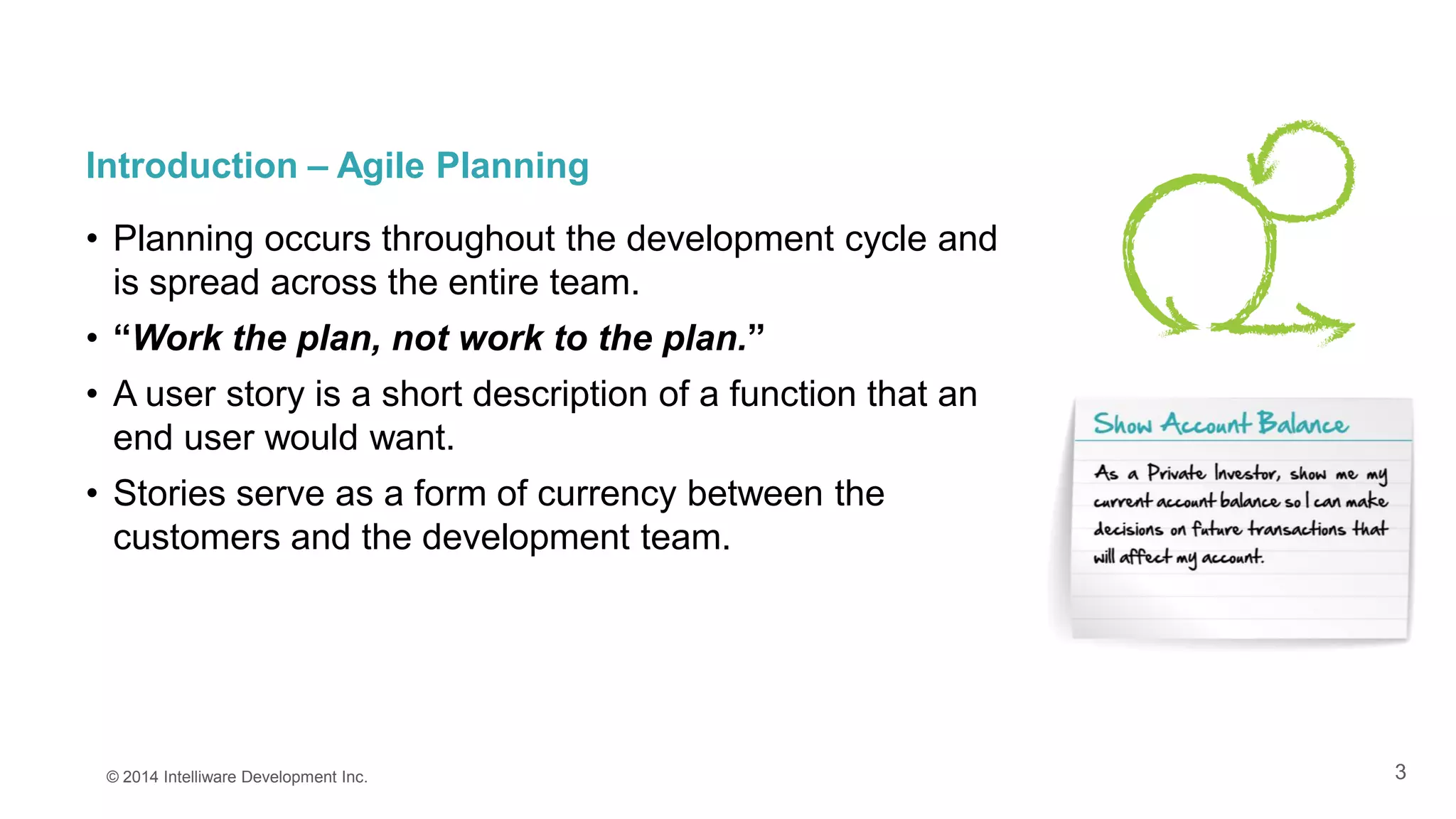
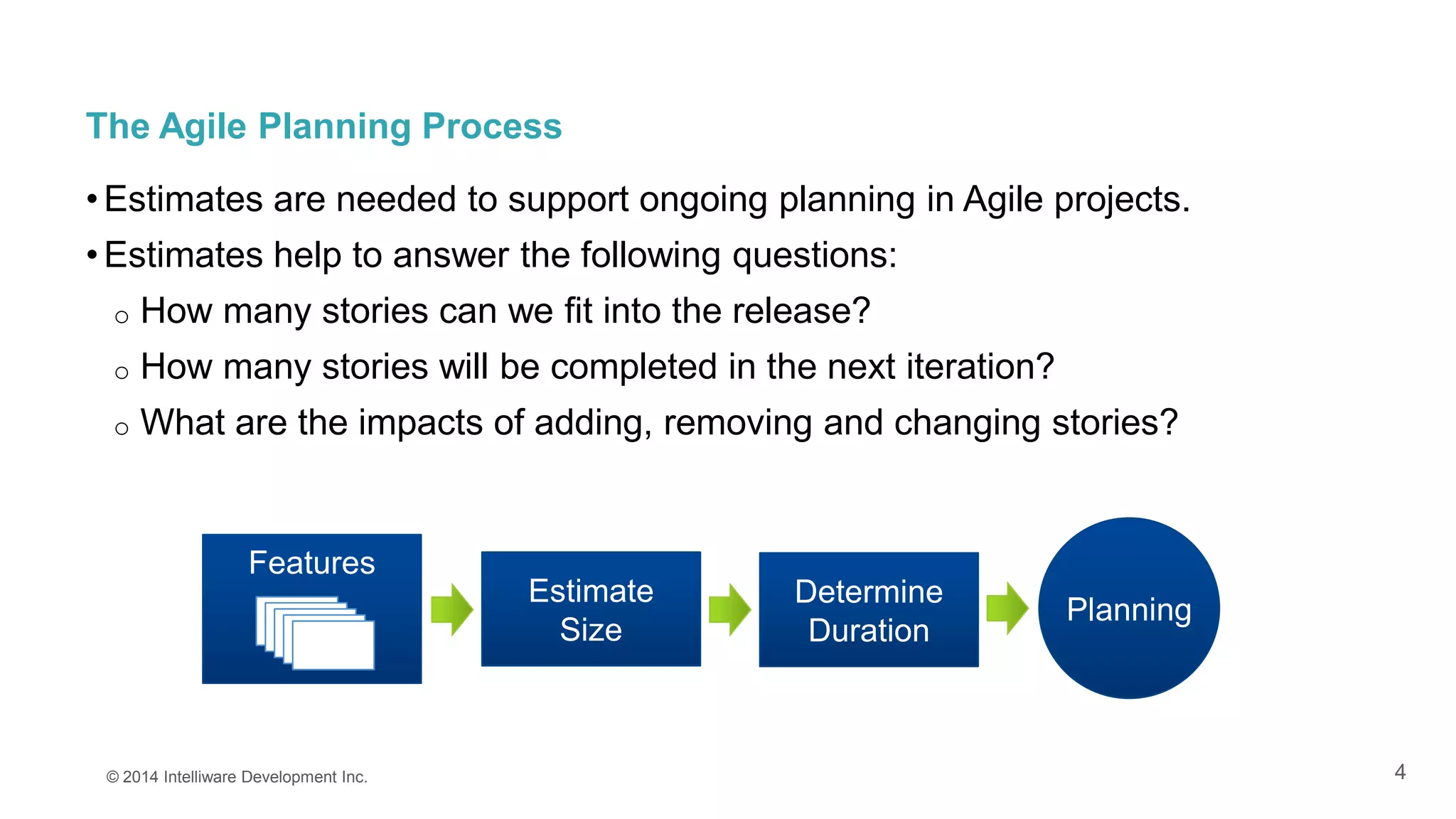
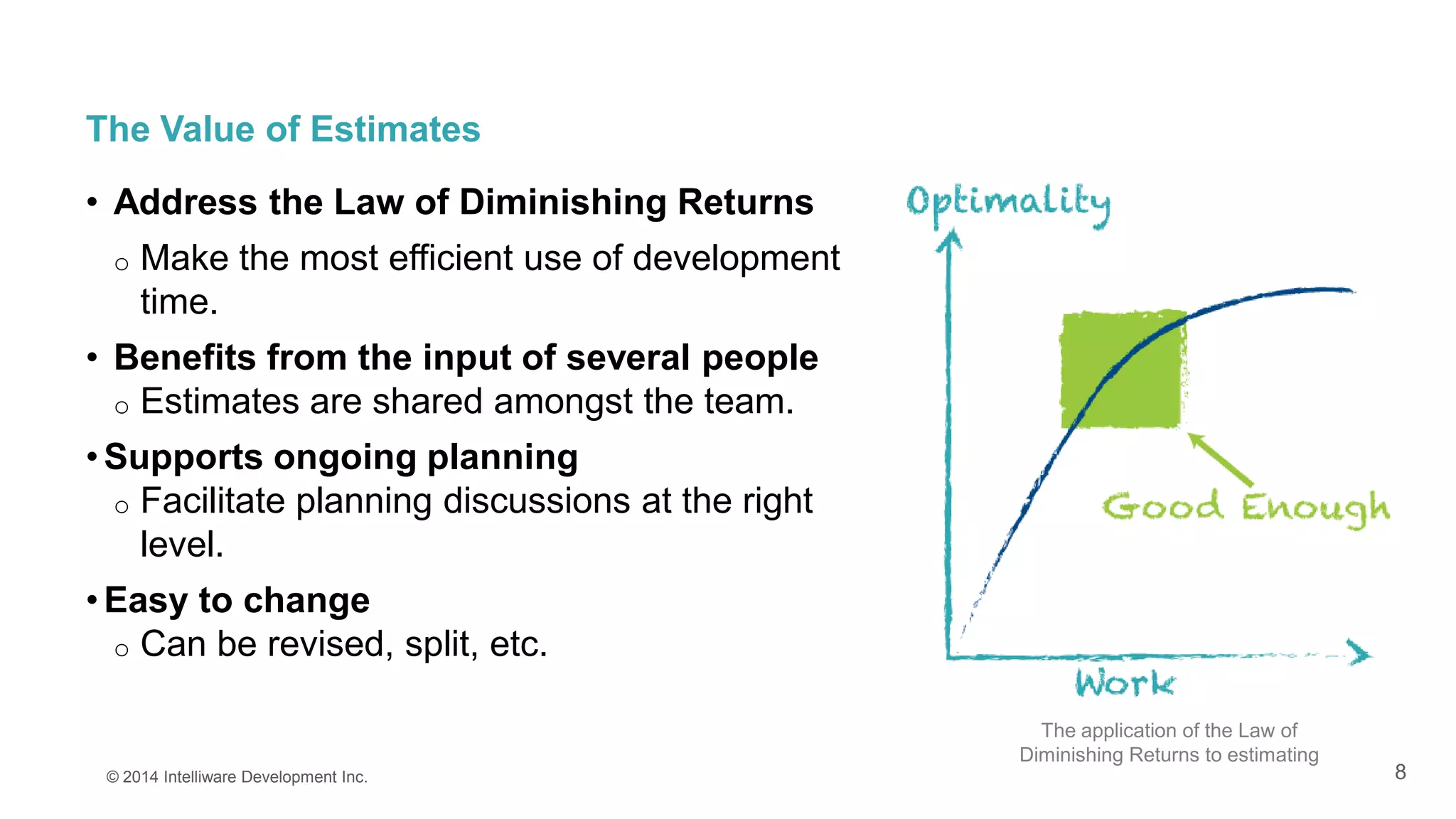
