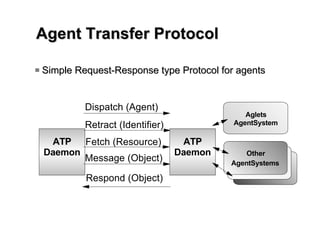
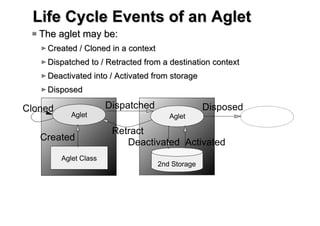
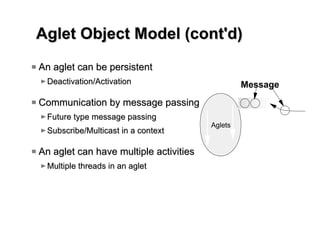
Aglets is a Java-based framework that allows programmers to create mobile software agents. The Aglets API provides functionality for agent creation, movement between systems, communication via message passing, and more. Potential applications of mobile agents created with Aglets include network management, distributed database access, auctions, and online shopping. The framework handles agent transport and ensures platform independence so agents can move freely across systems written in Java.