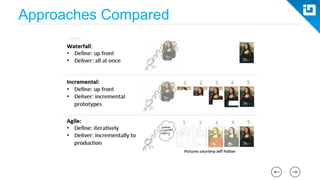
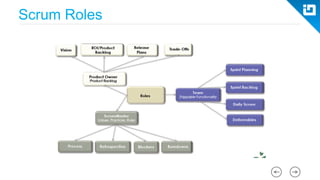
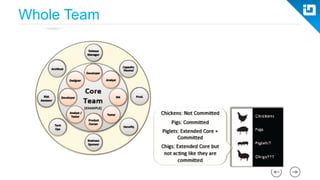
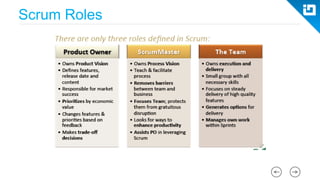
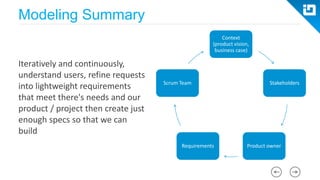
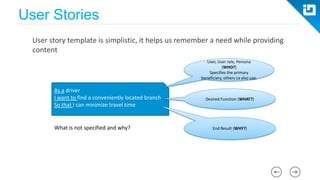
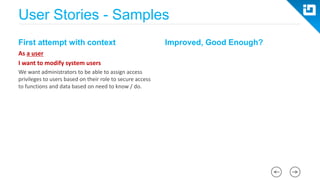
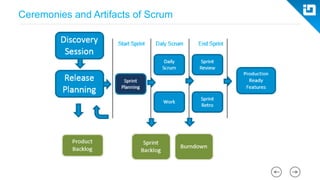
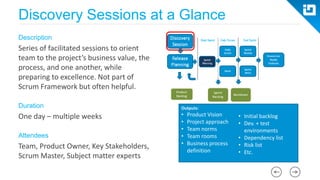
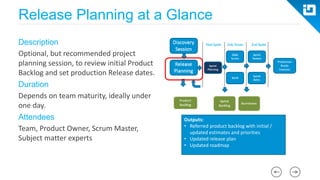
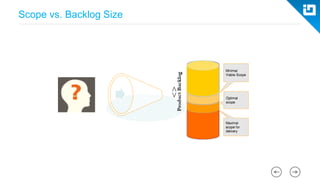
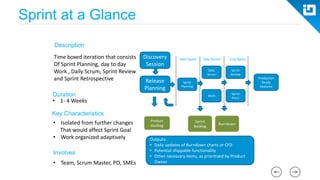
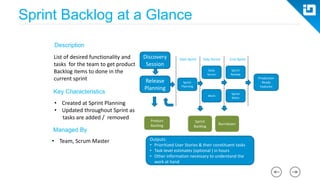
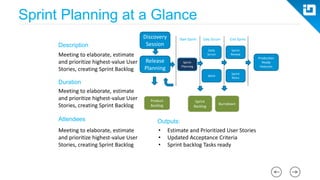
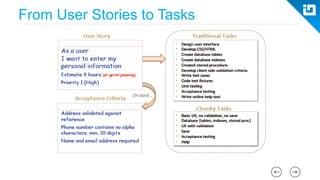
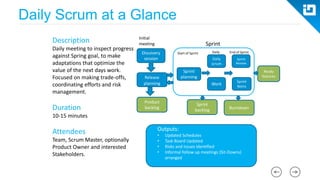
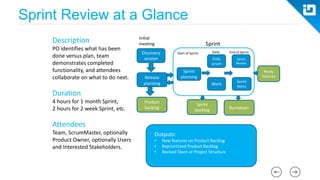
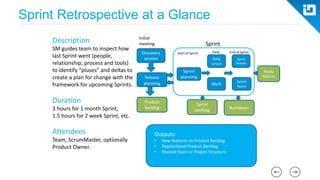
This document provides an agenda and overview for a Scrum training session. The training will cover topics such as the principles and ceremonies of Scrum, including roles, product backlog, sprints, daily standups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. It will use presentations and a Lego game to help illustrate key Scrum concepts. The goal is to introduce participants to Scrum and provide them a basic level of knowledge about how to implement Scrum practices in their work.