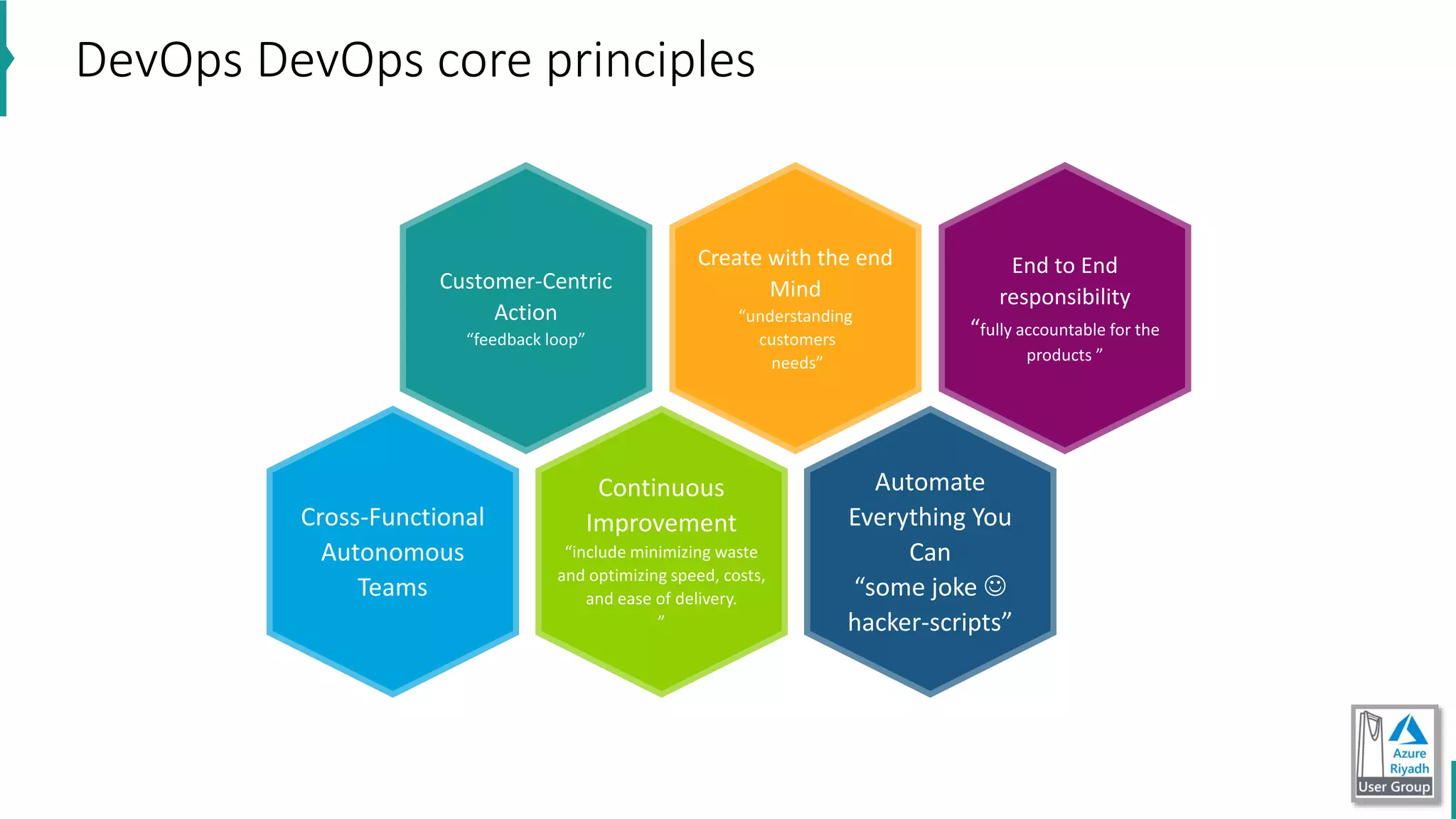
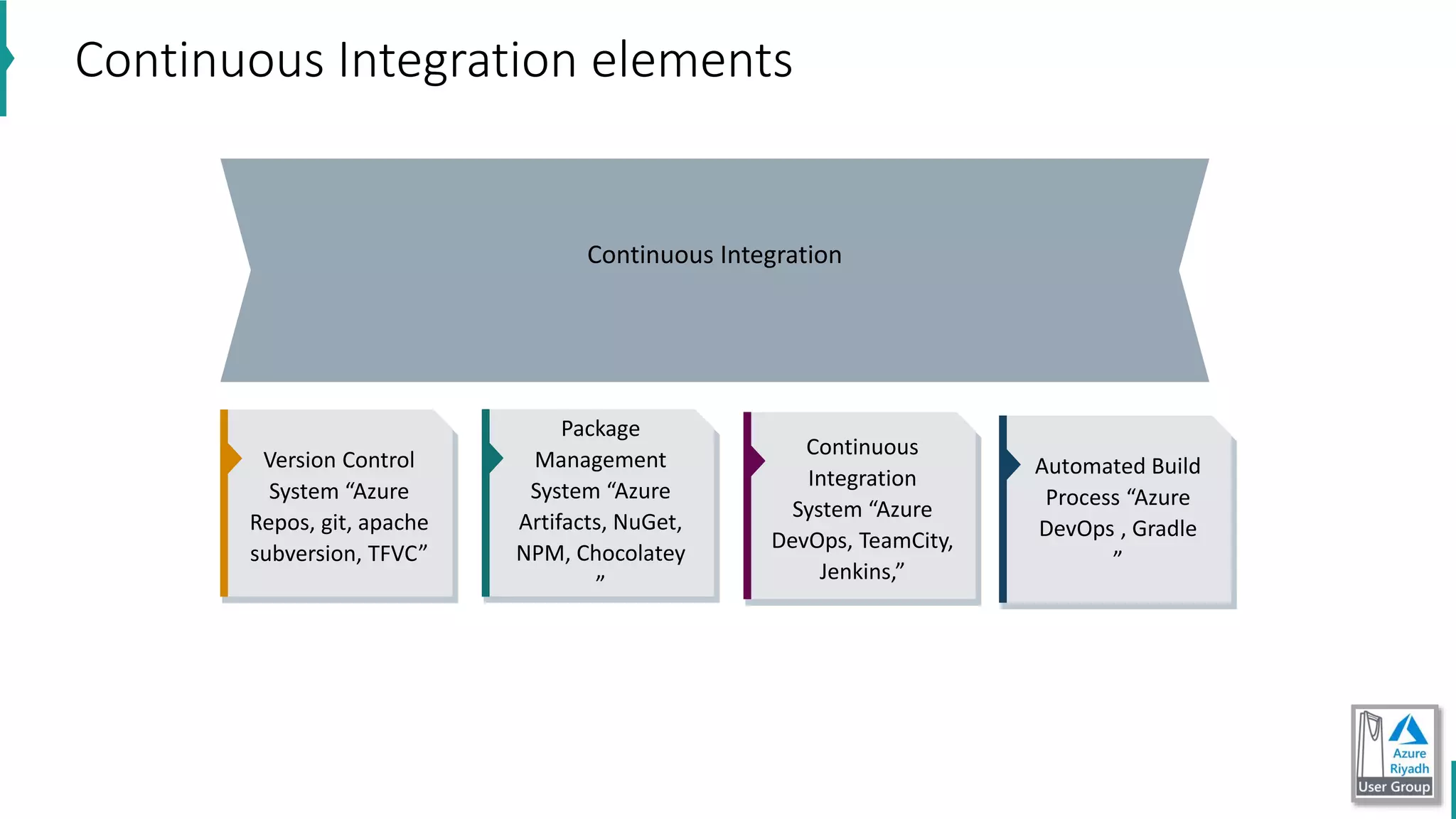
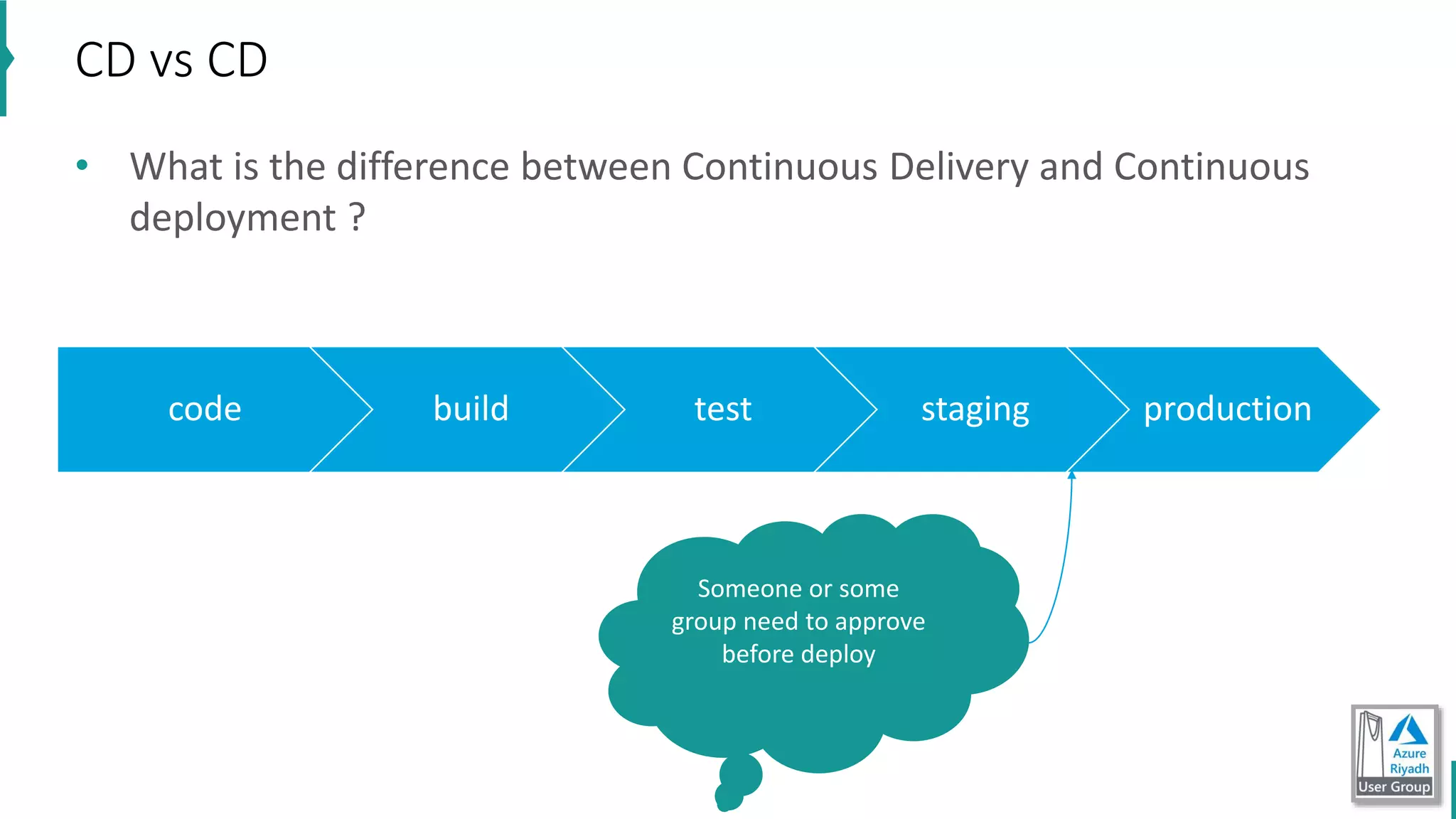
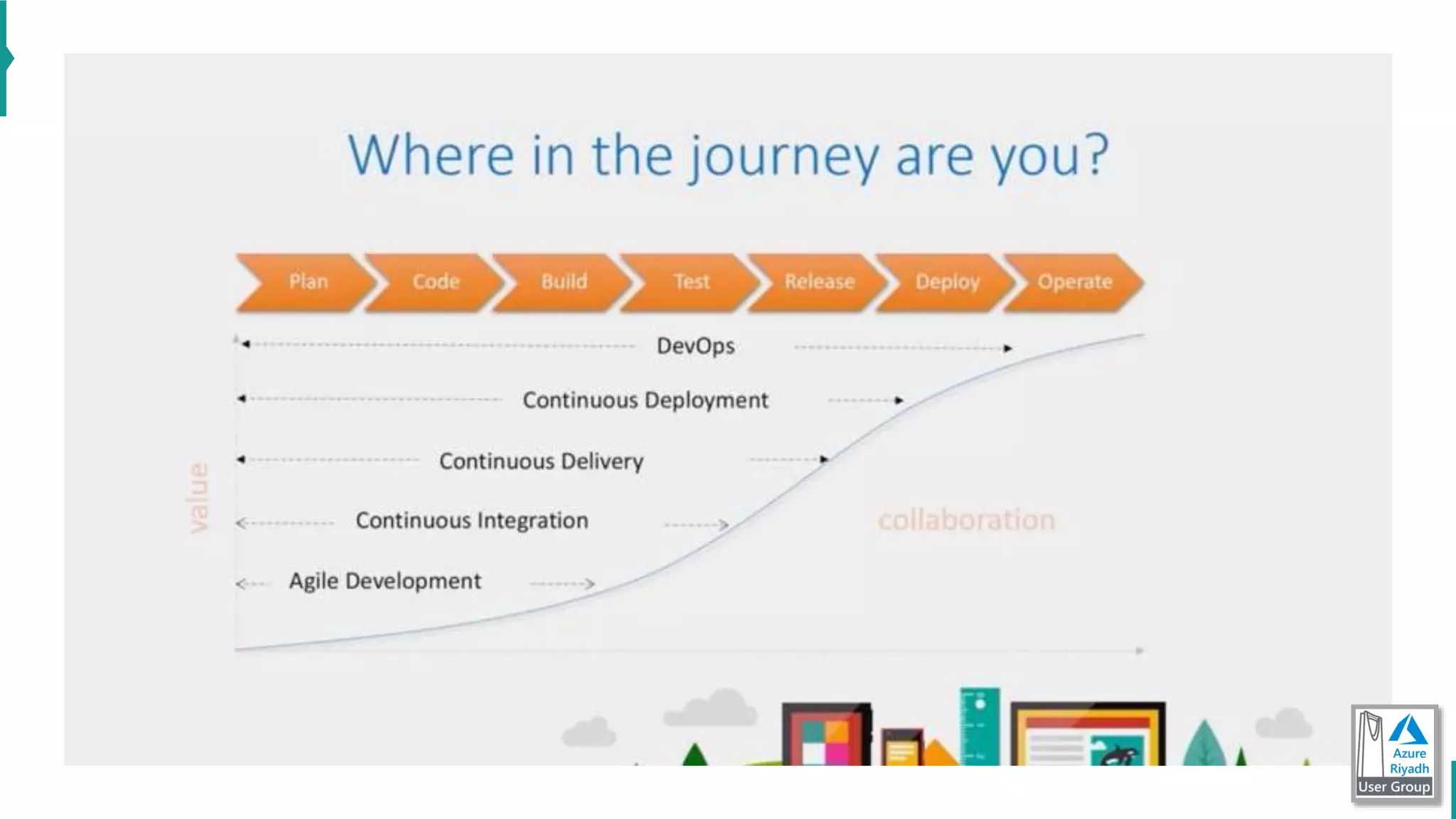
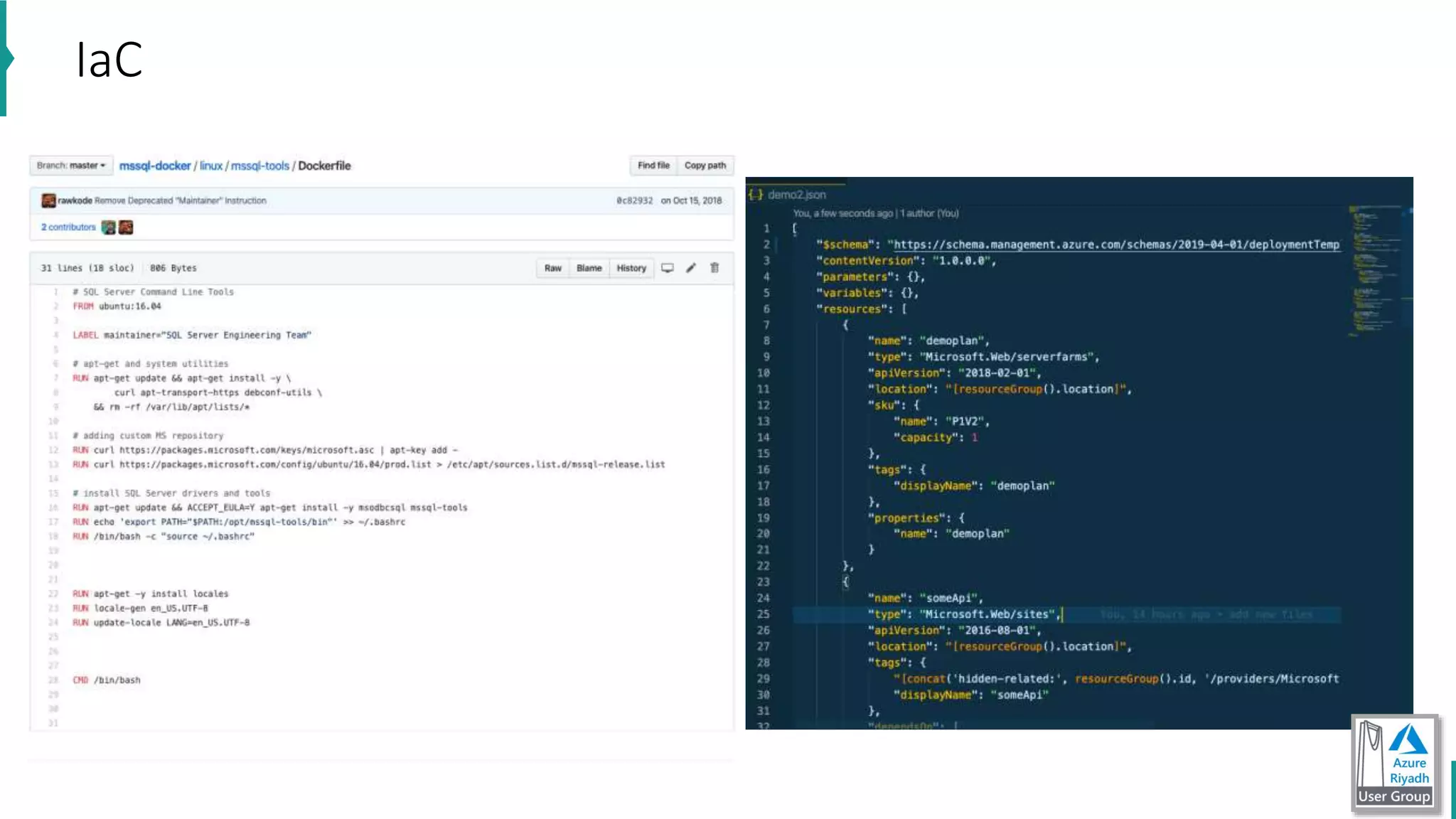
