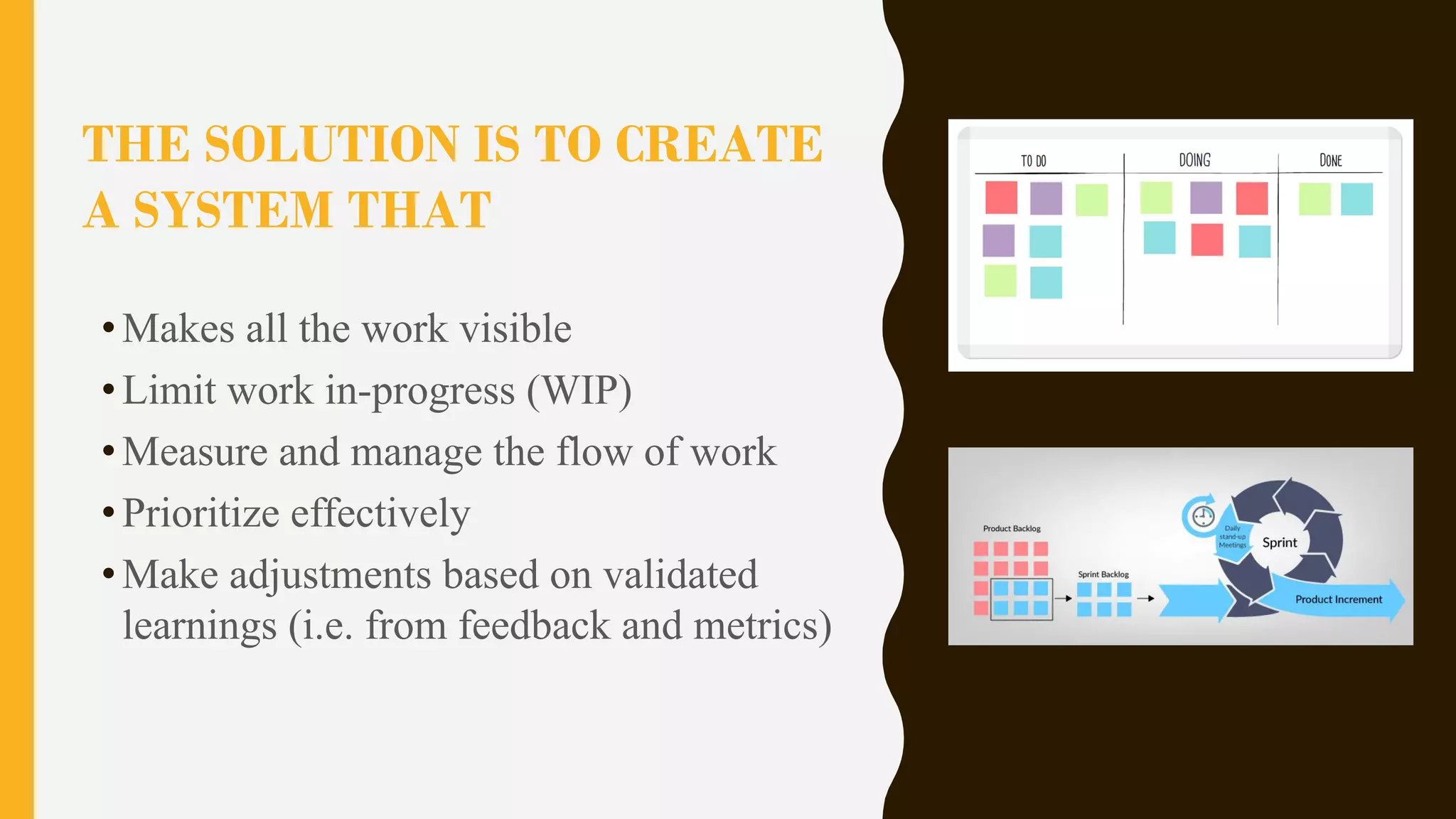
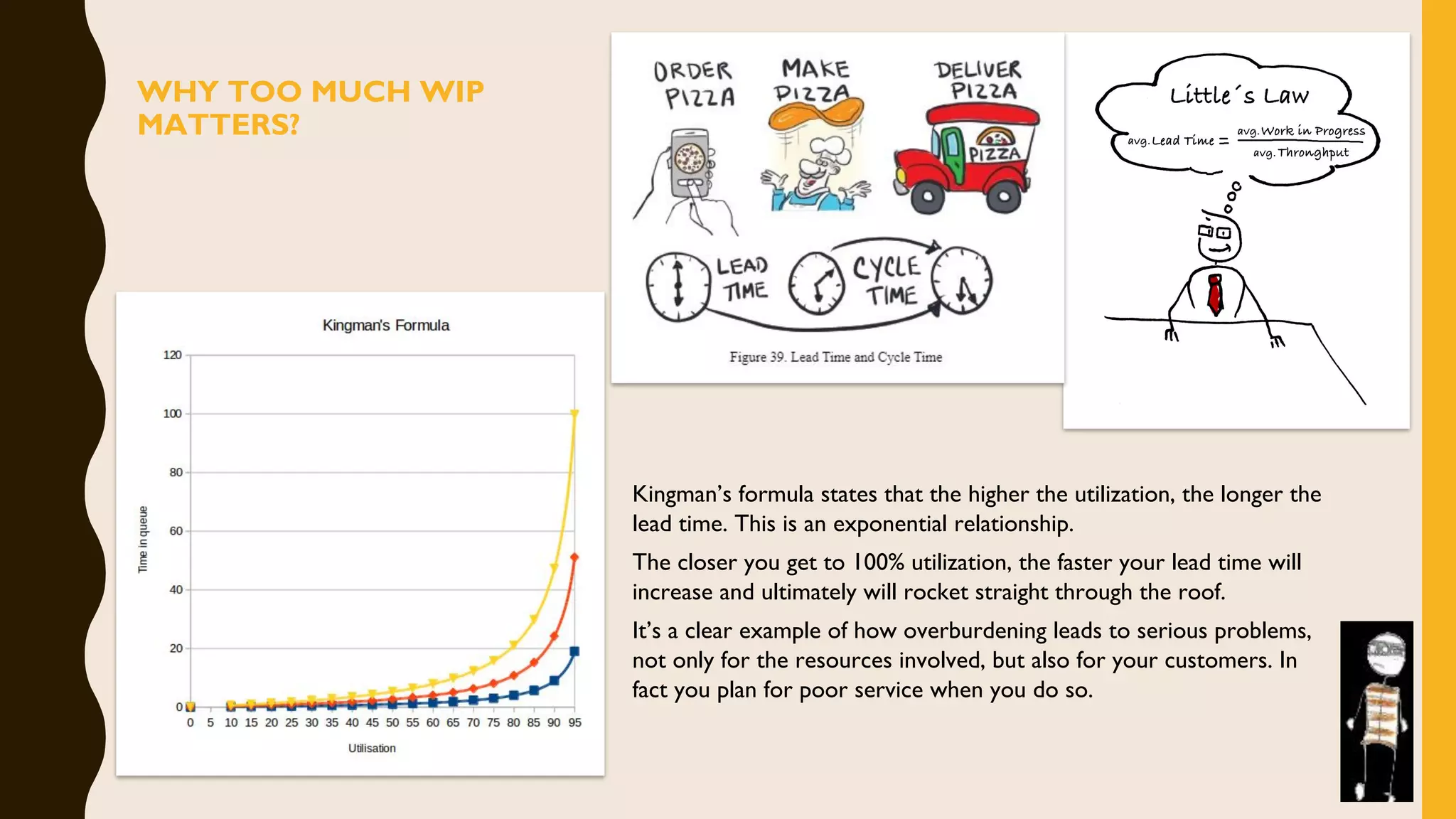
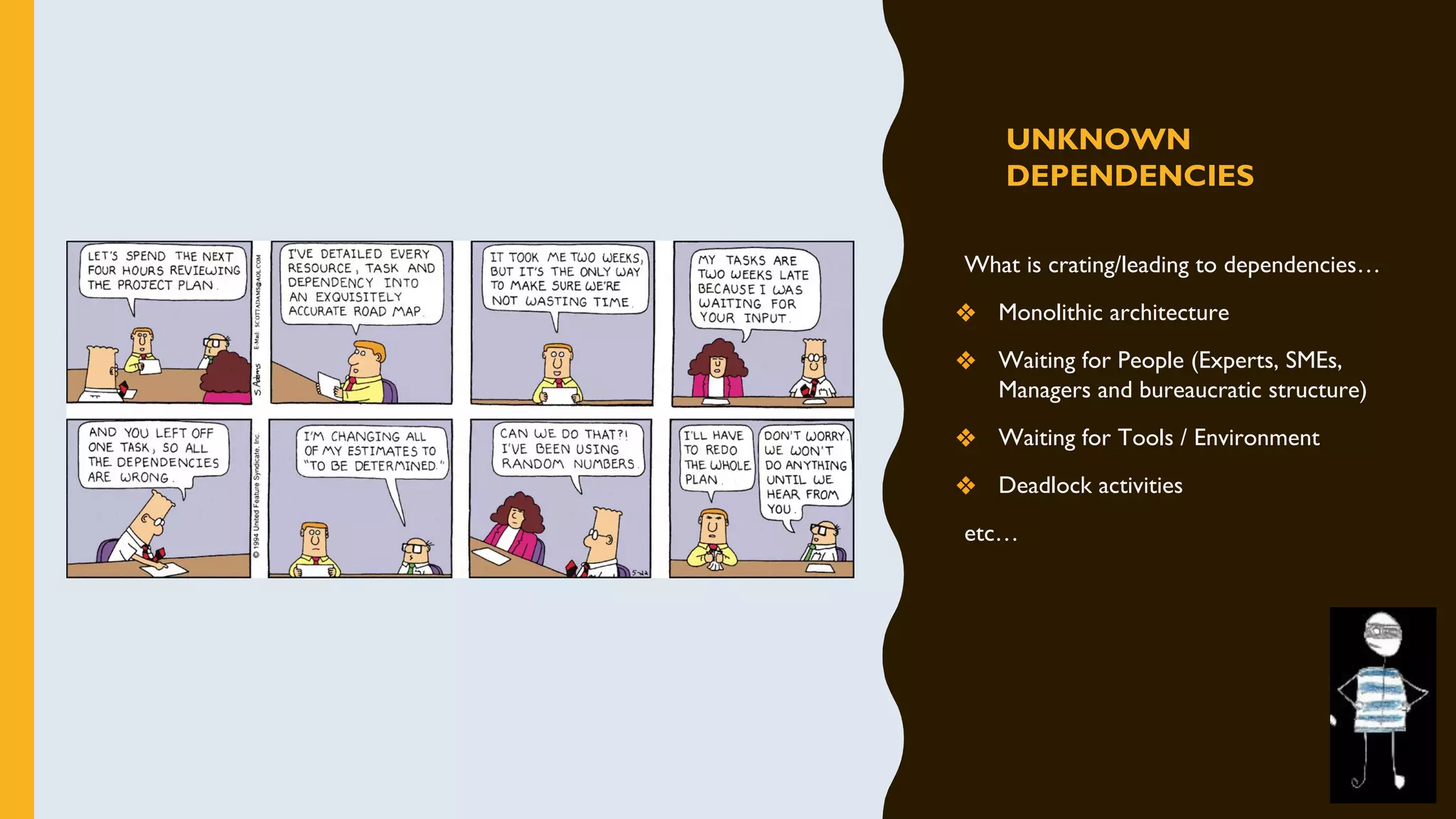
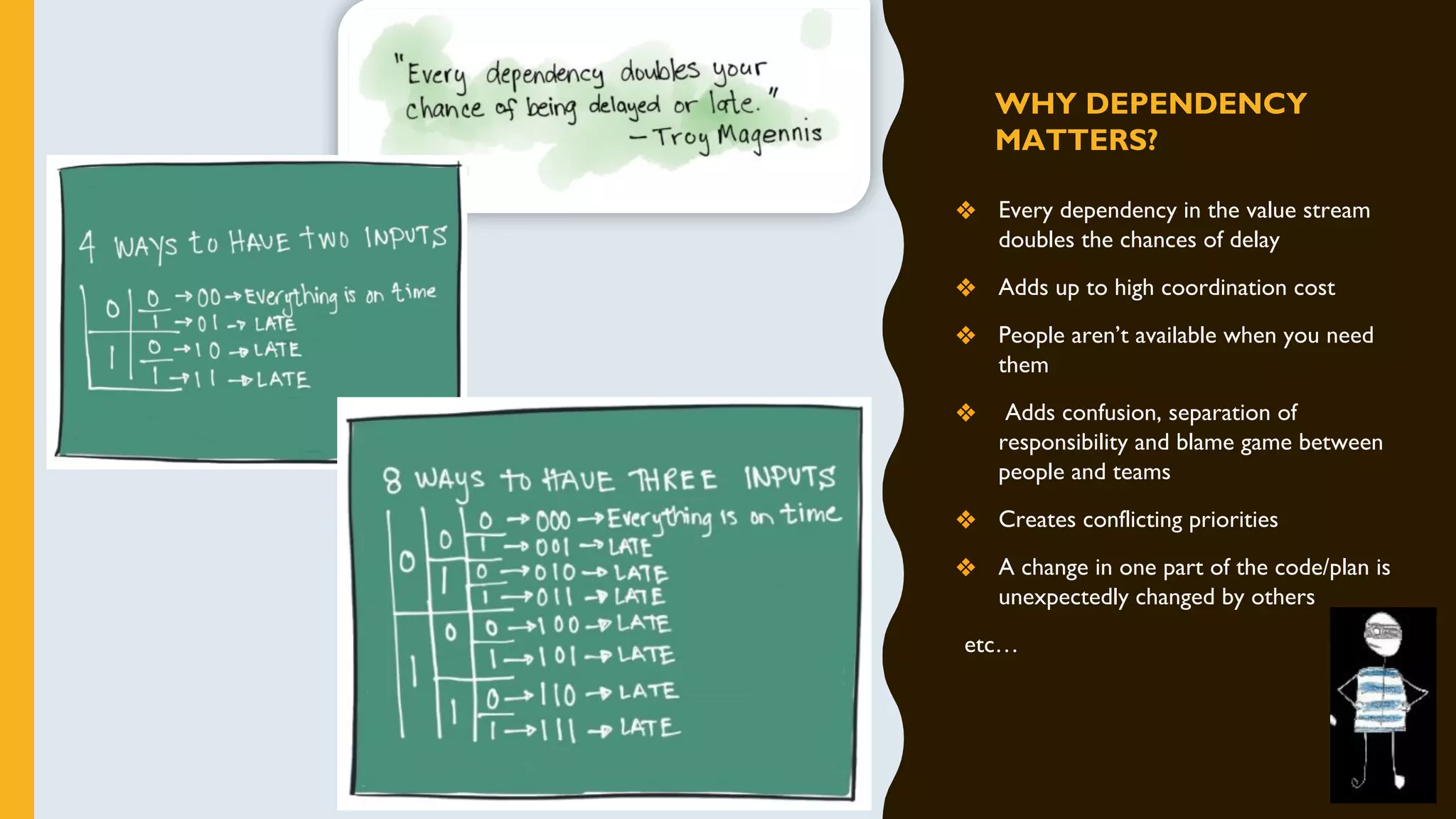
