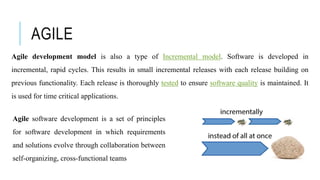
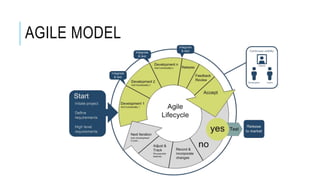
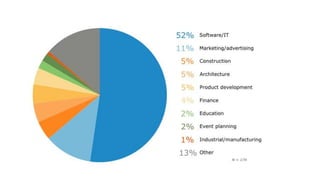
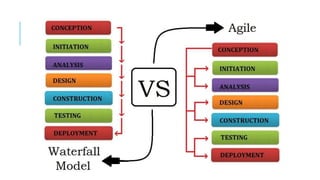
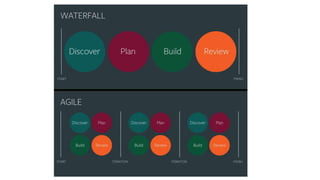
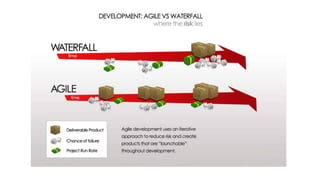
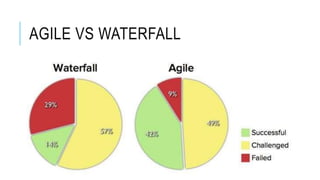
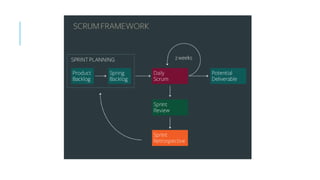
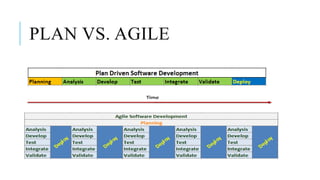
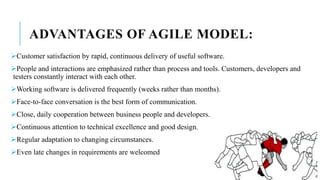
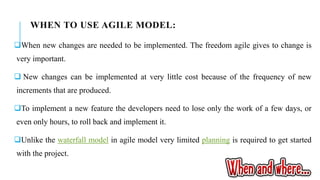
The document provides an overview of agile software development. It defines agile development as a collaborative approach where requirements and solutions evolve through self-organizing cross-functional teams. The document outlines several agile methodologies introduced in the Agile Manifesto in 2001 including Scrum, Extreme Programming, Crystal, FDD, and DSDM. It also discusses lean practices as part of the agile development approach and compares agile to traditional waterfall models. Finally, it covers advantages and disadvantages of the agile model and considerations for when it is best applied.