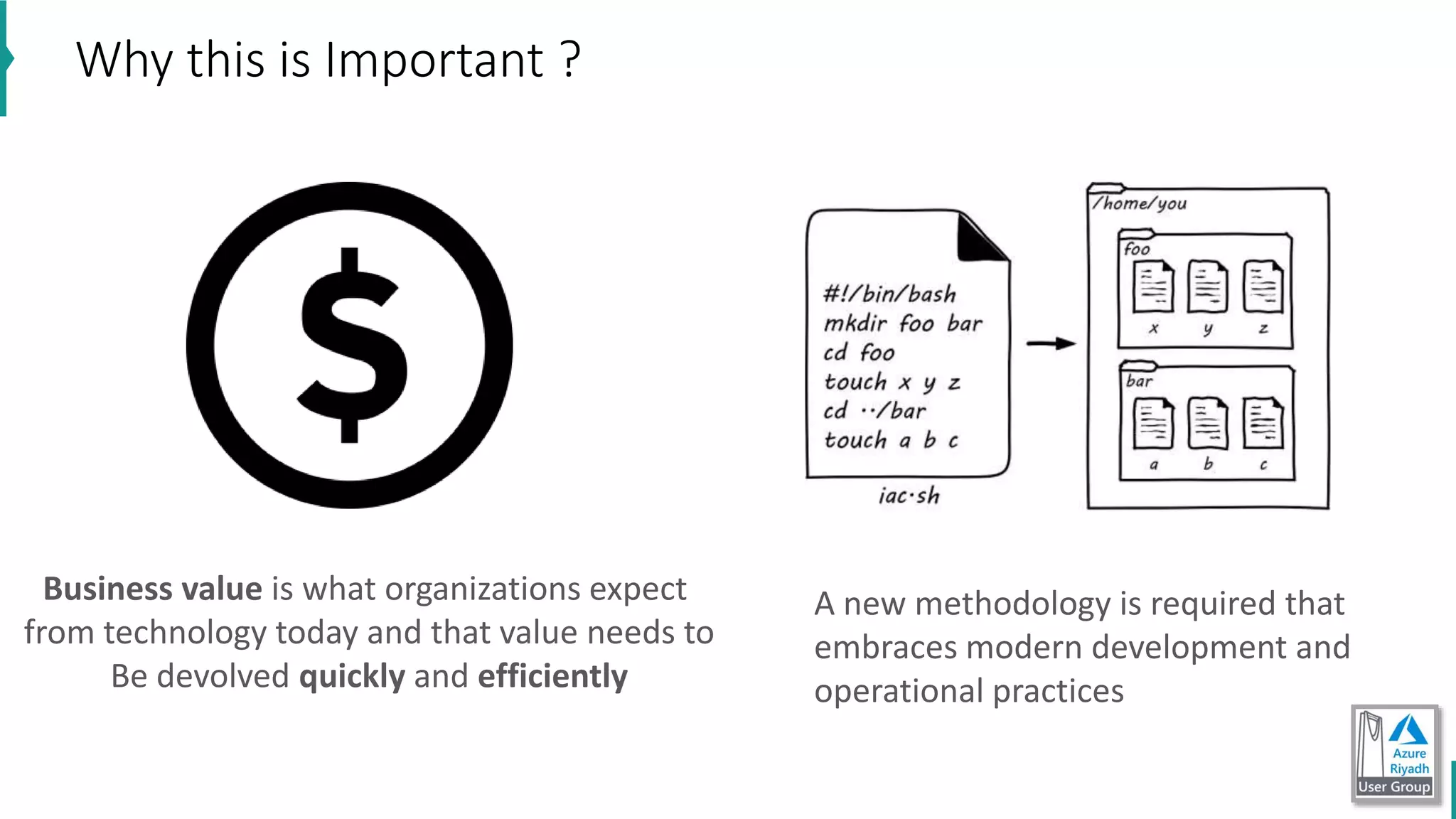
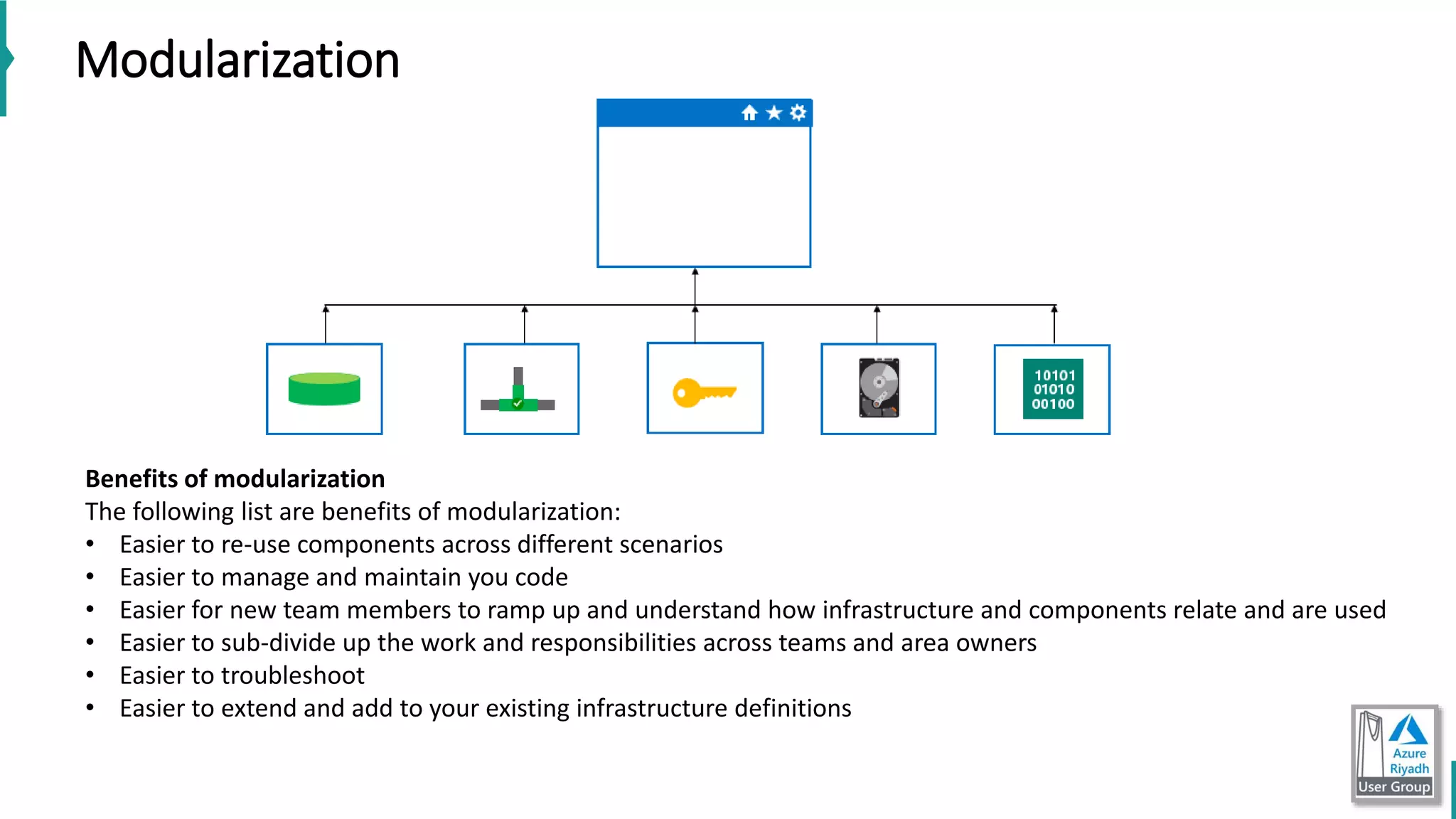
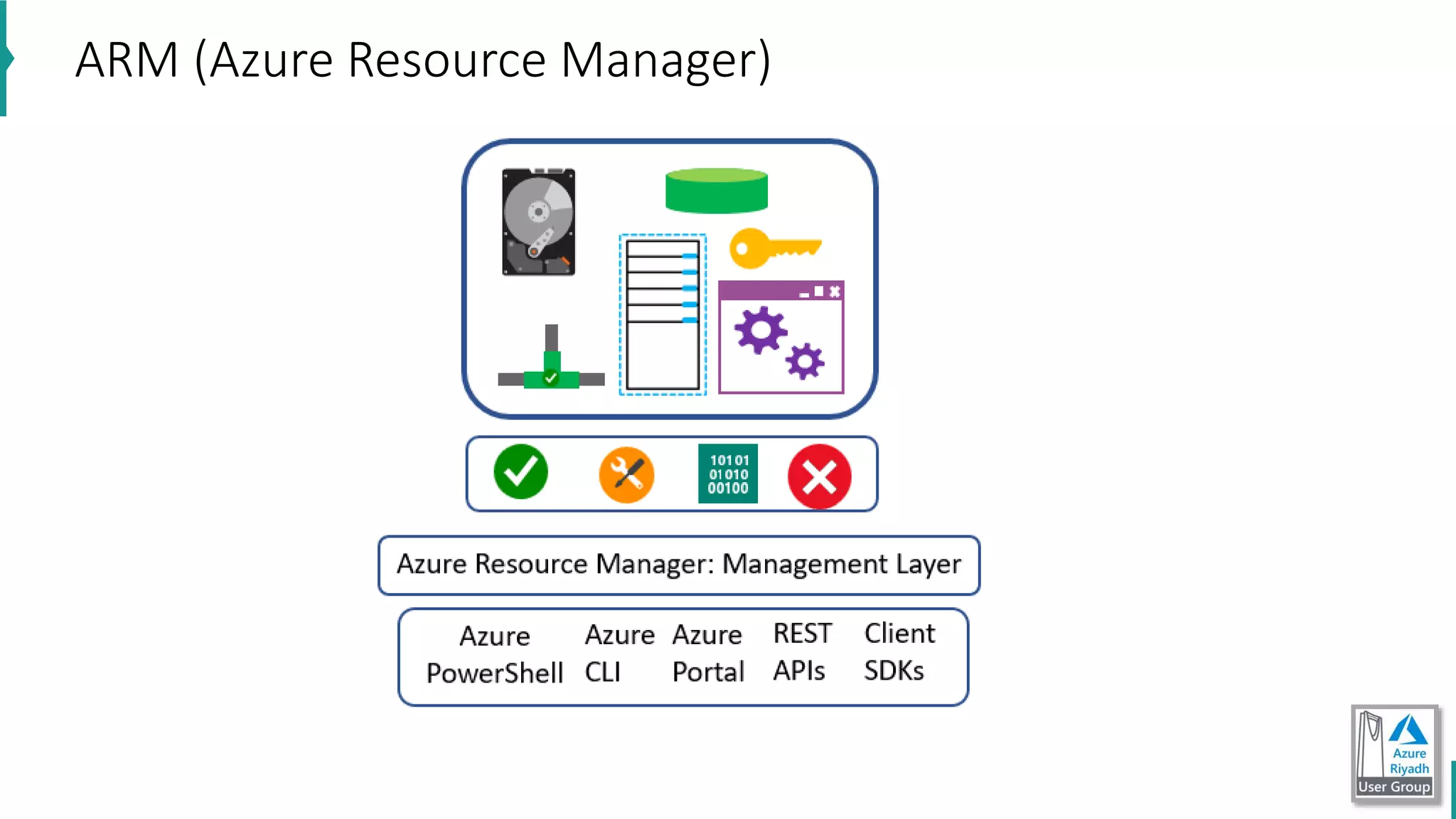
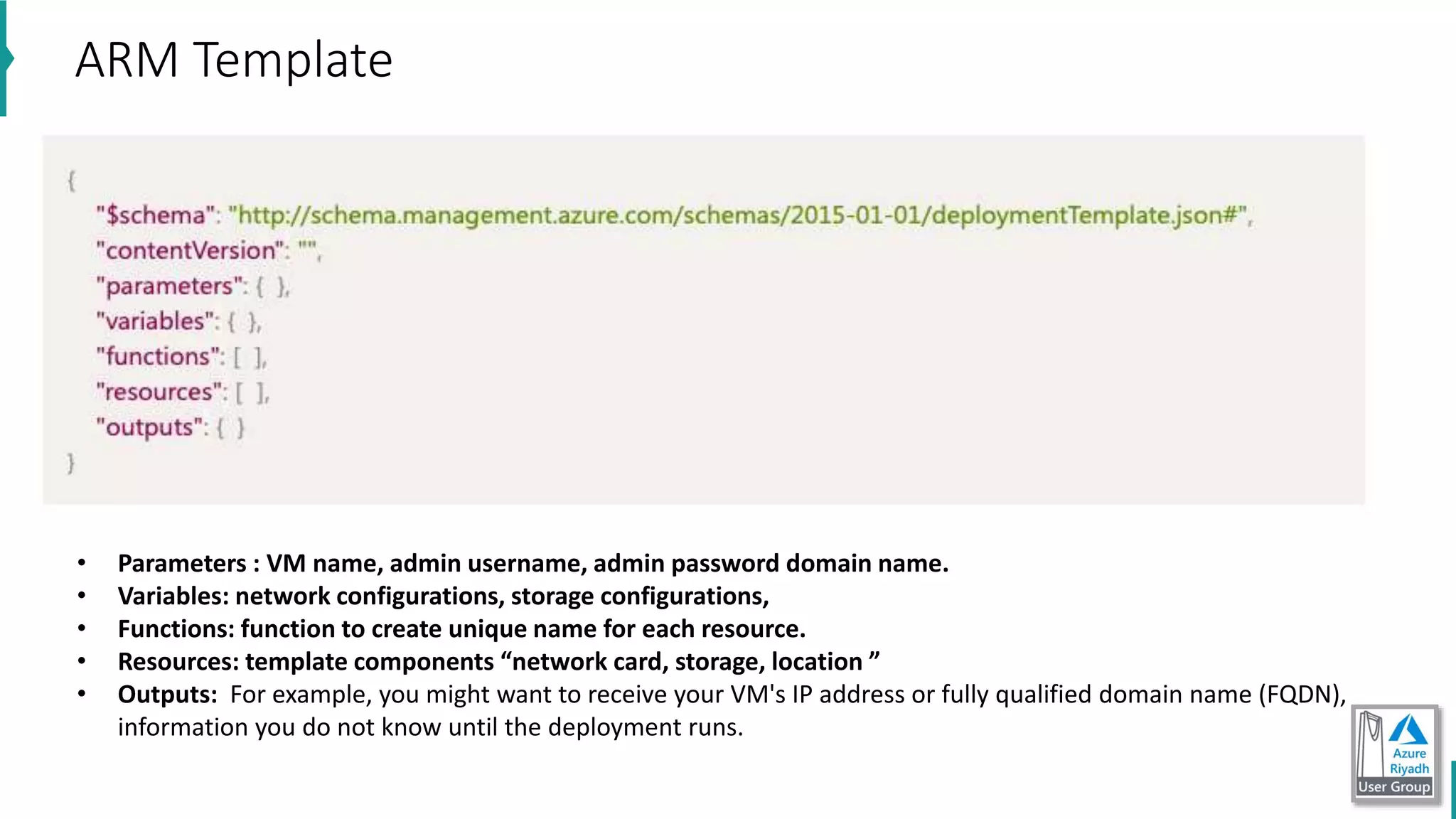