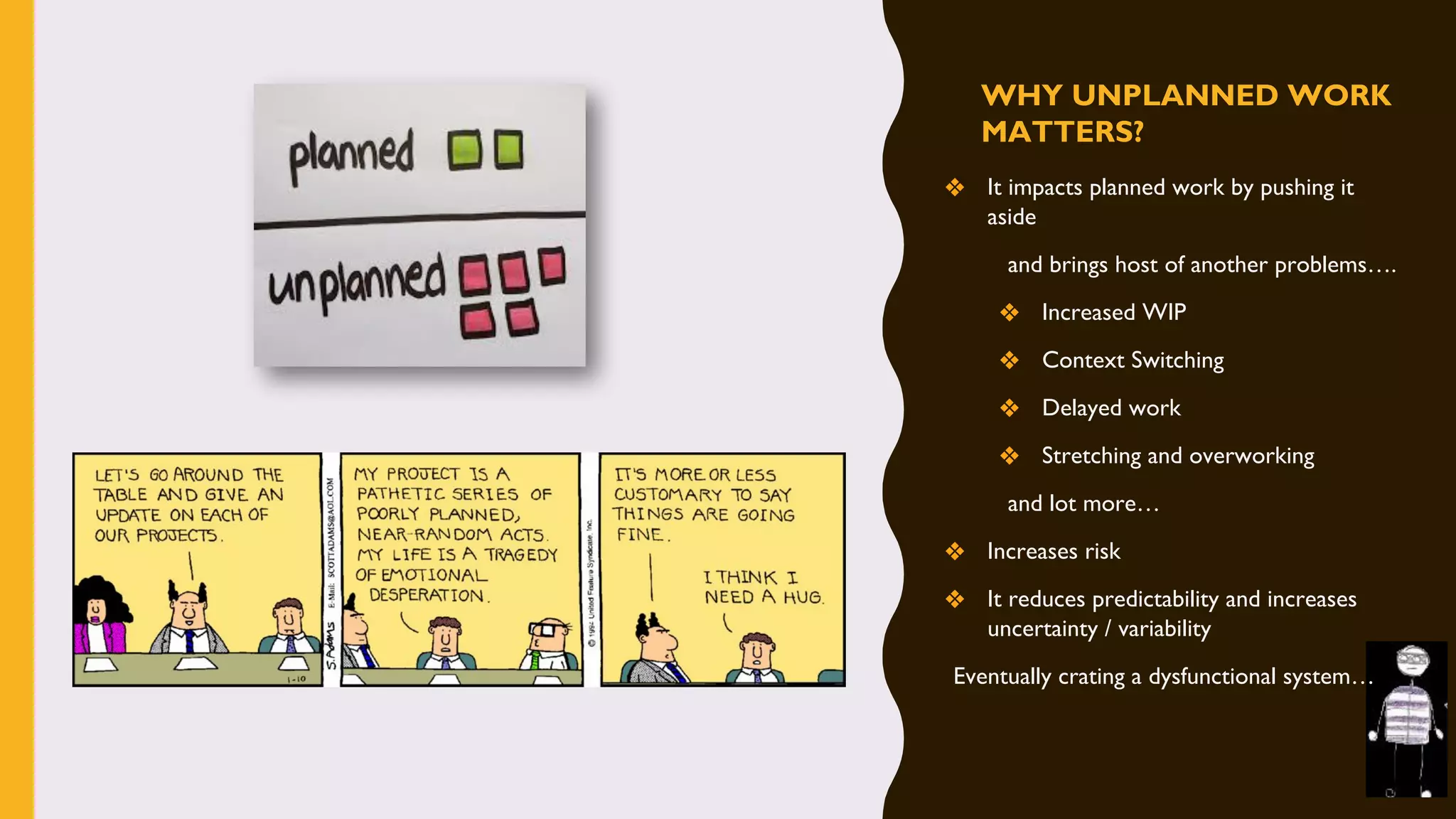
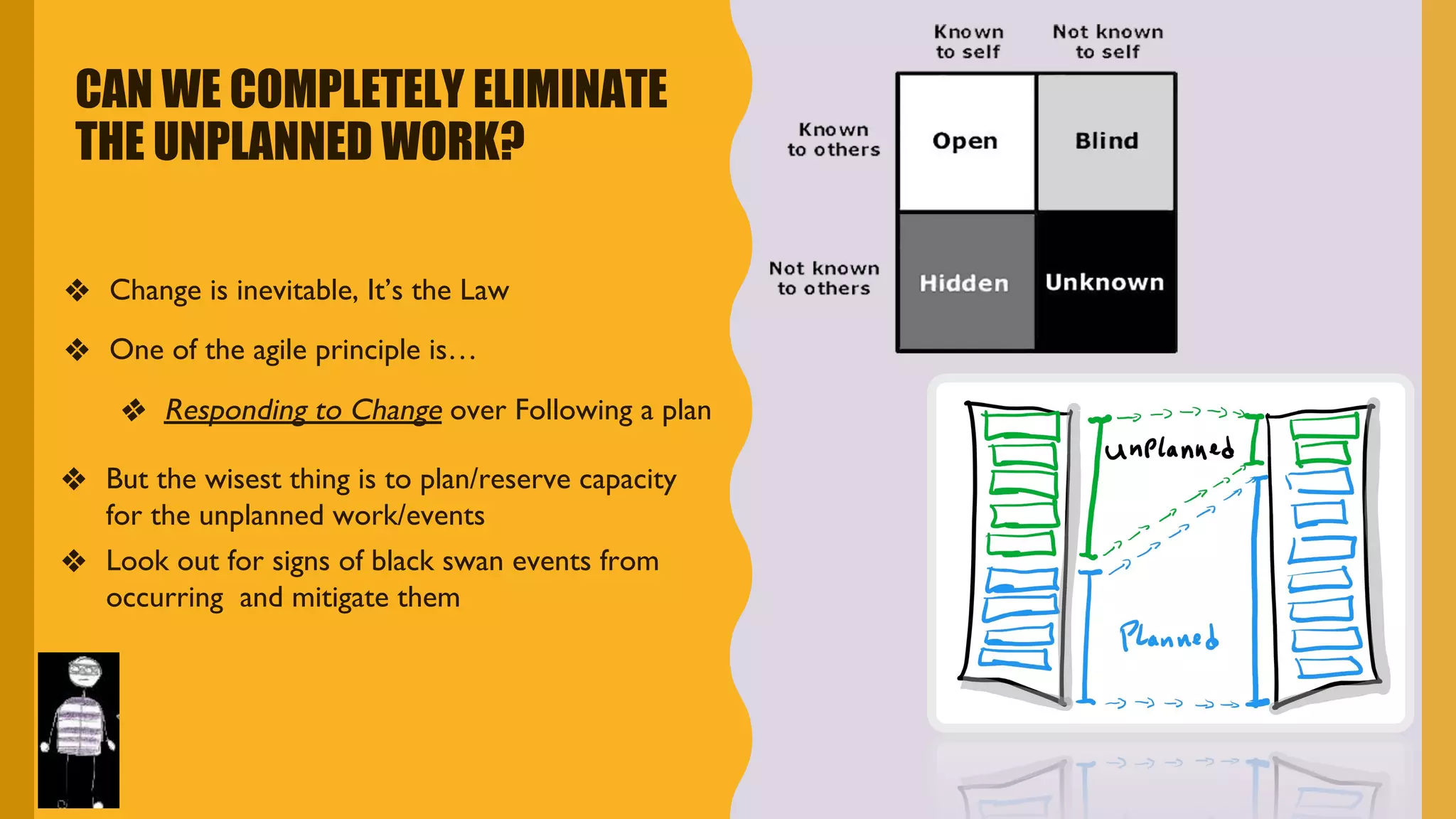
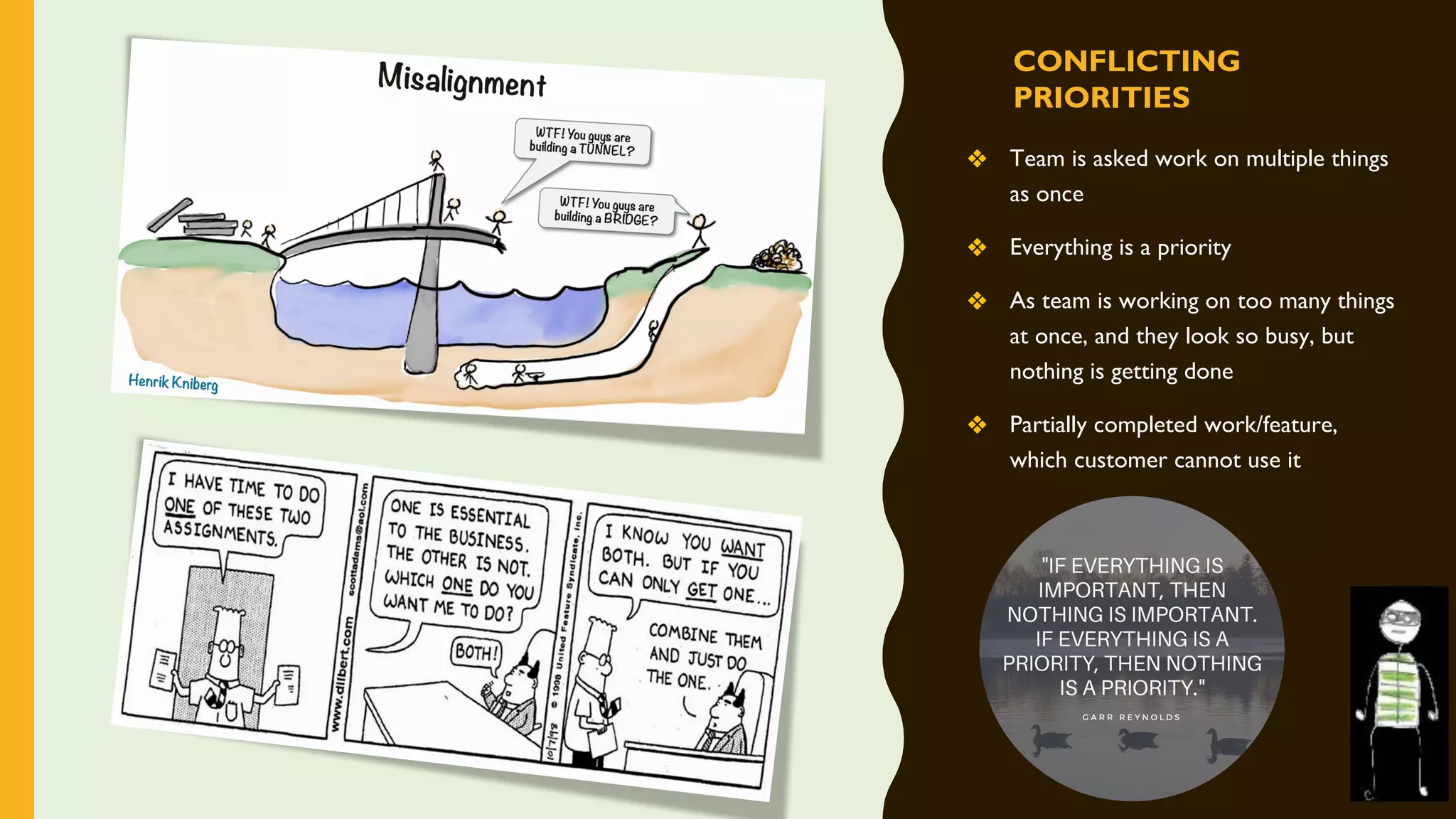
