-phpapp01/75/Solving-Real-World-Challenges-with-Enterprise-Search-22-2048.jpg)