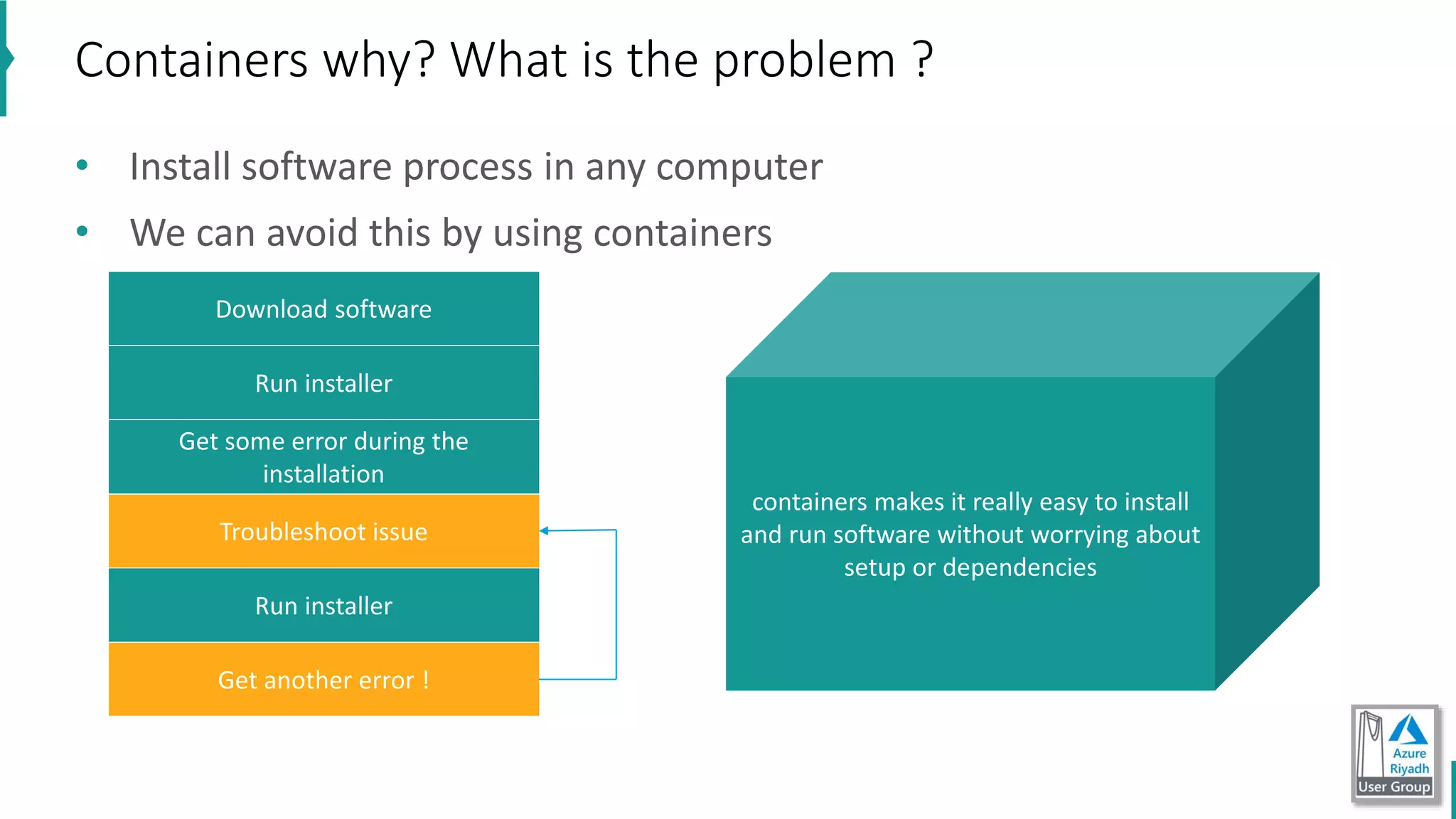
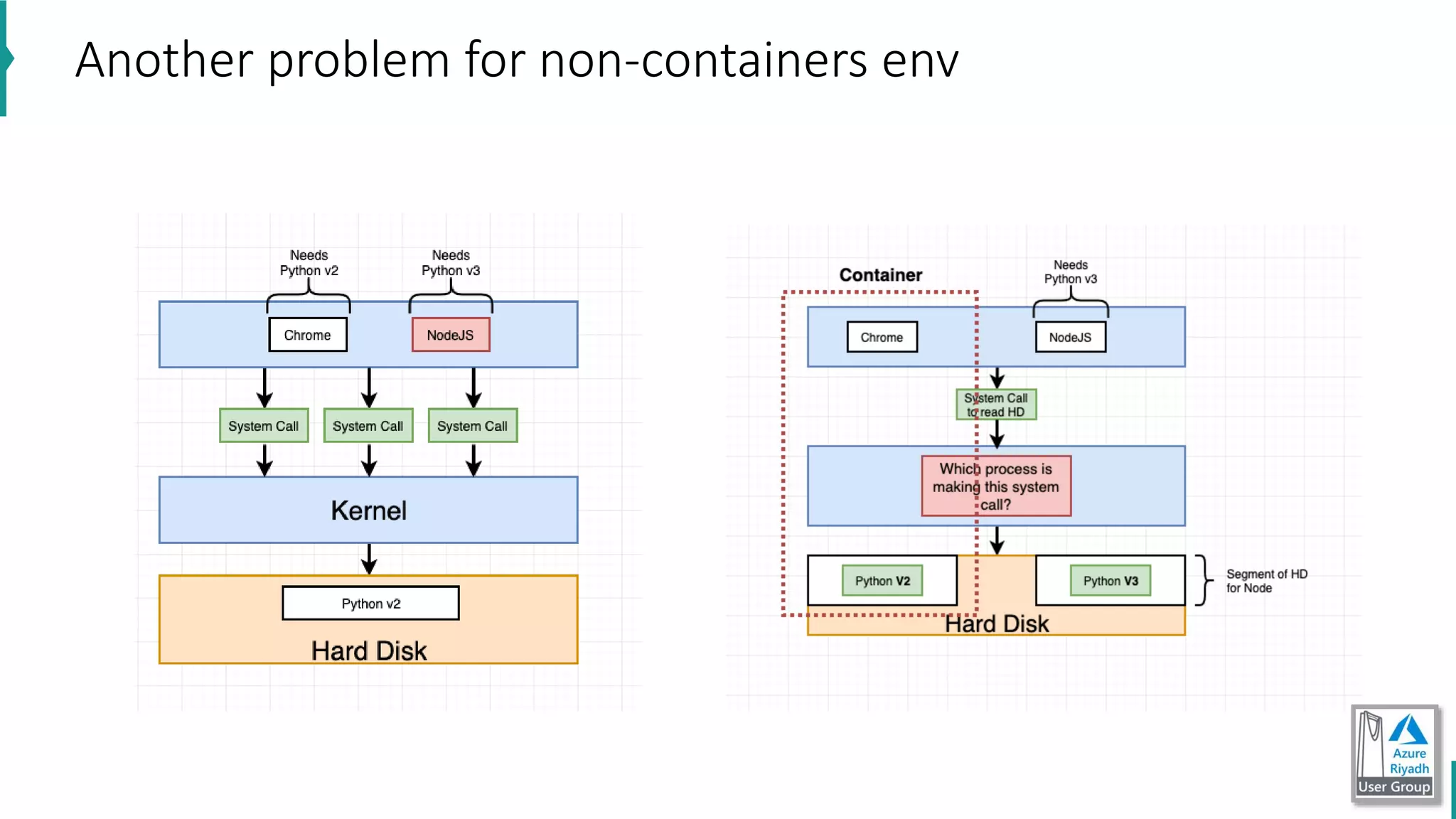
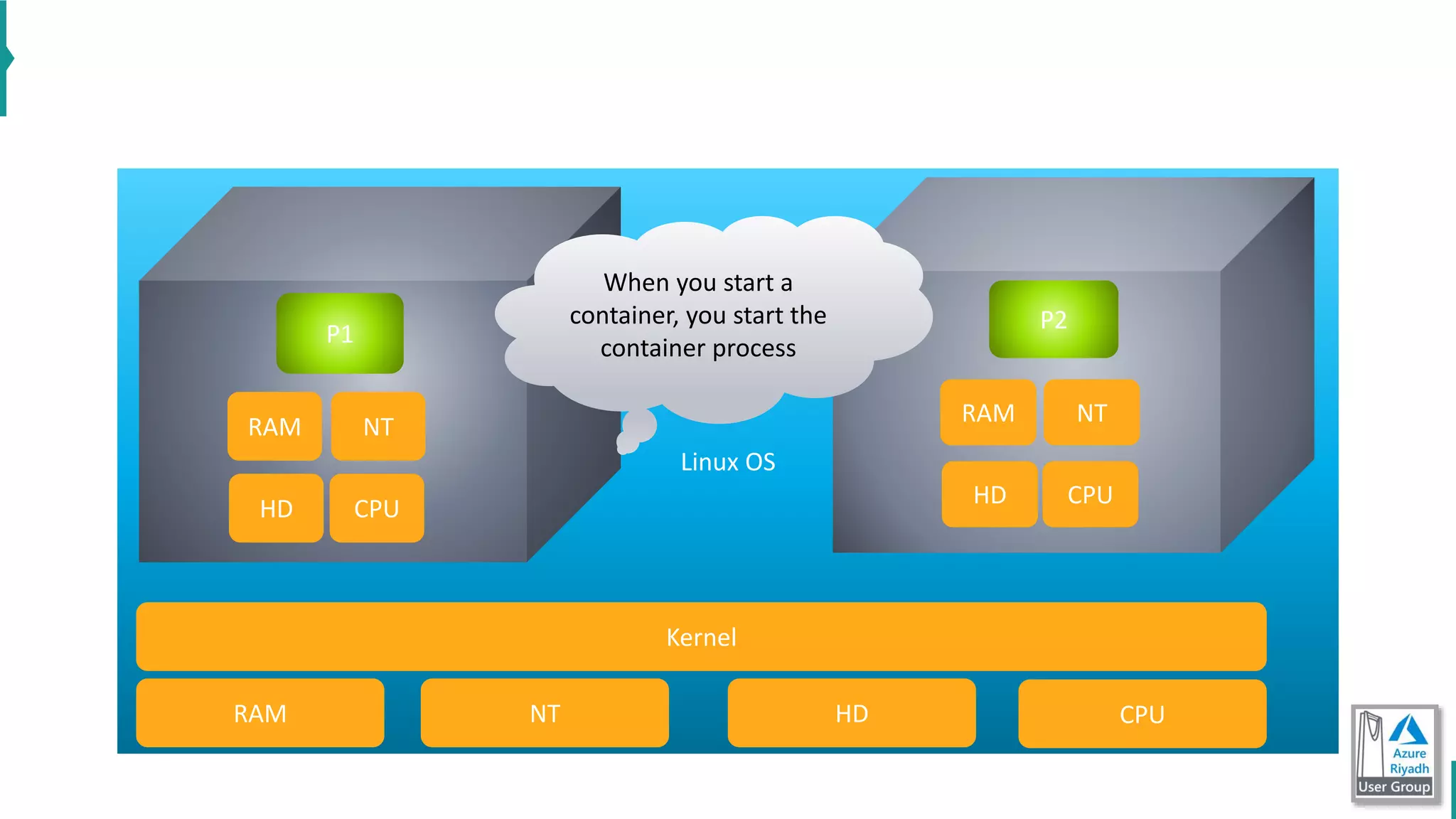
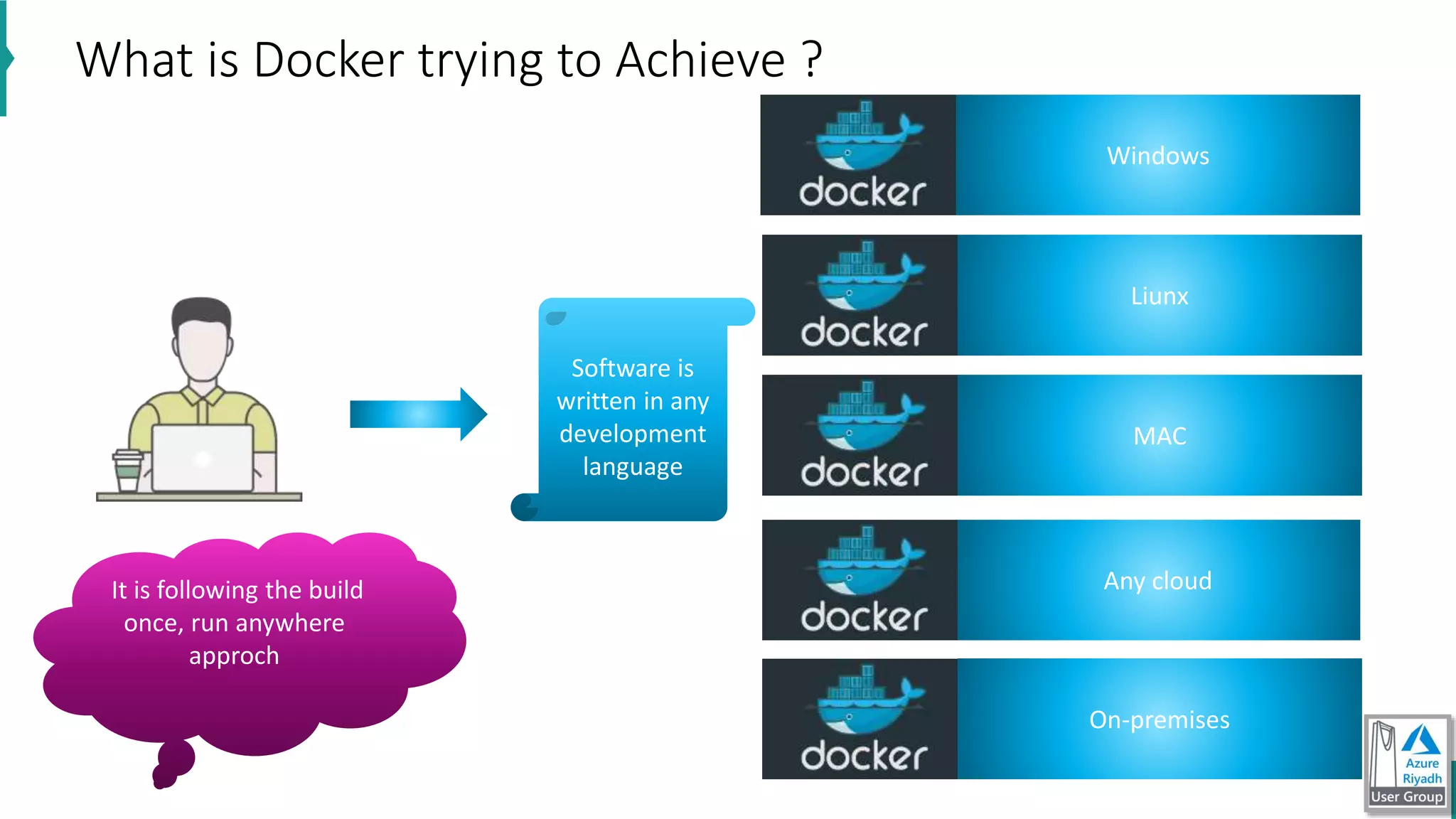
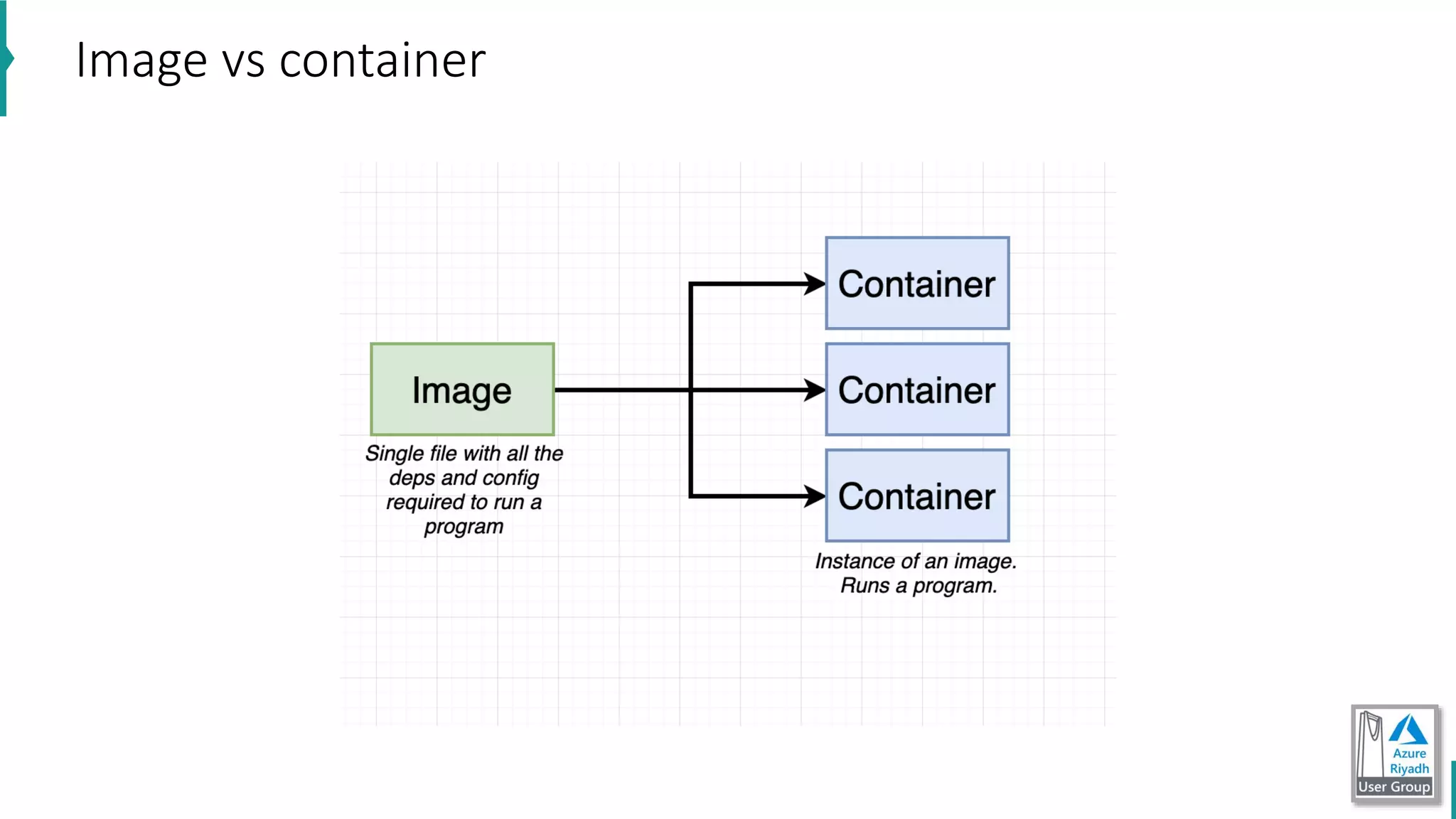