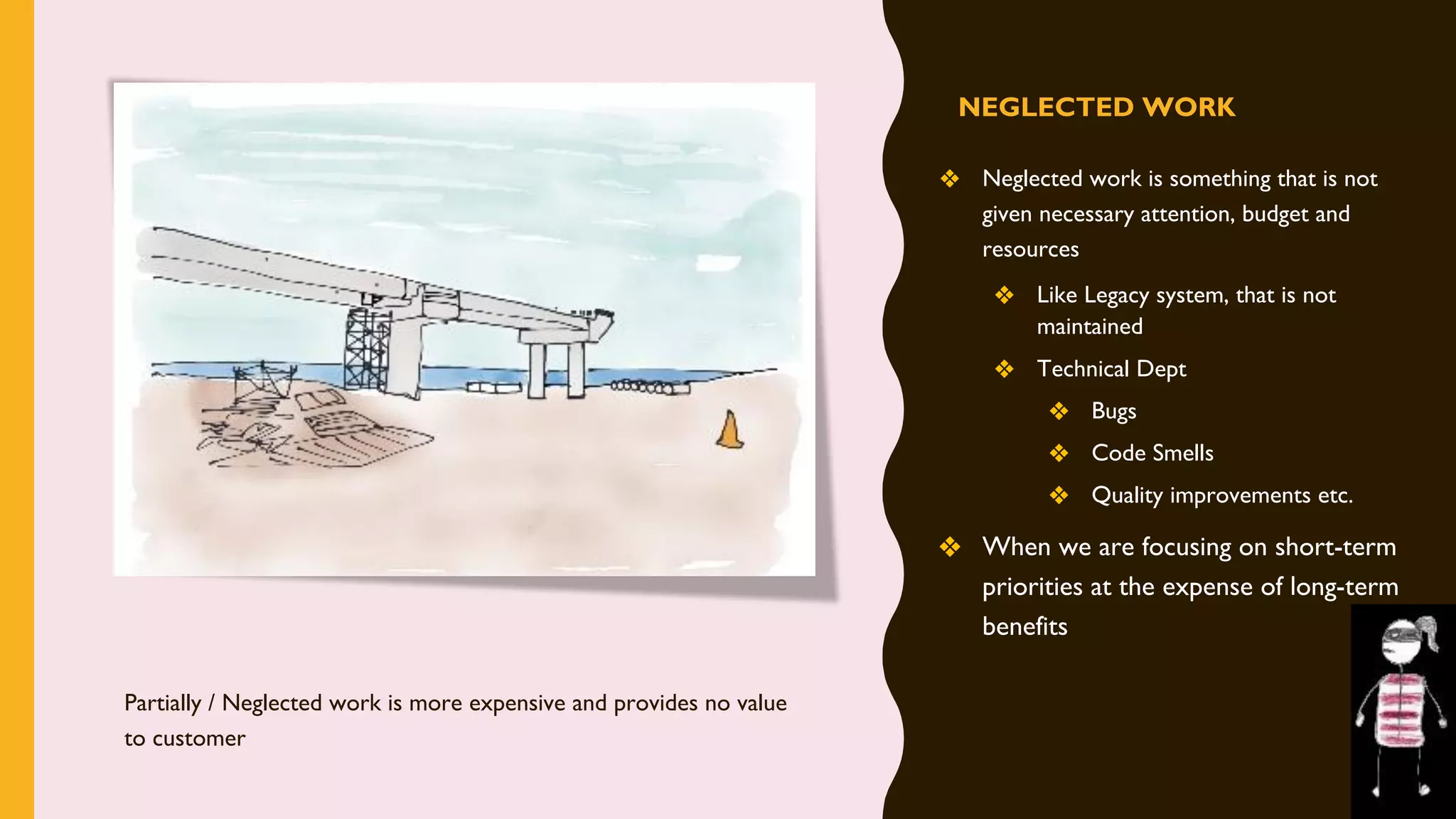
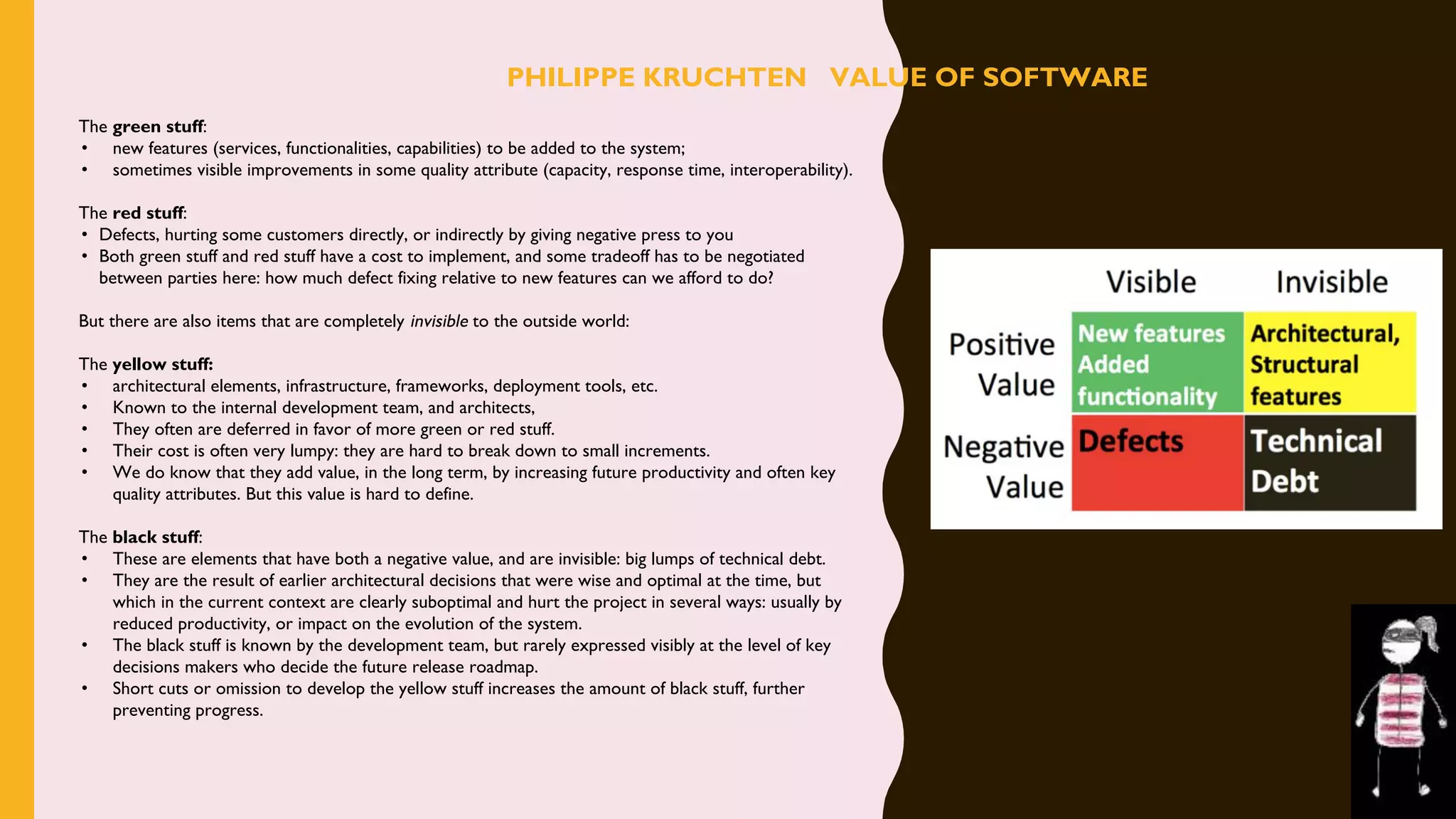
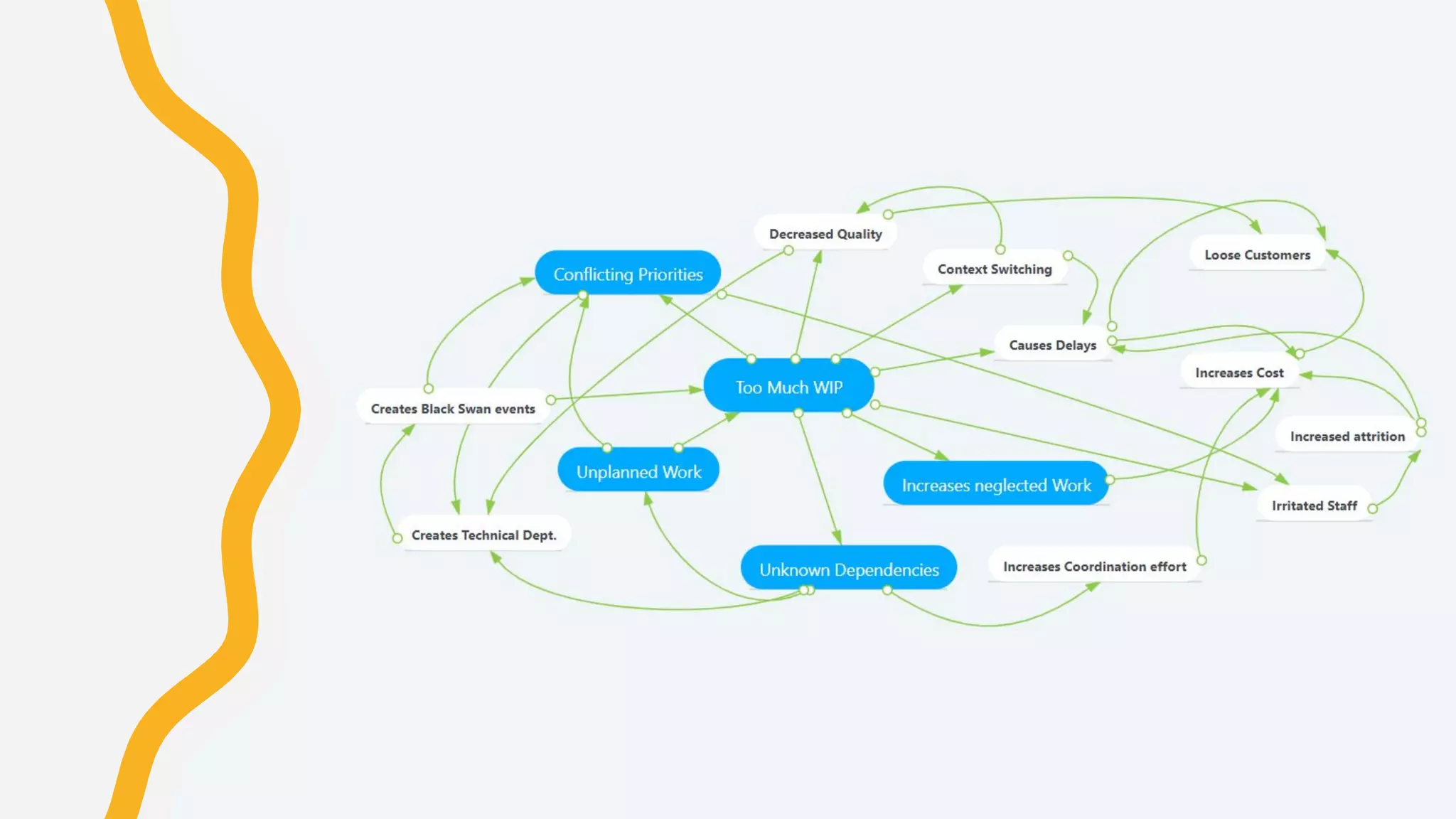
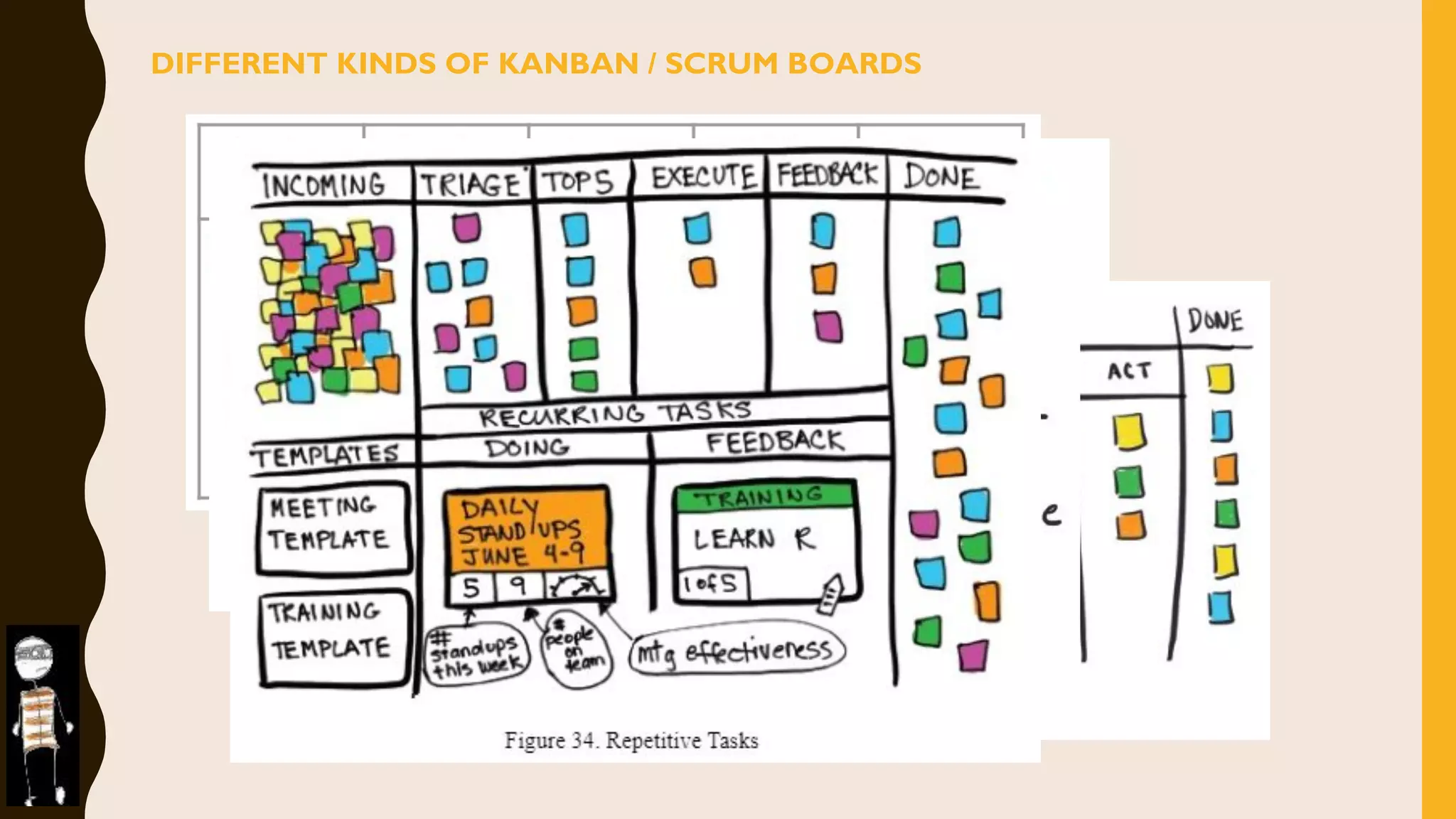