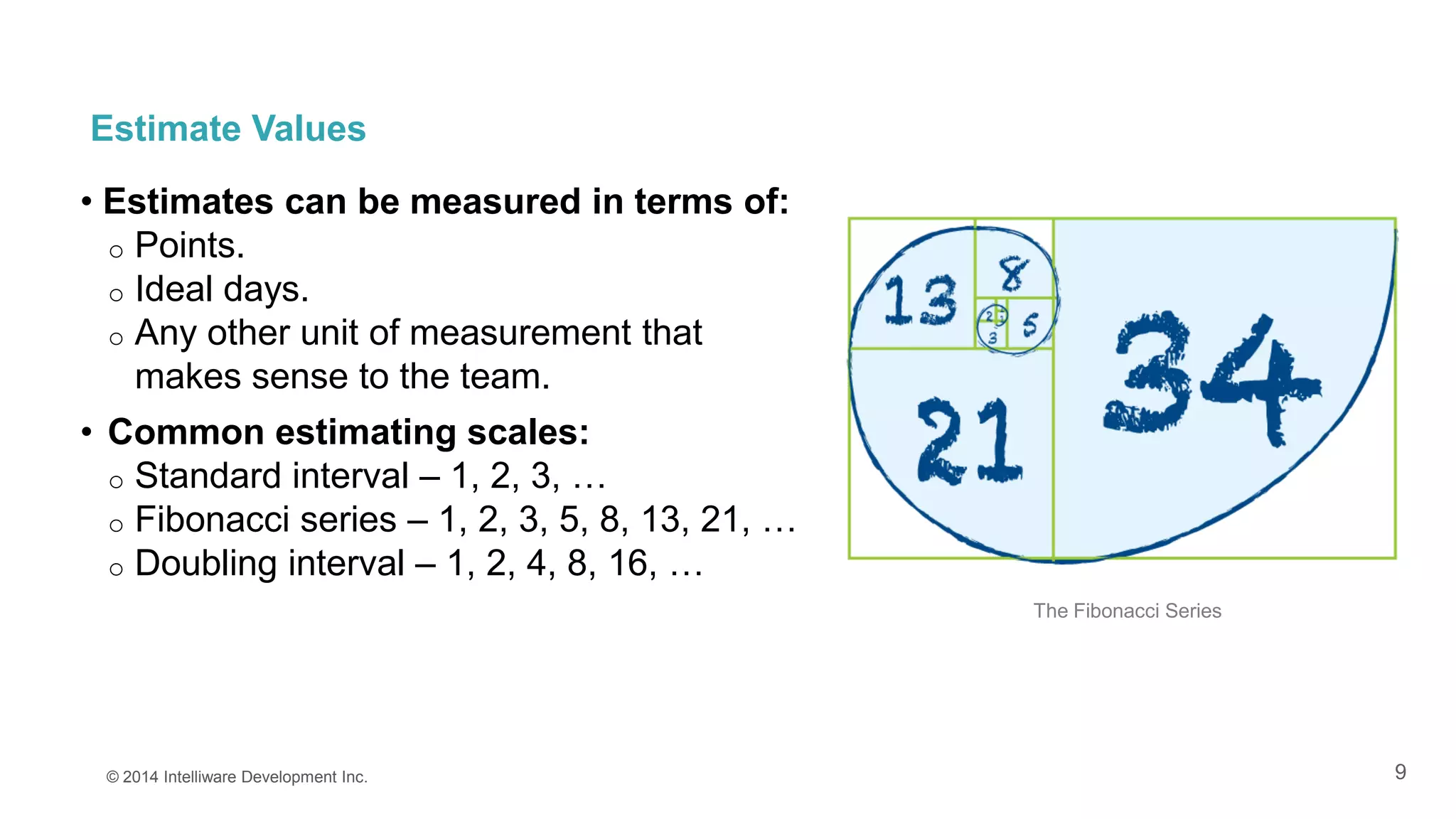
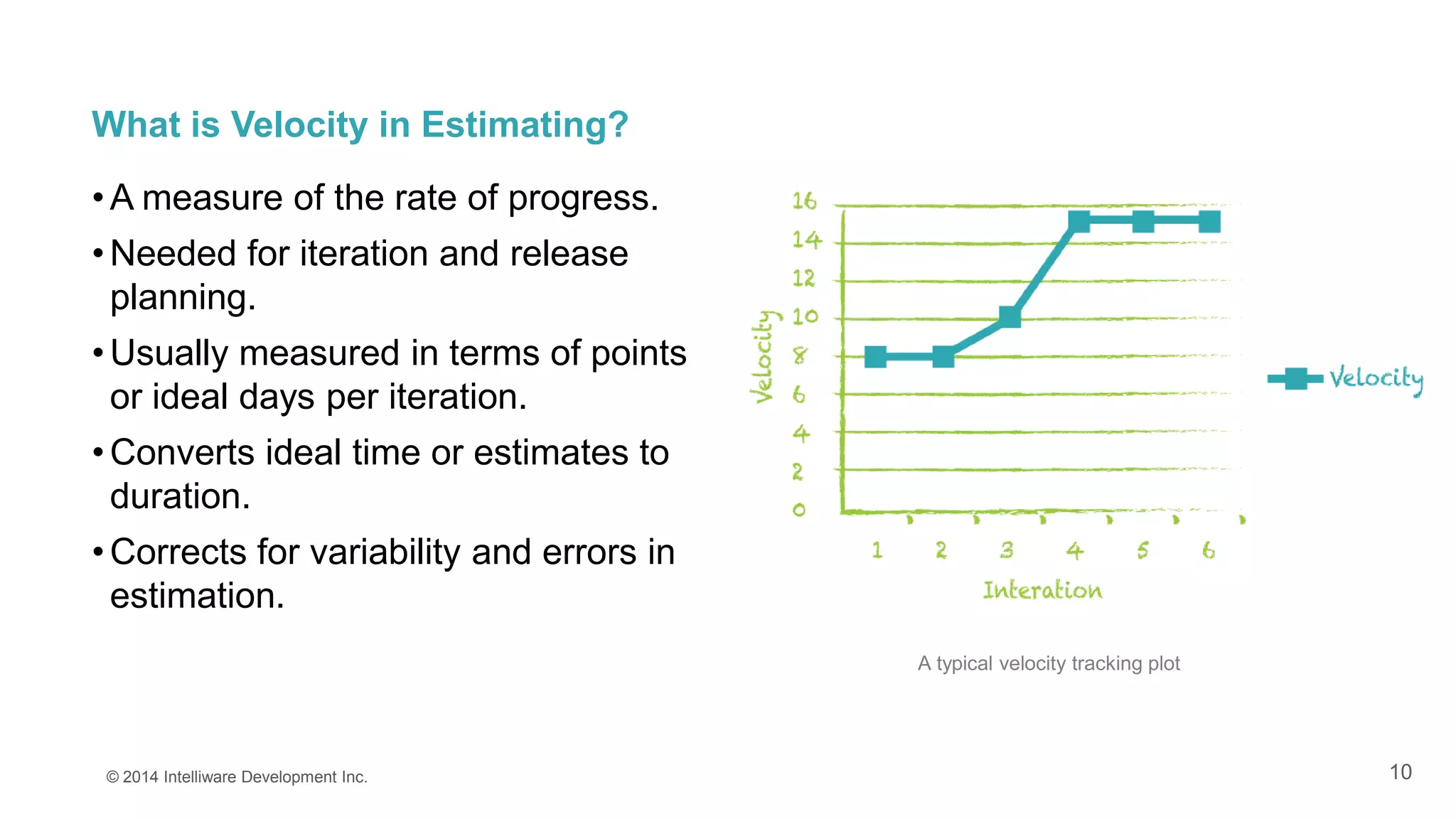