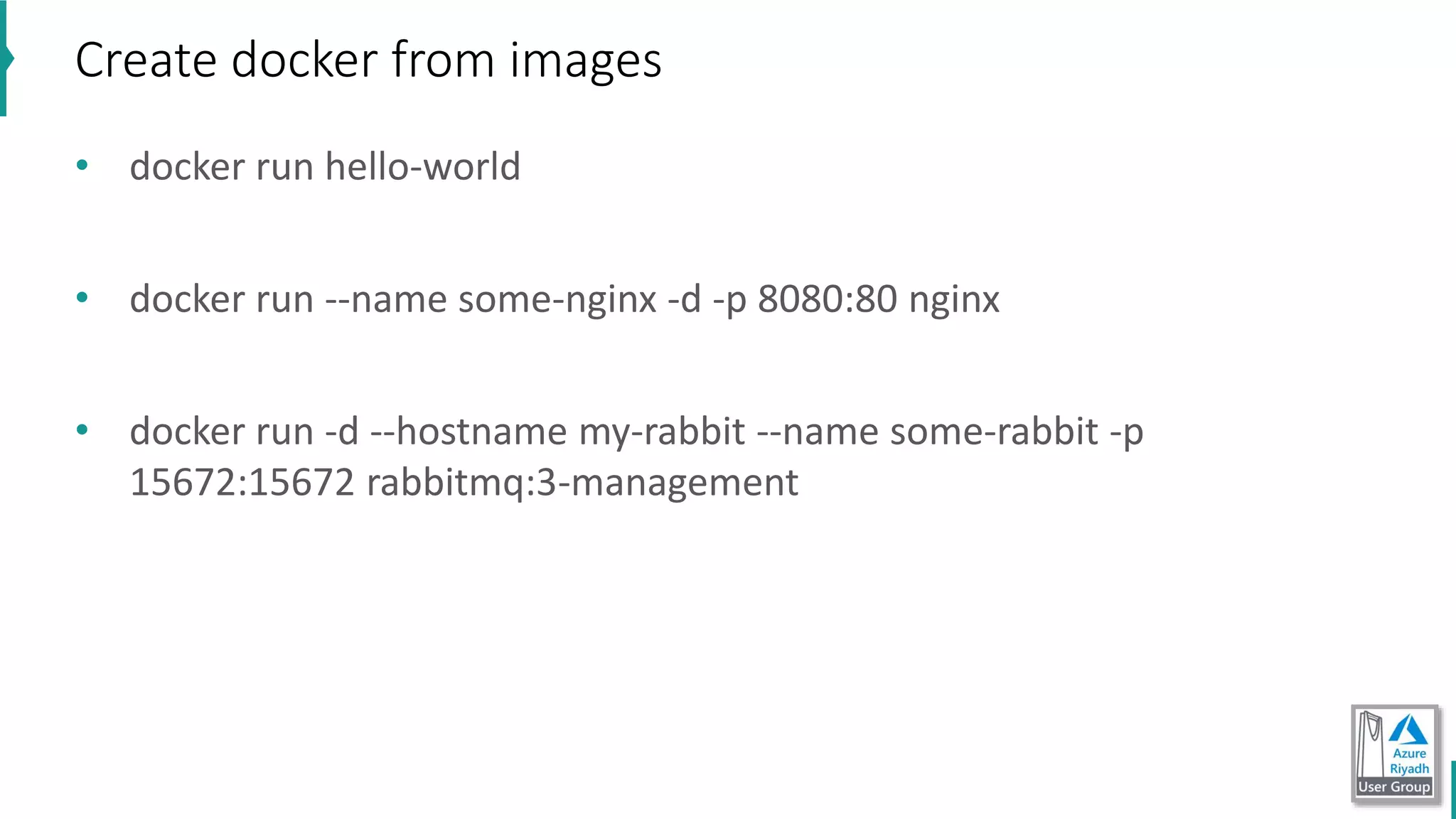
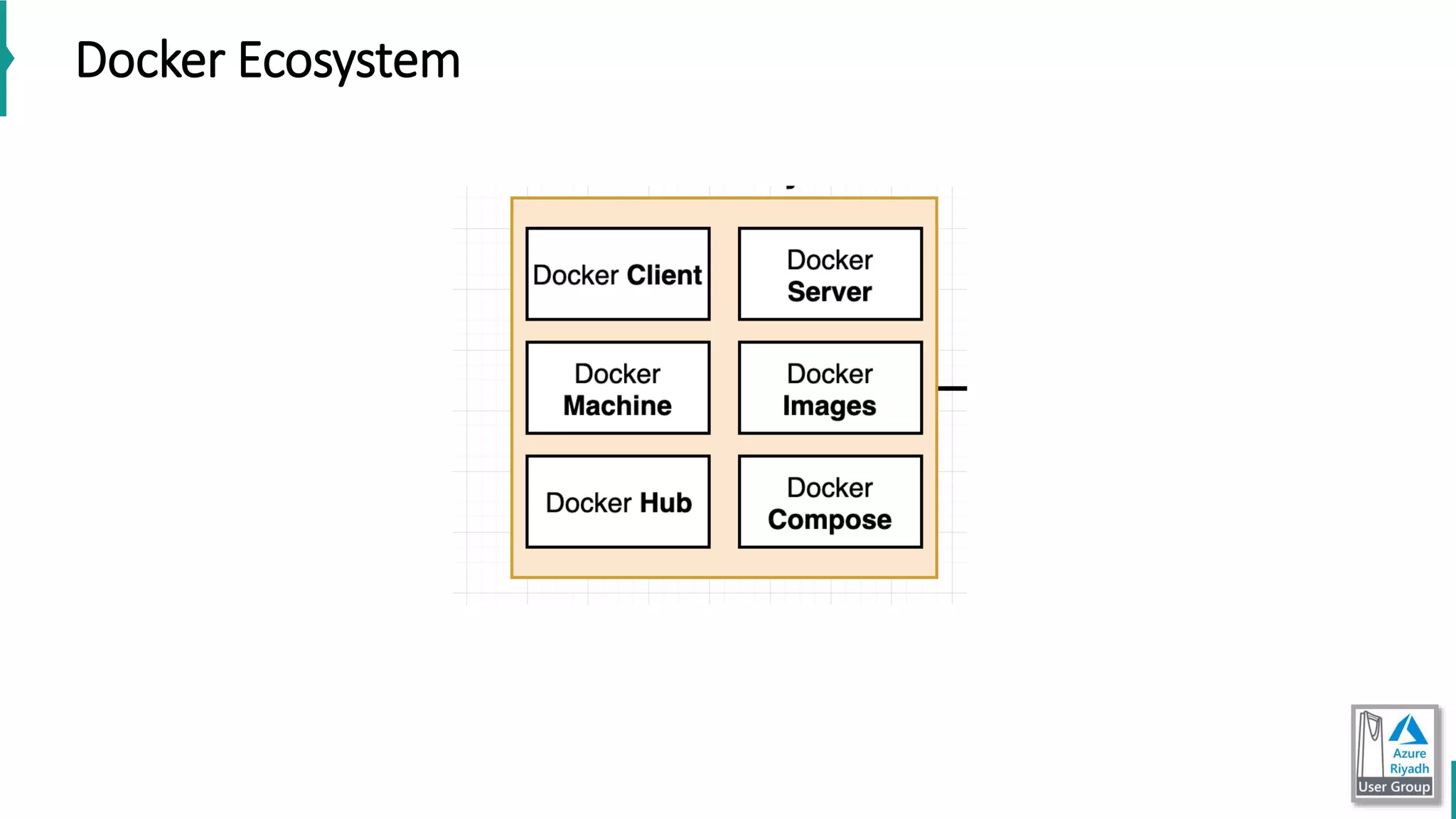
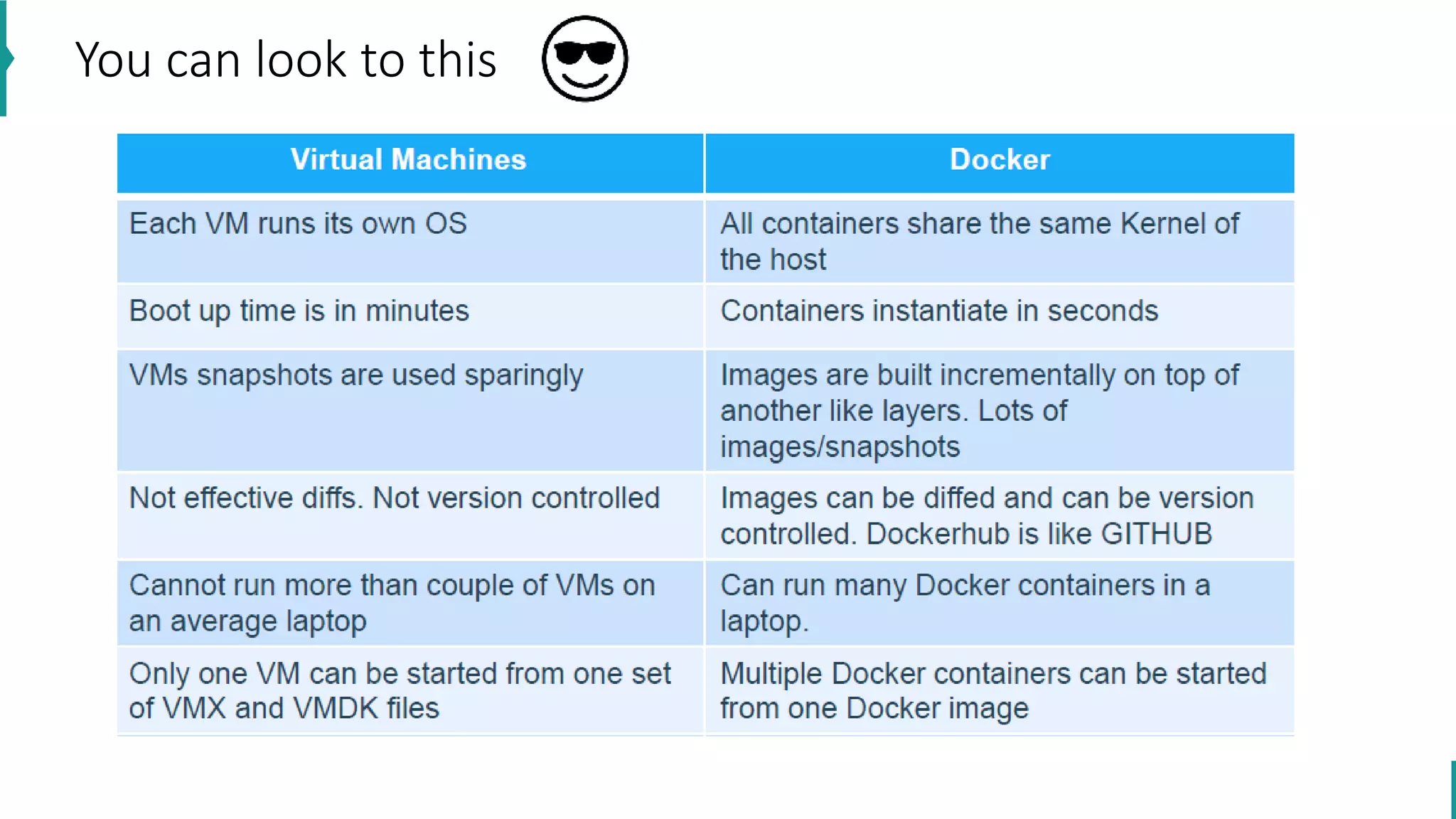
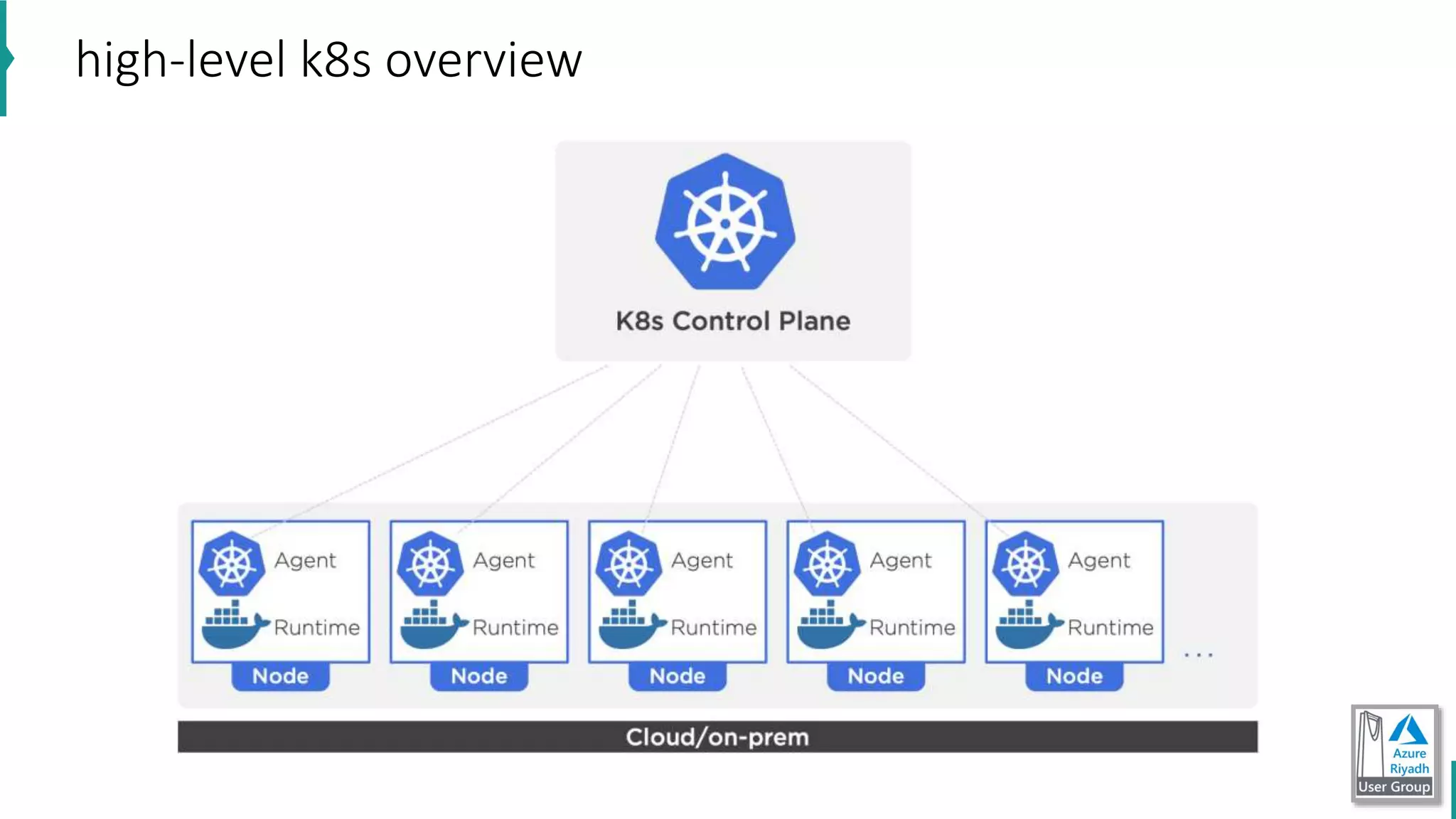