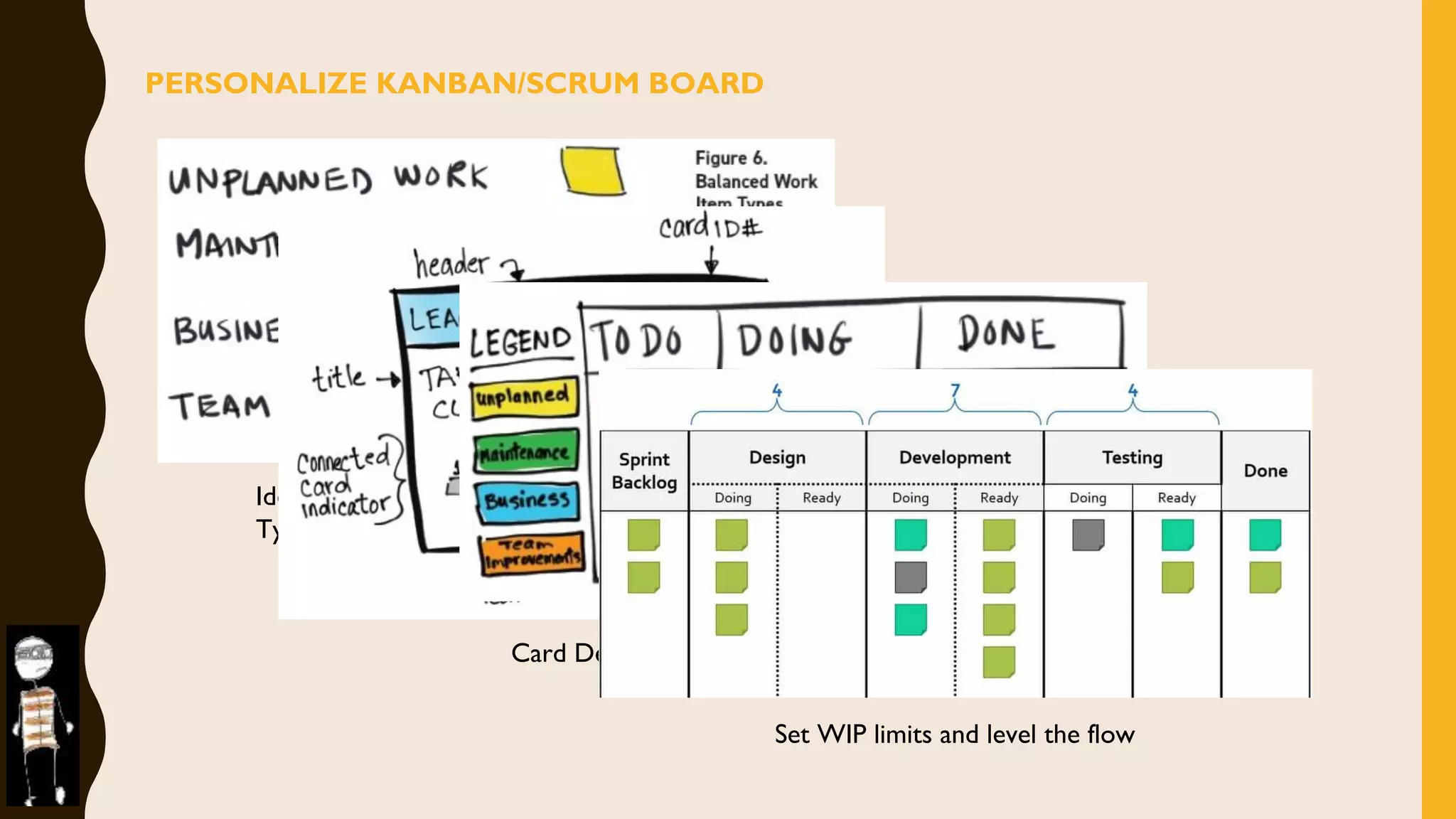
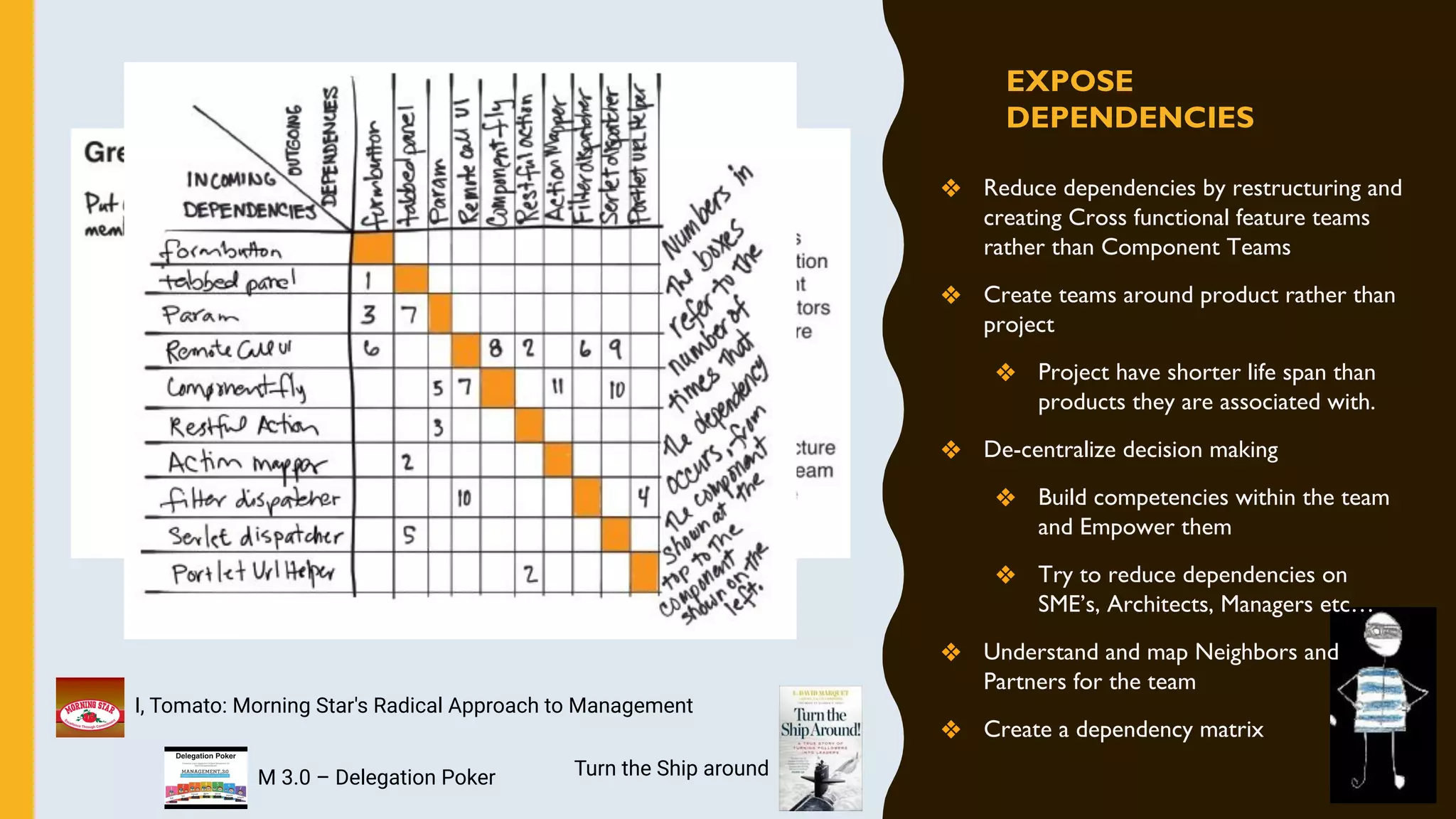
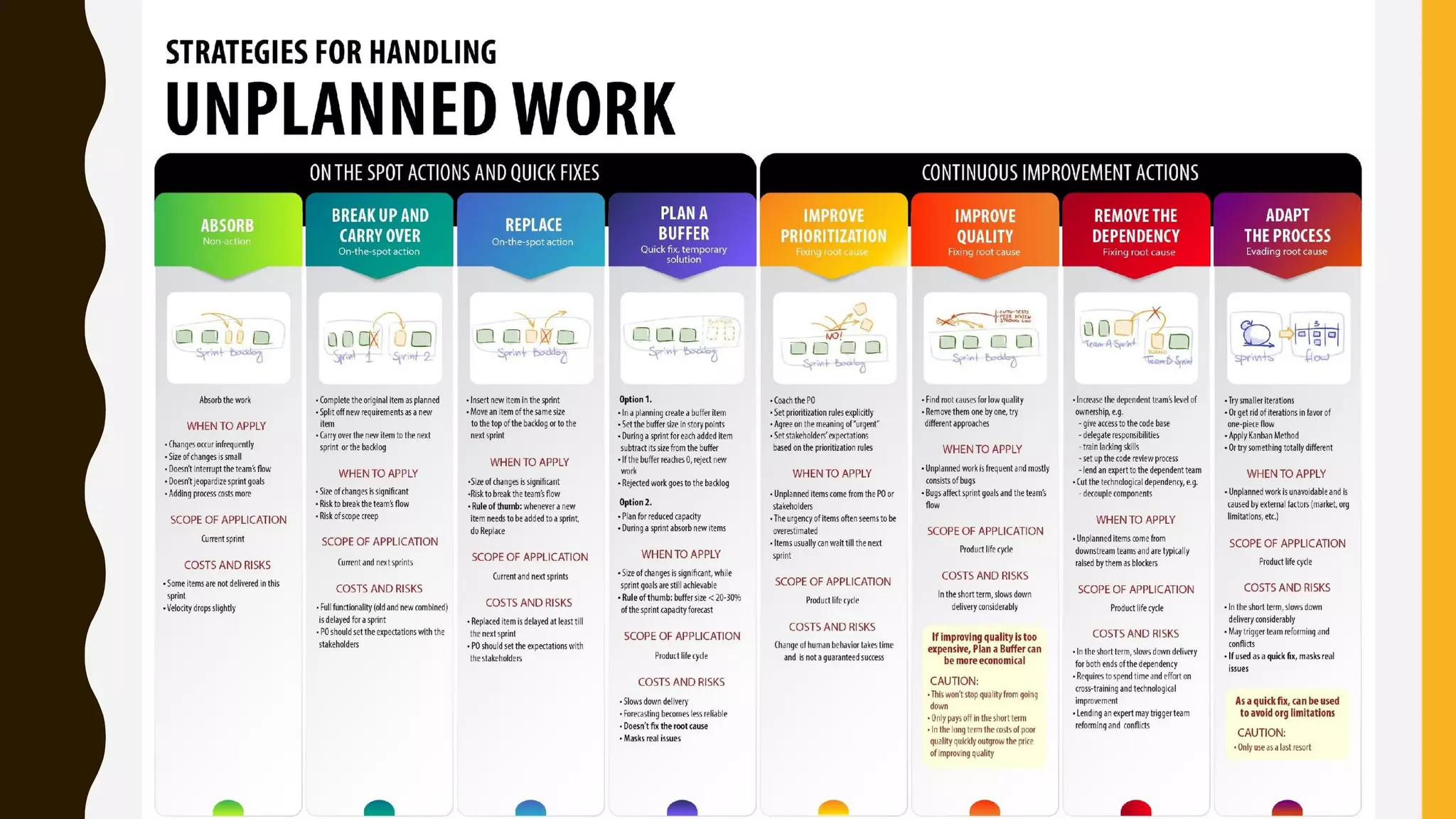
