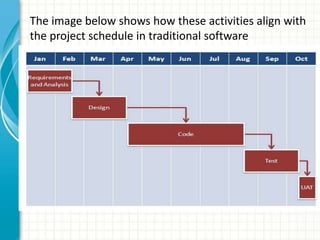
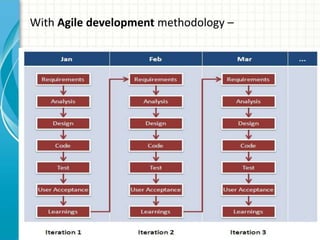
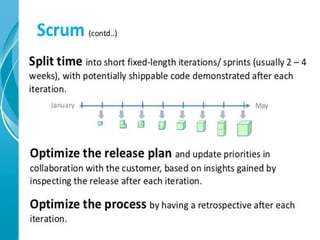
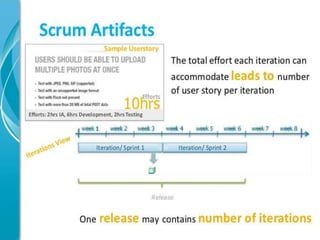
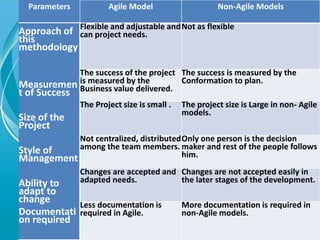
This document provides an overview of agile software development methods. It begins with introducing the presenters and stating the topics to be covered, which include the agile manifesto, terminology, methodologies like Scrum and XP, and a comparison of agile and non-agile models. It then discusses what agility means in software development and the background and history leading to the emergence of agile methods. Key aspects of agile like lightweight processes, frequent delivery of value, and adaptability to change are contrasted with traditional plan-driven models. The document concludes with providing resources for further information on agile methodology.