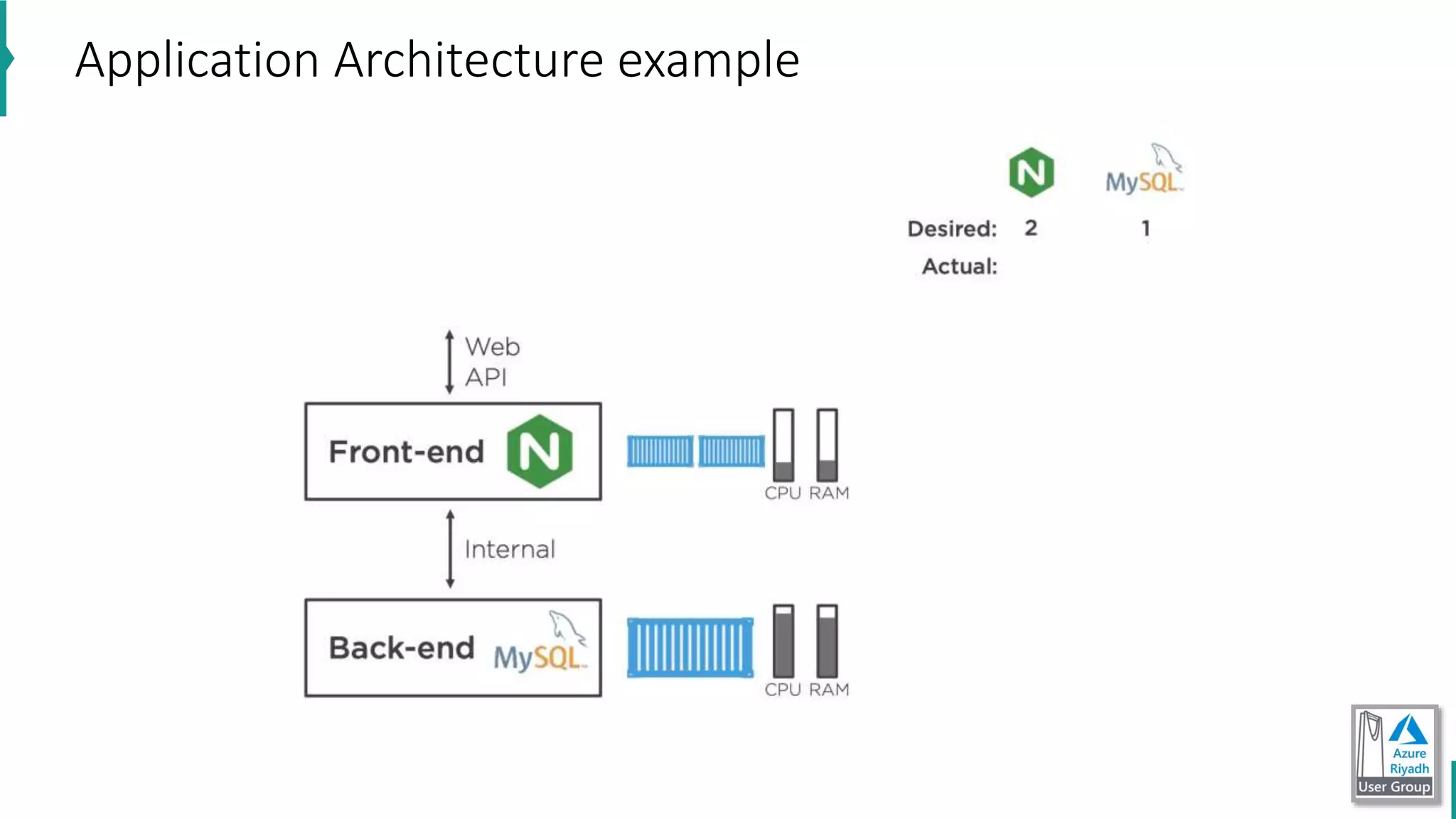
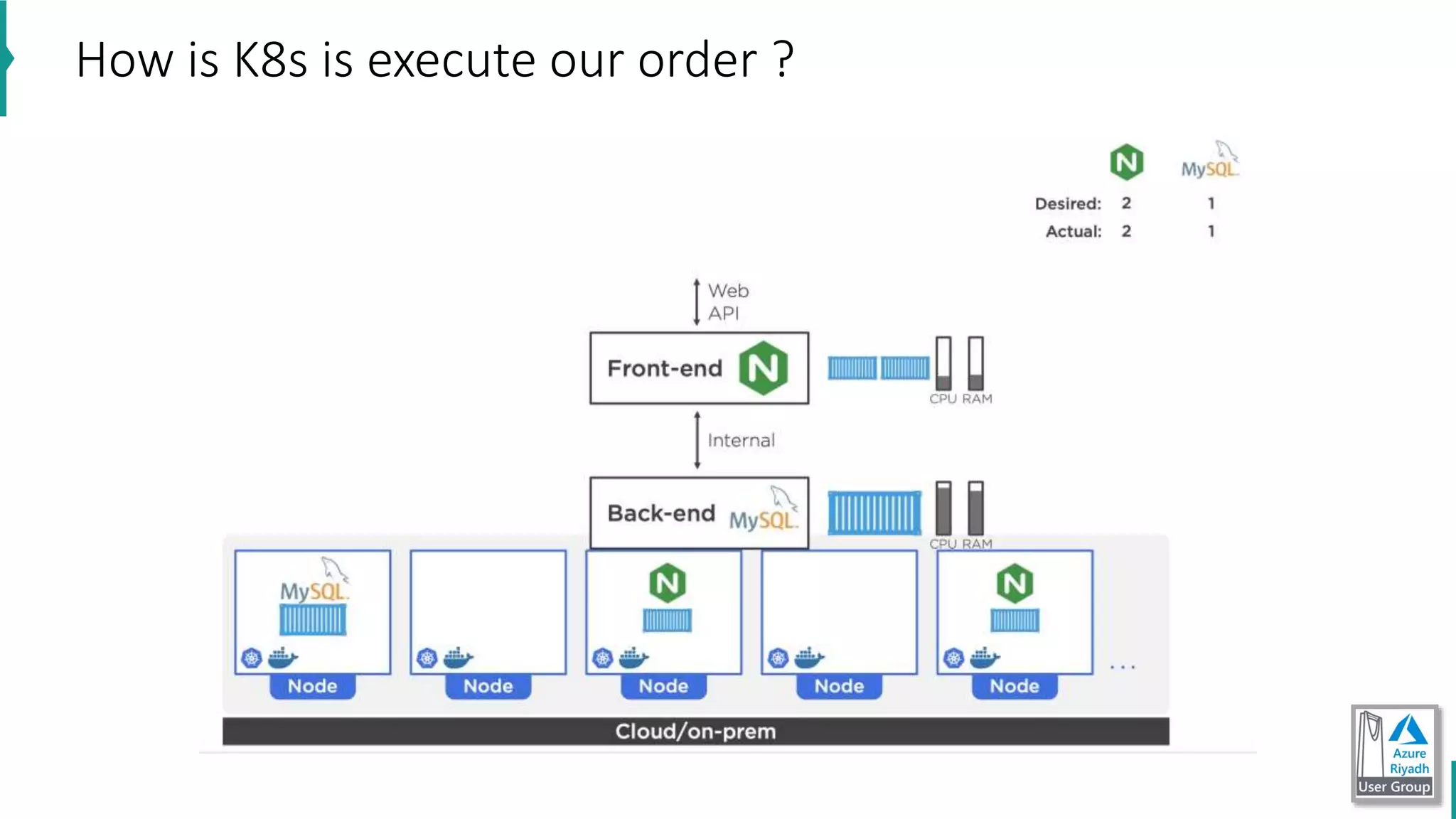
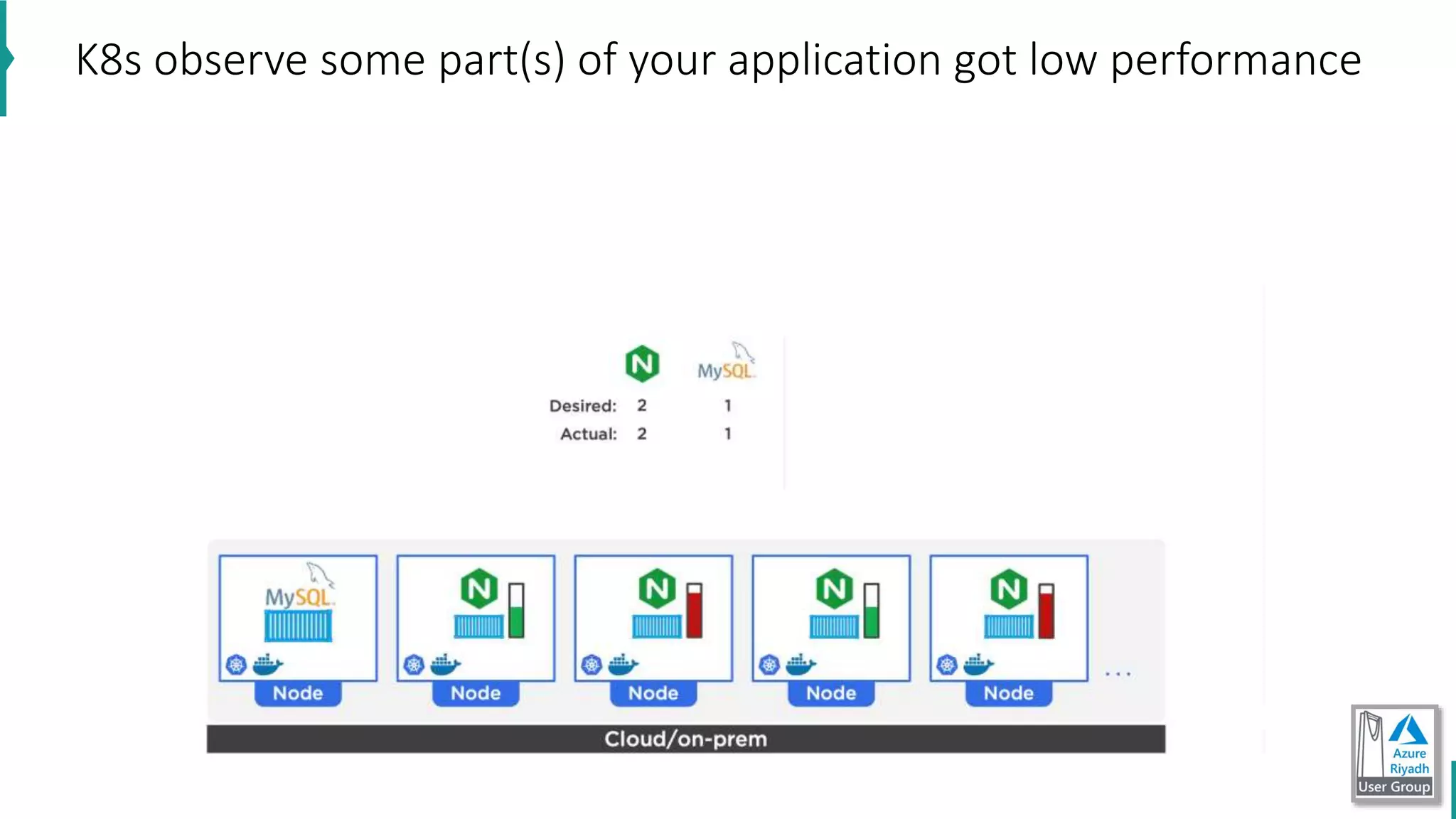
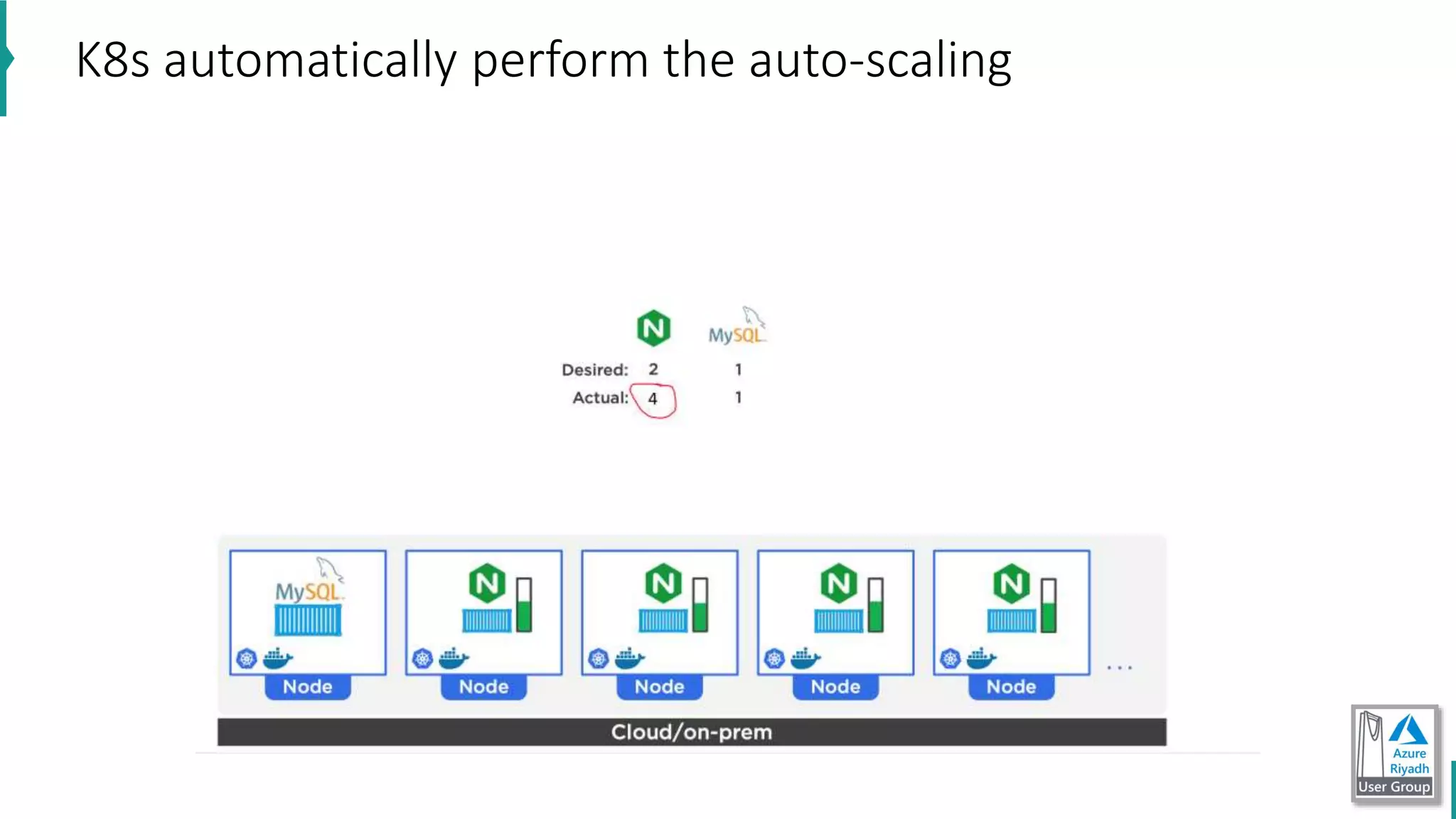
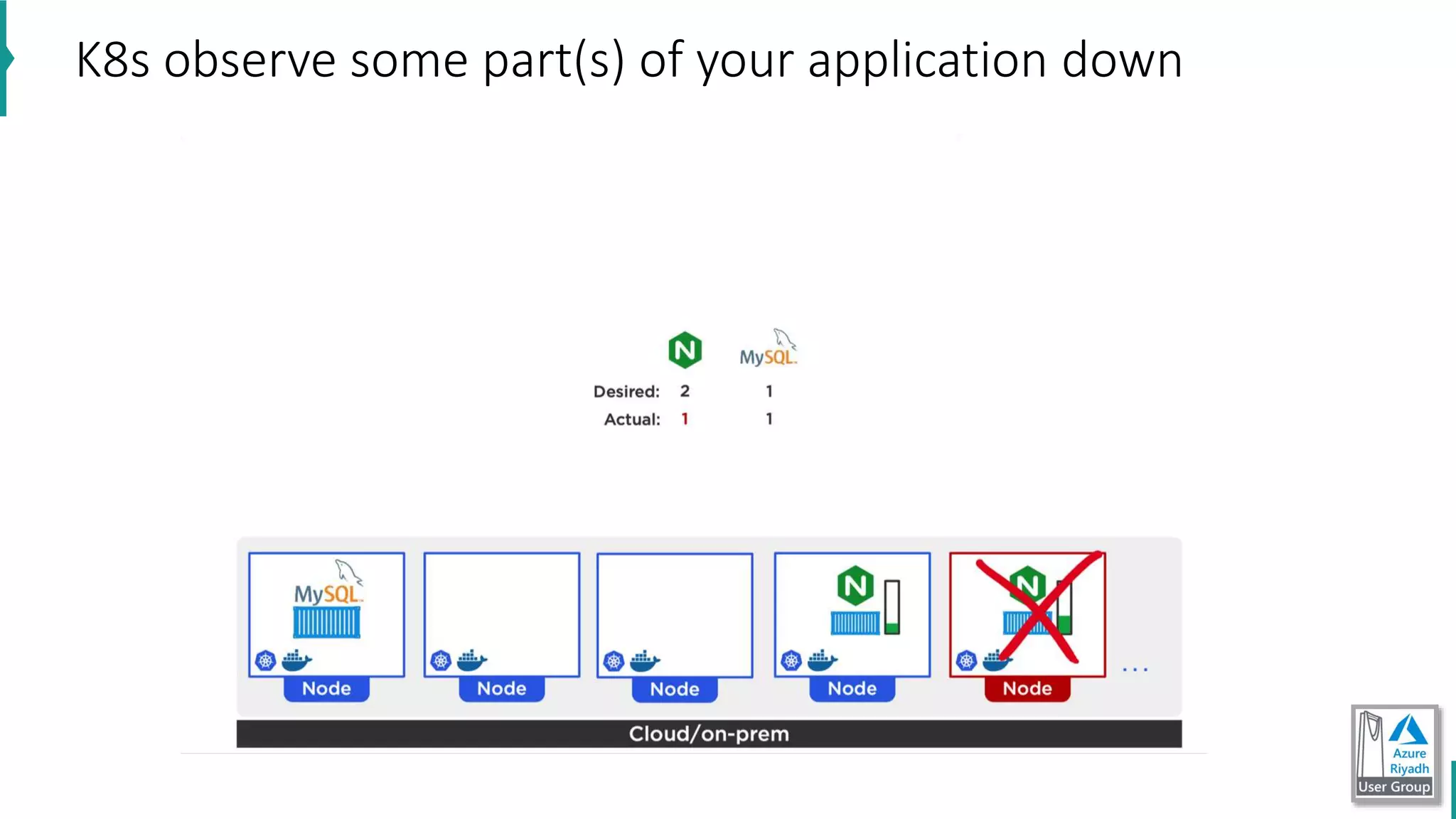