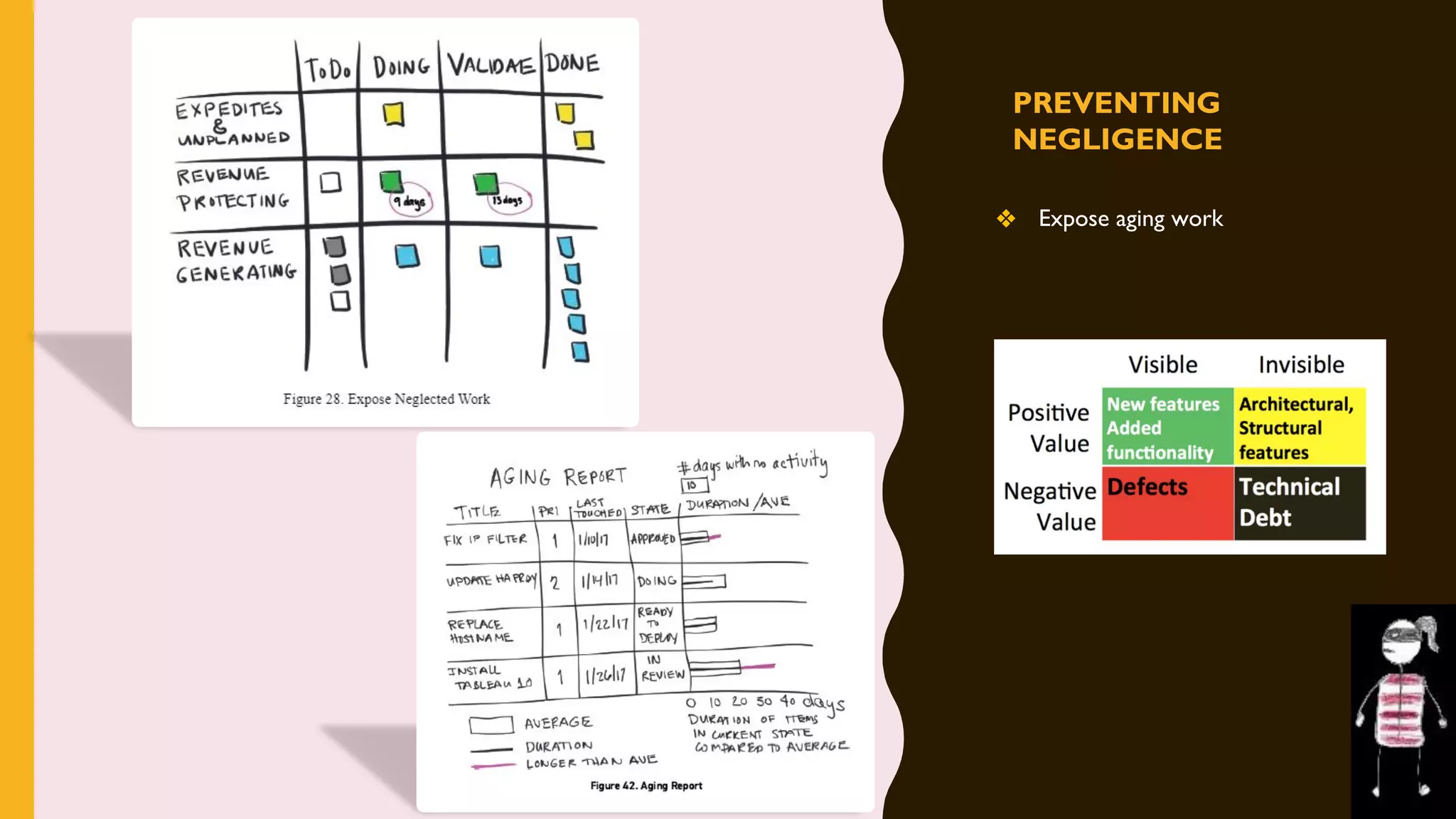
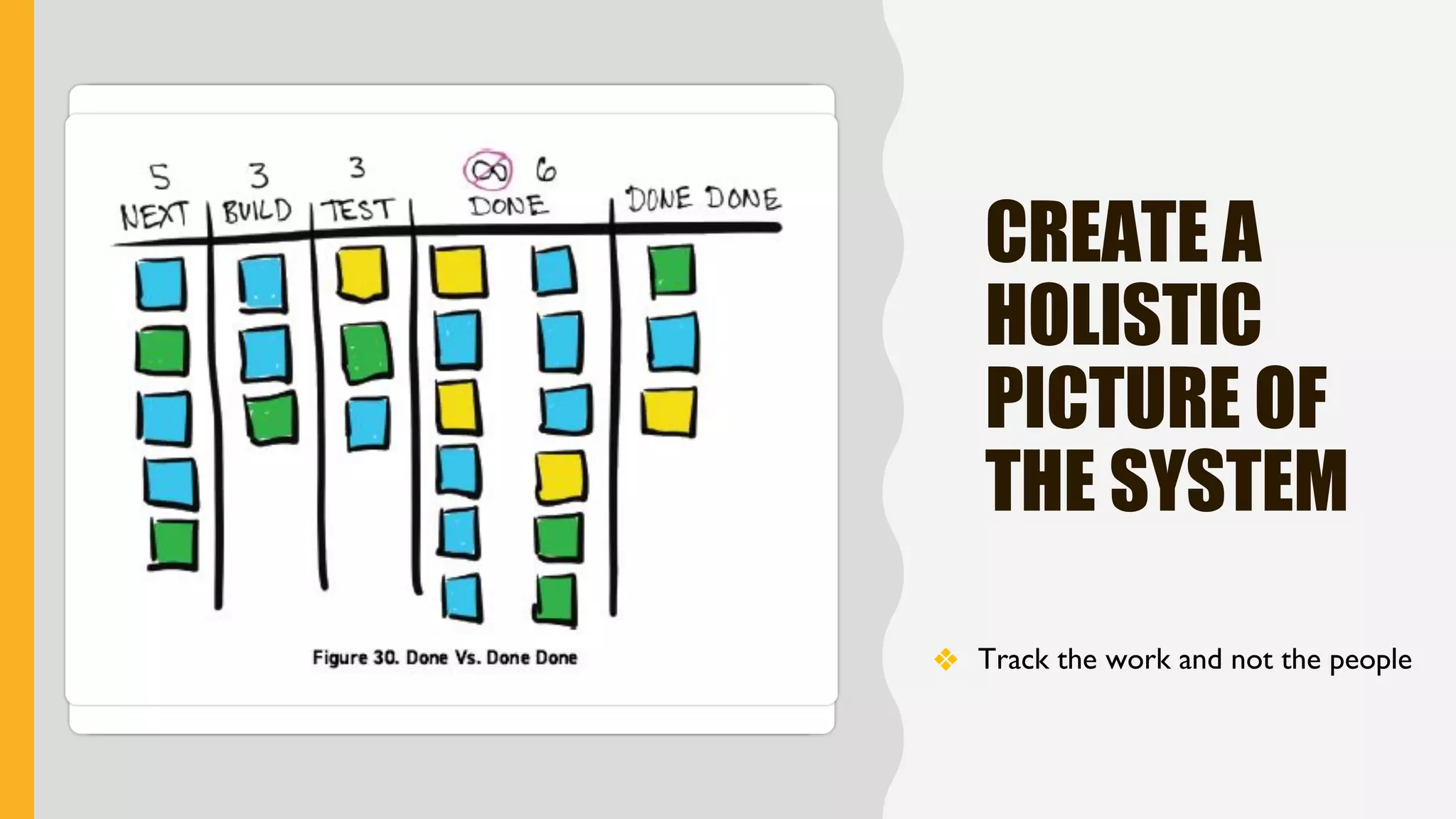
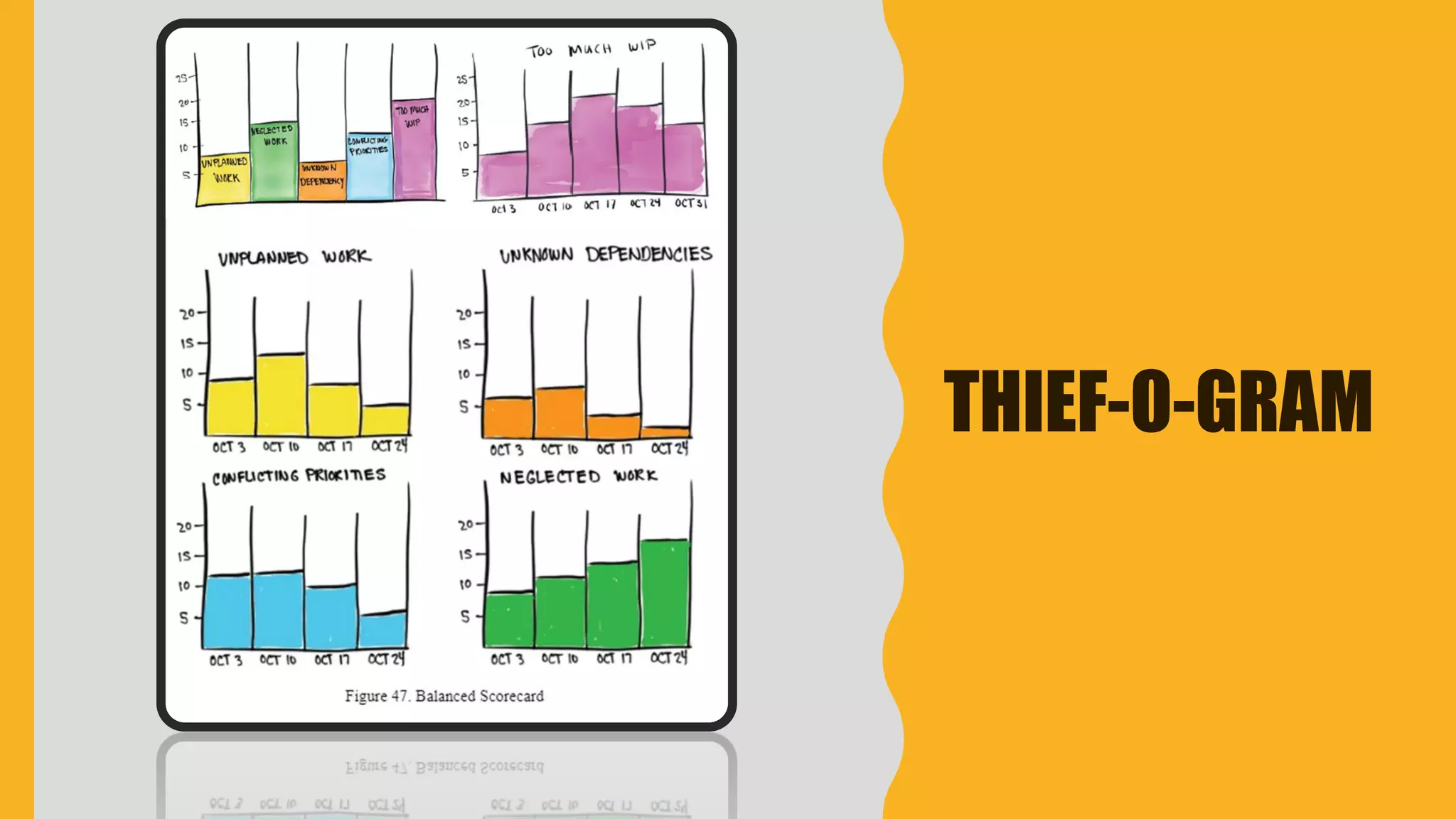
The document discusses how to identify and address five "time thieves" - too much work-in-progress, conflicting priorities, unknown dependencies, unplanned work, and neglected work - that can stall workflow optimization. It recommends making all work visible using tools like Kanban boards, setting work-in-progress limits, exposing dependencies between teams, prioritizing work, and tracking aging tasks to create transparency and accountability that will optimize the flow of work.