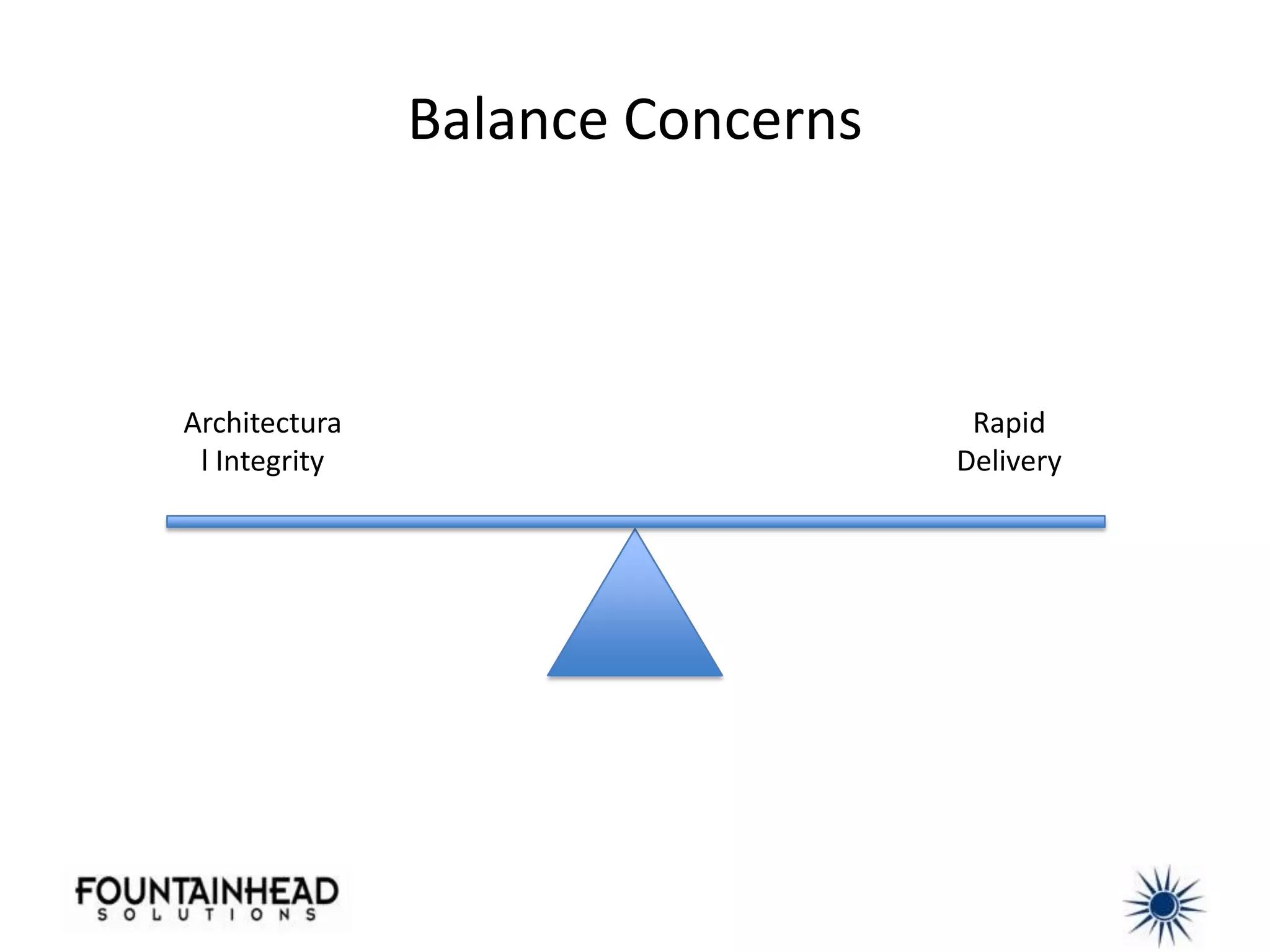
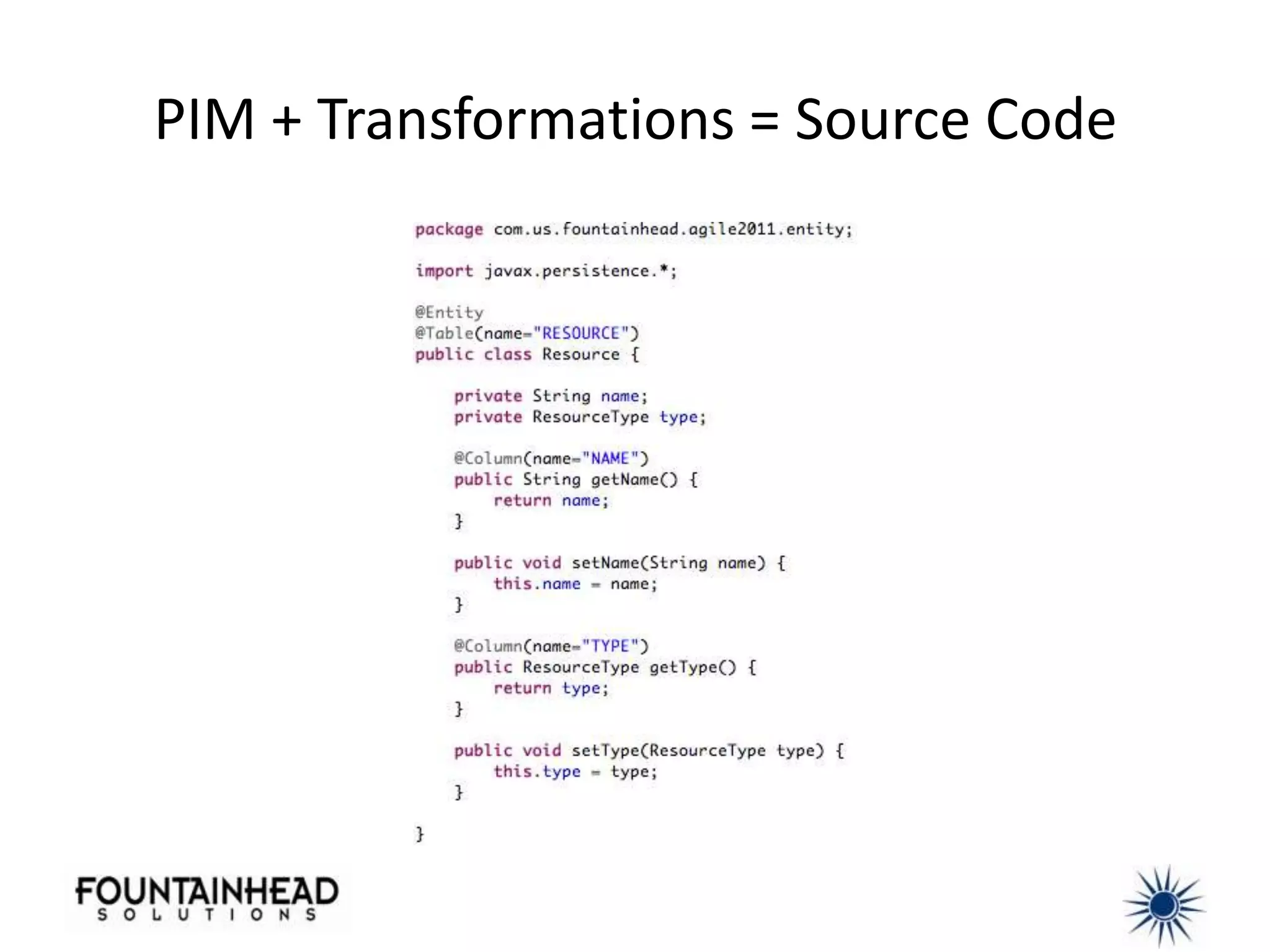
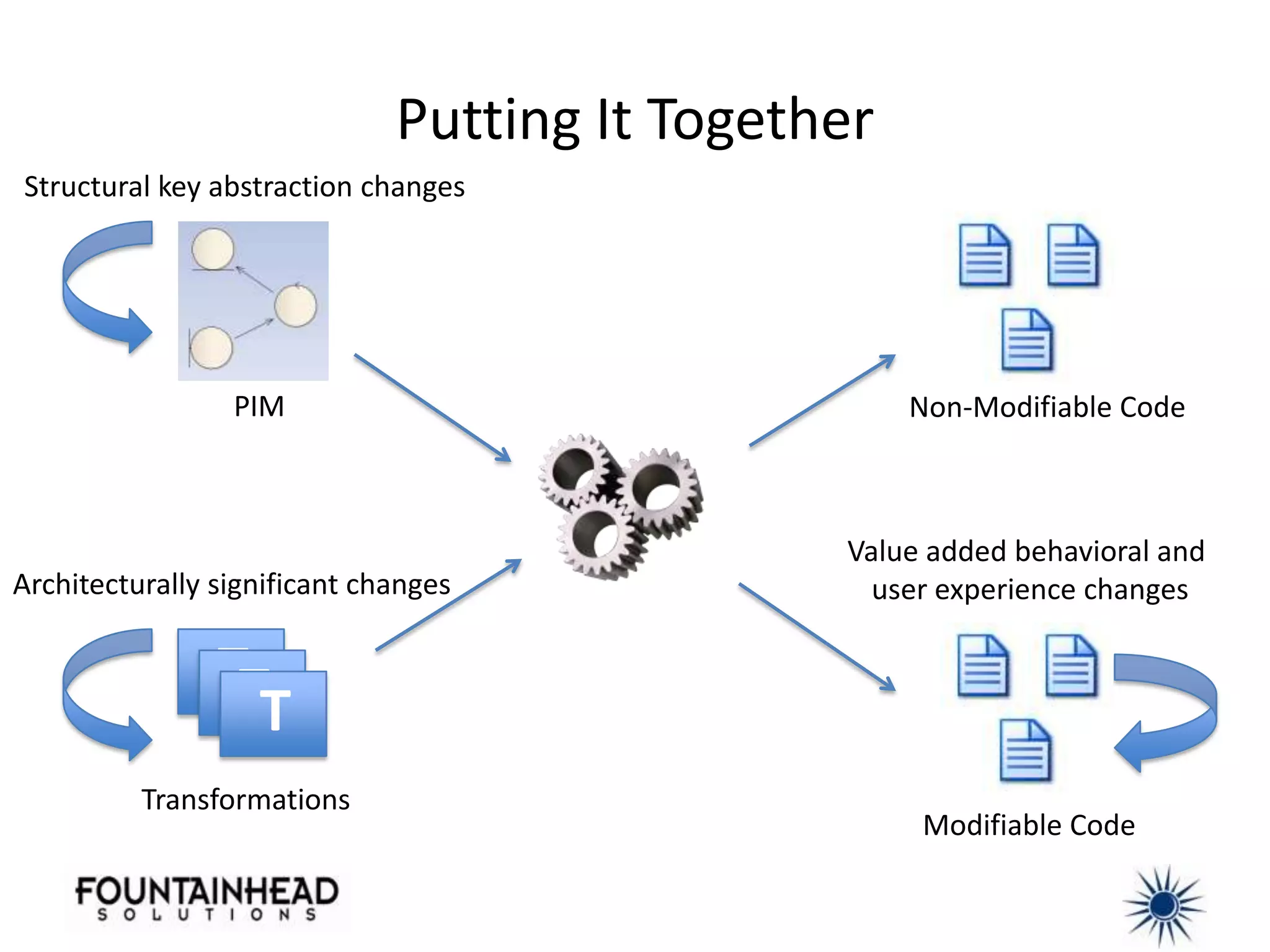
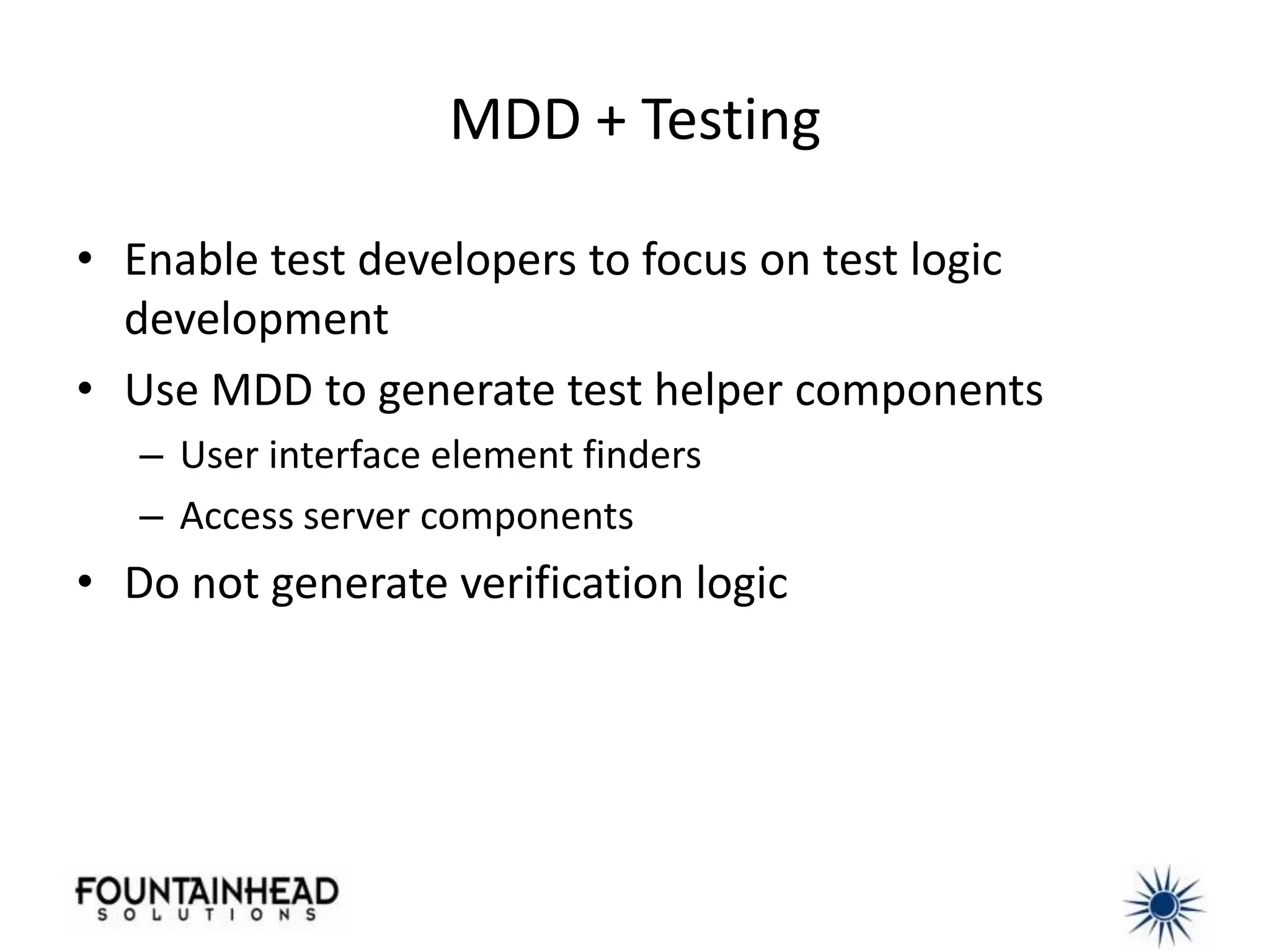