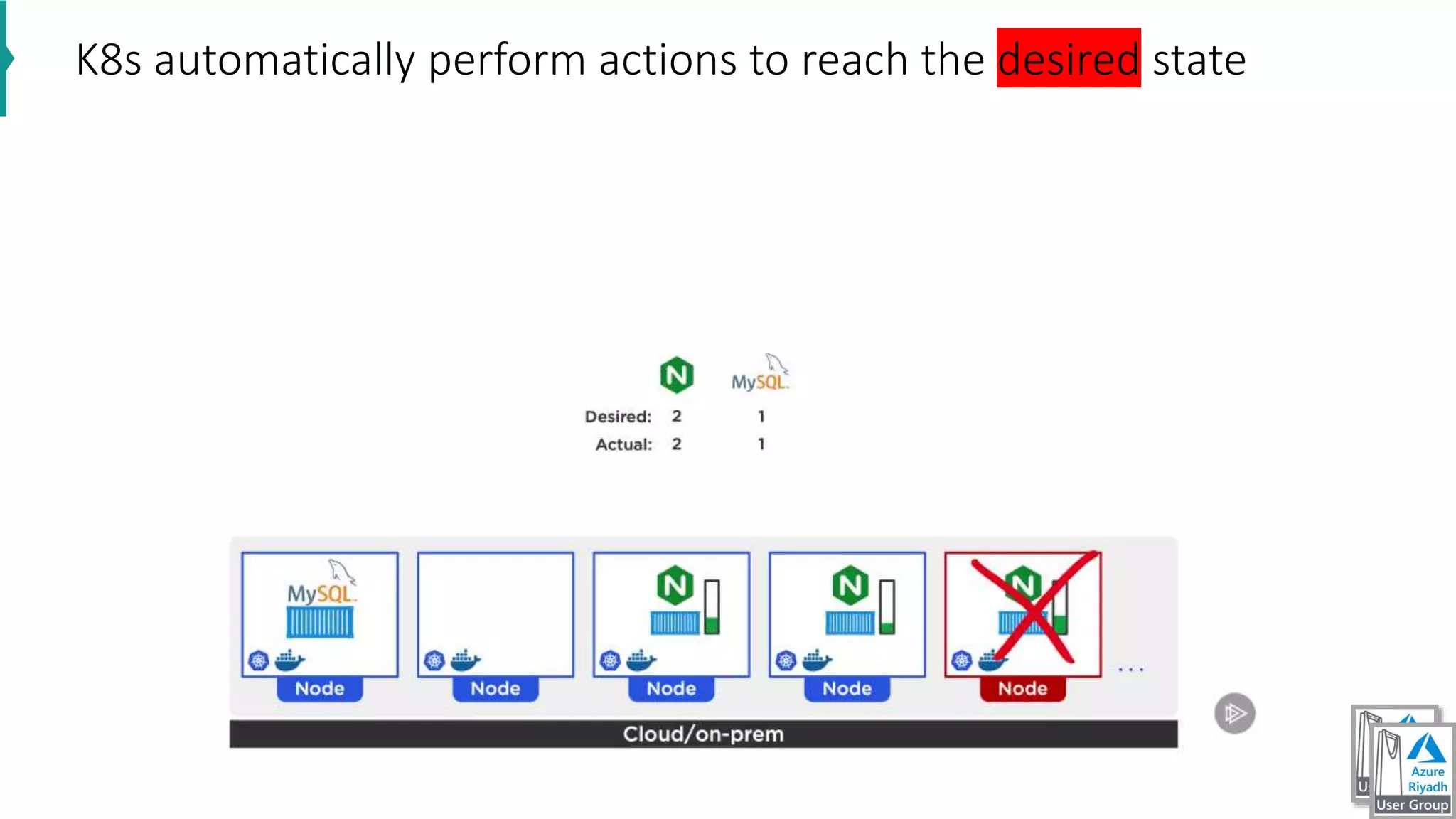
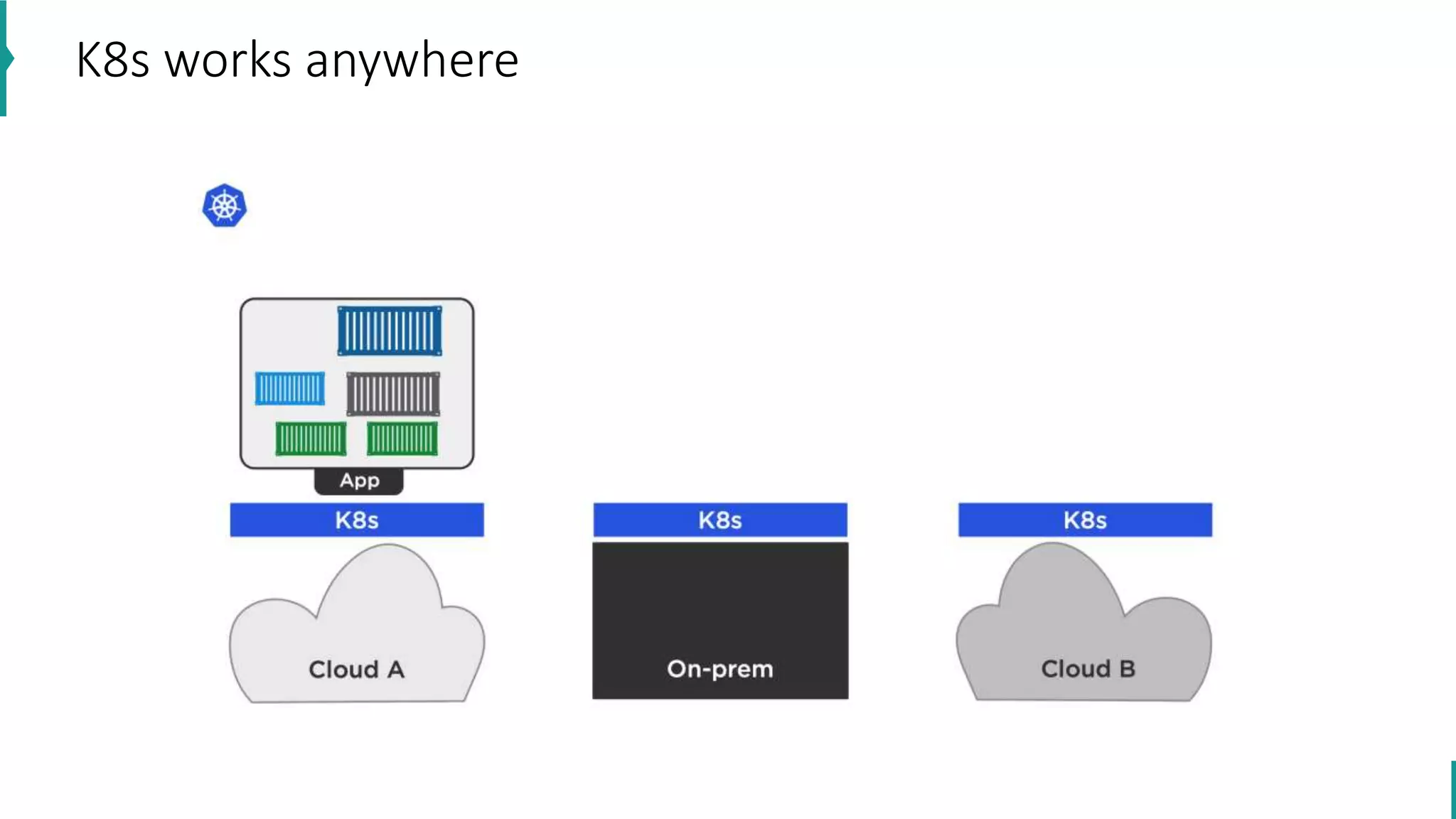
The document discusses key concepts in DevOps, including principles, continuous integration (CI), continuous delivery (CD), and infrastructure as code (IaC). It highlights the importance of tools like Azure DevOps, Docker, and Kubernetes in optimizing development and operational workflows. Additionally, the document provides demos and explanations of deployment methods, organizational benefits of modularization, and essential aspects of containerization.