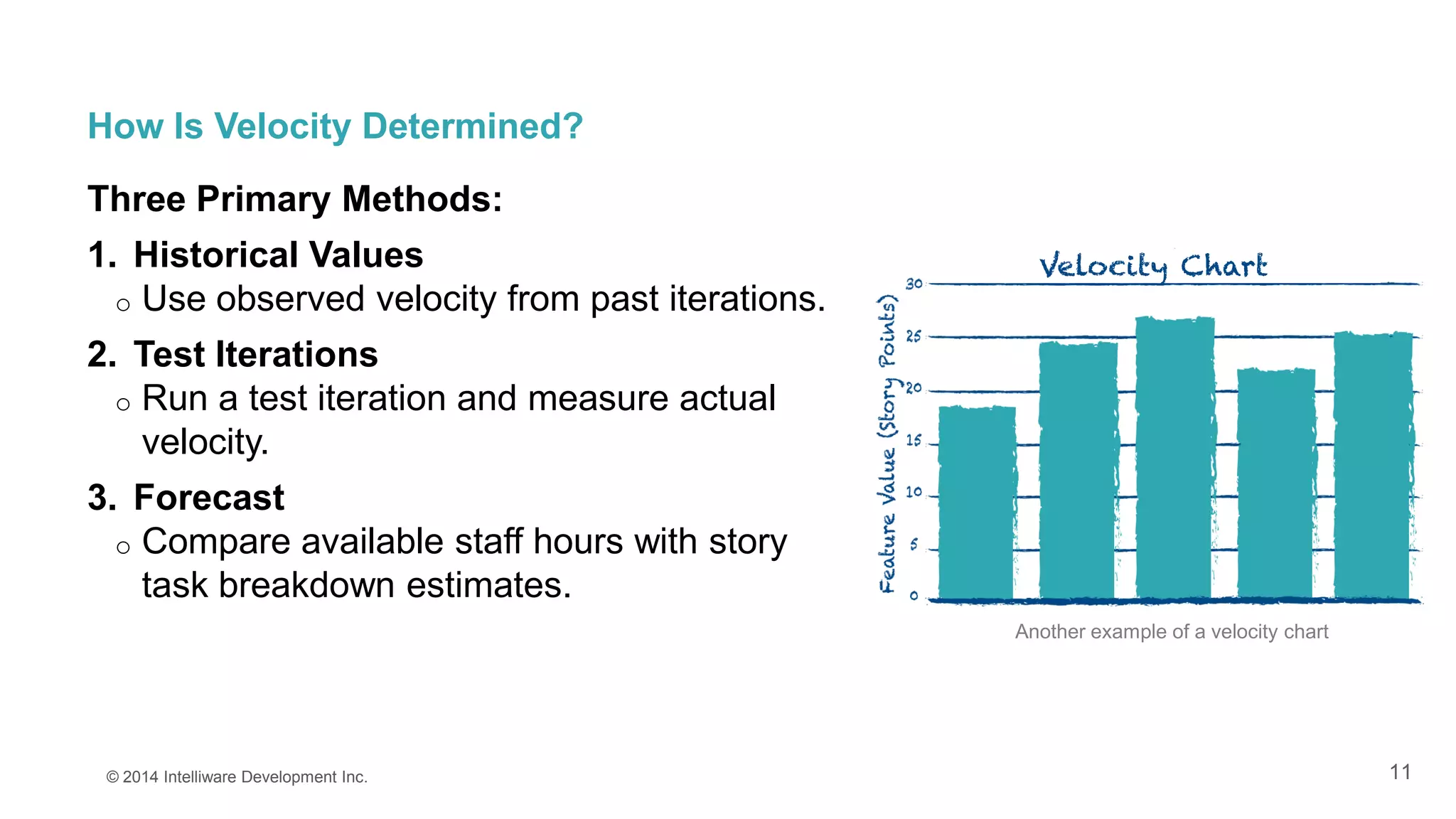
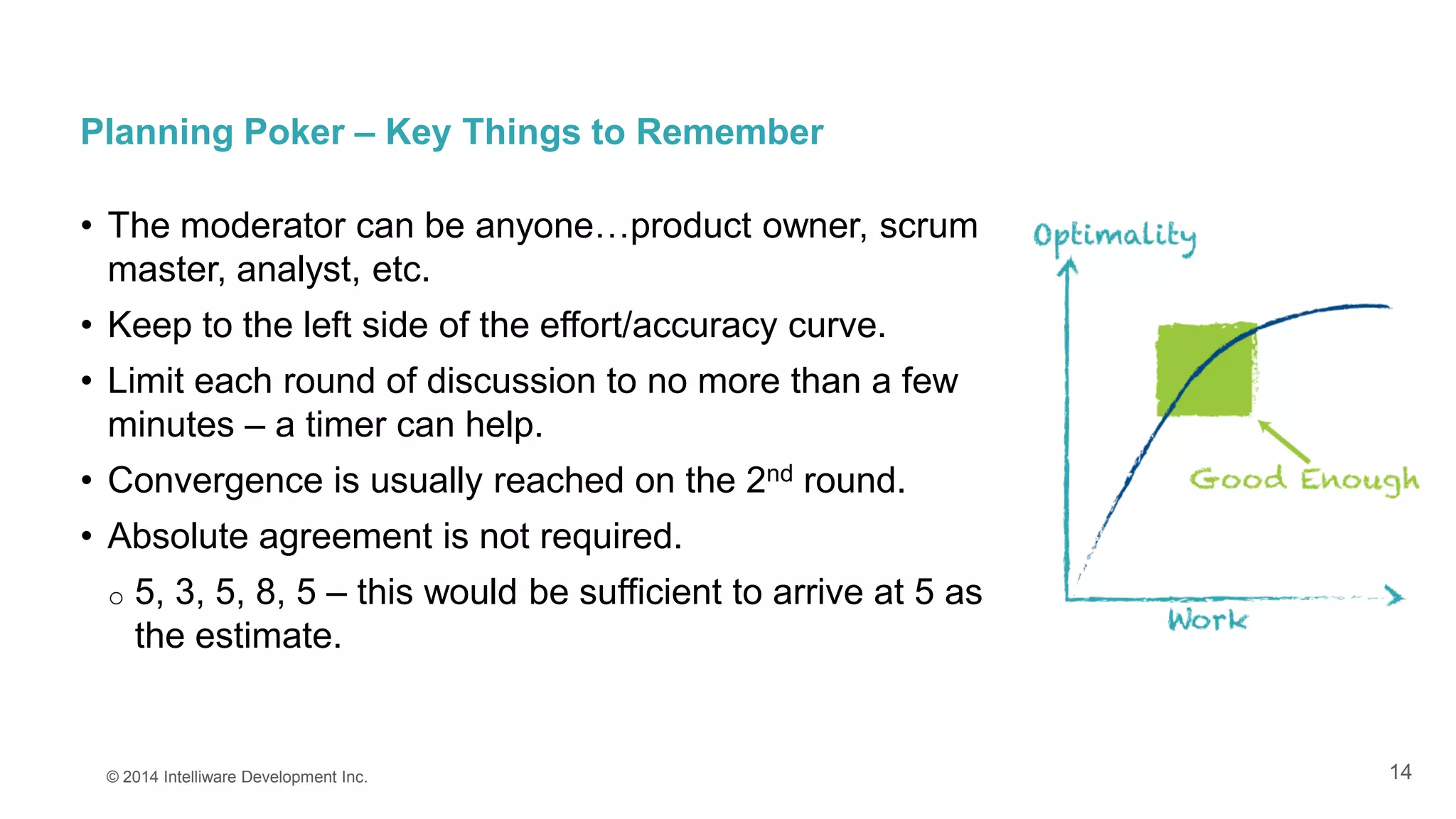
This presentation covers the importance of estimates in agile projects, explaining how they aid planning and decision-making within development cycles. It describes techniques such as 'planning poker' for effective estimation and emphasizes the distinction between effort and duration in project management. The document highlights that accurate estimates help maximize efficiency and enable better resource allocation throughout the development process.