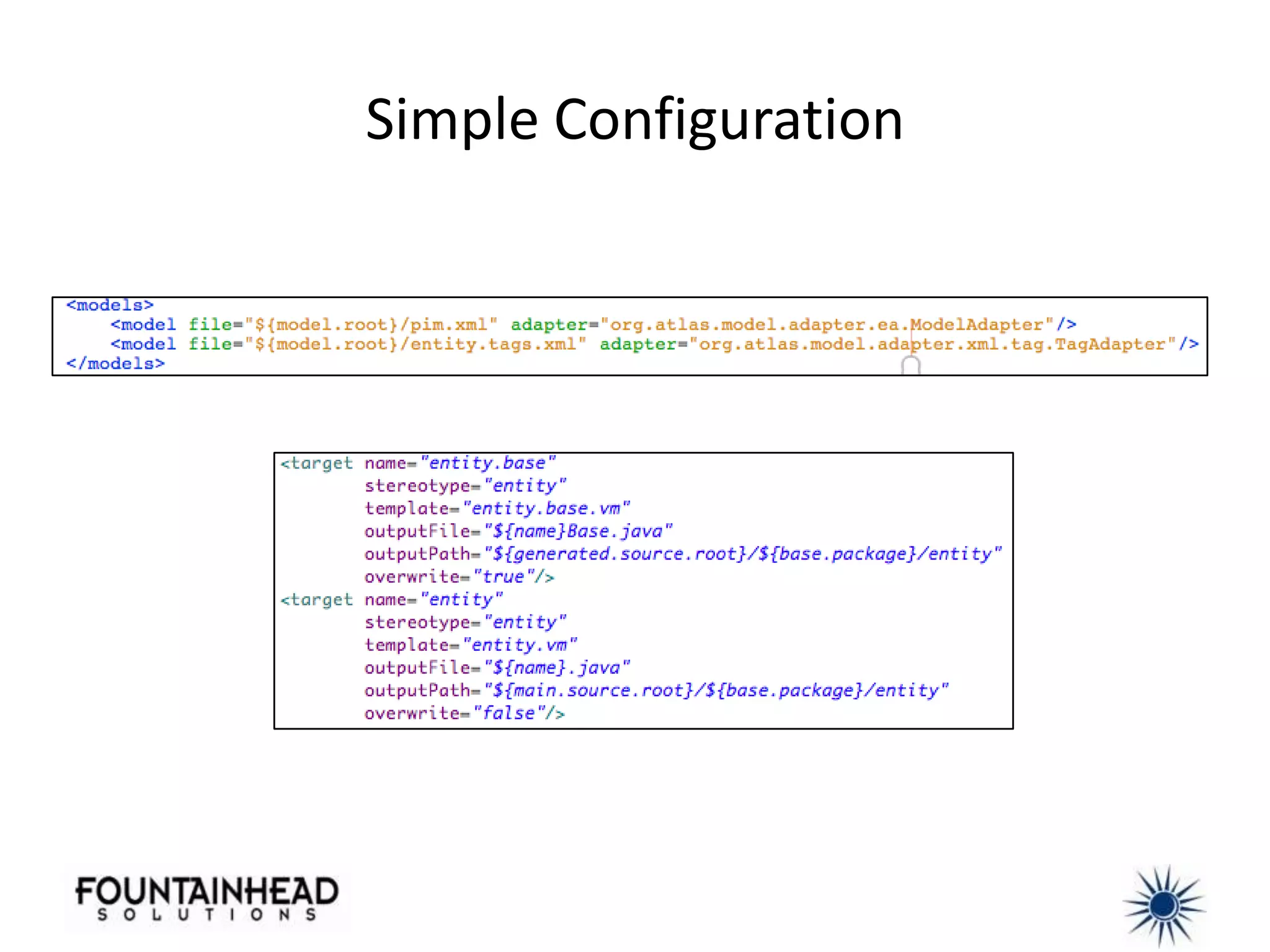
This document discusses how model-driven development (MDD) can help balance architectural integrity and rapid delivery for agile projects. MDD uses models to represent problem and solution knowledge, provide a common lexicon, and serve as the basis for conversations about system relationships. Models and transformations can automate implementation knowledge to continually increase development velocity. The document provides examples of how to structure models and transformations simply and integrate MDD into agile processes and continuous integration/delivery practices. Case studies demonstrate how MDD rescued a failed project and bootstrapped a new development team.