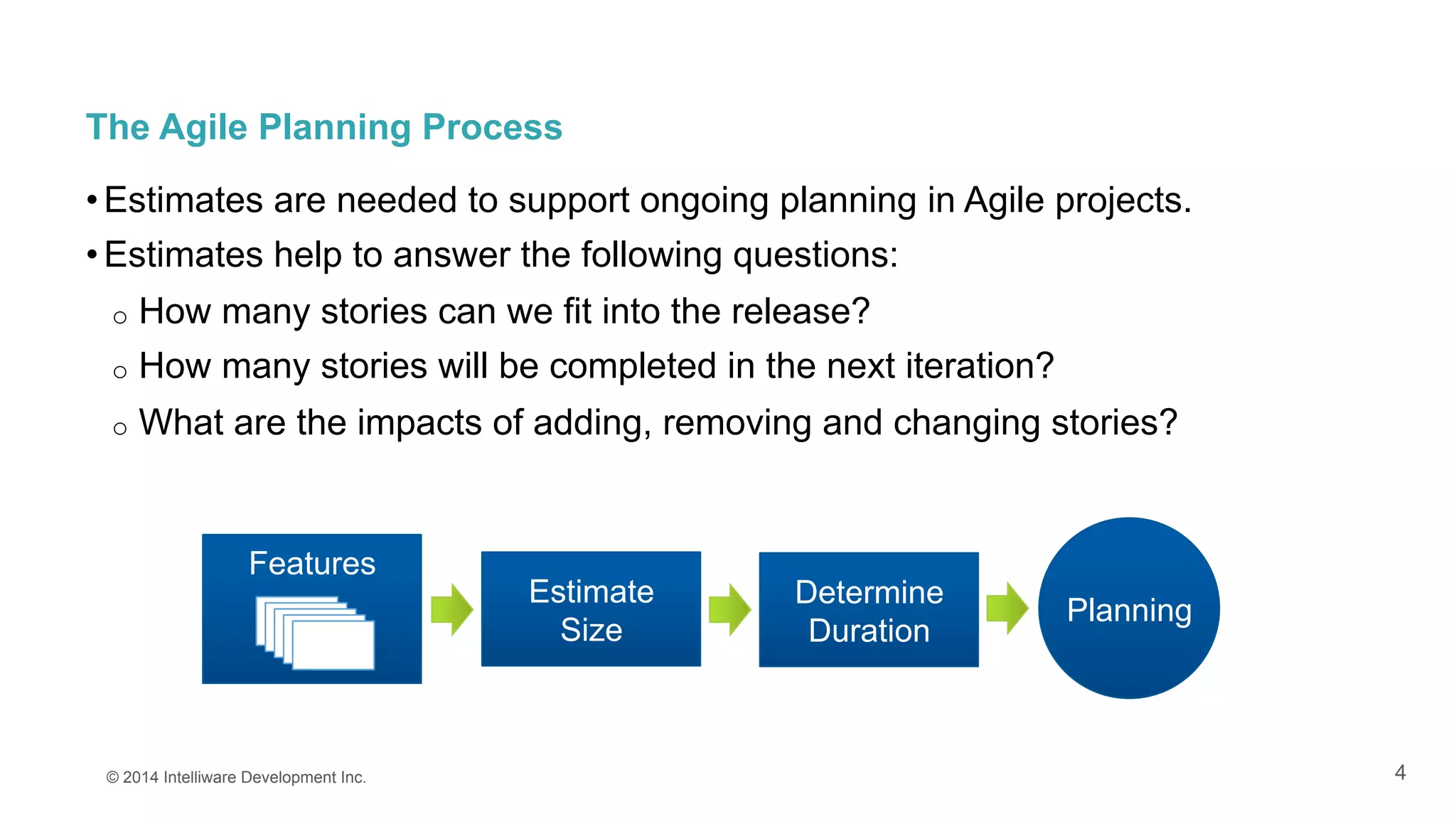
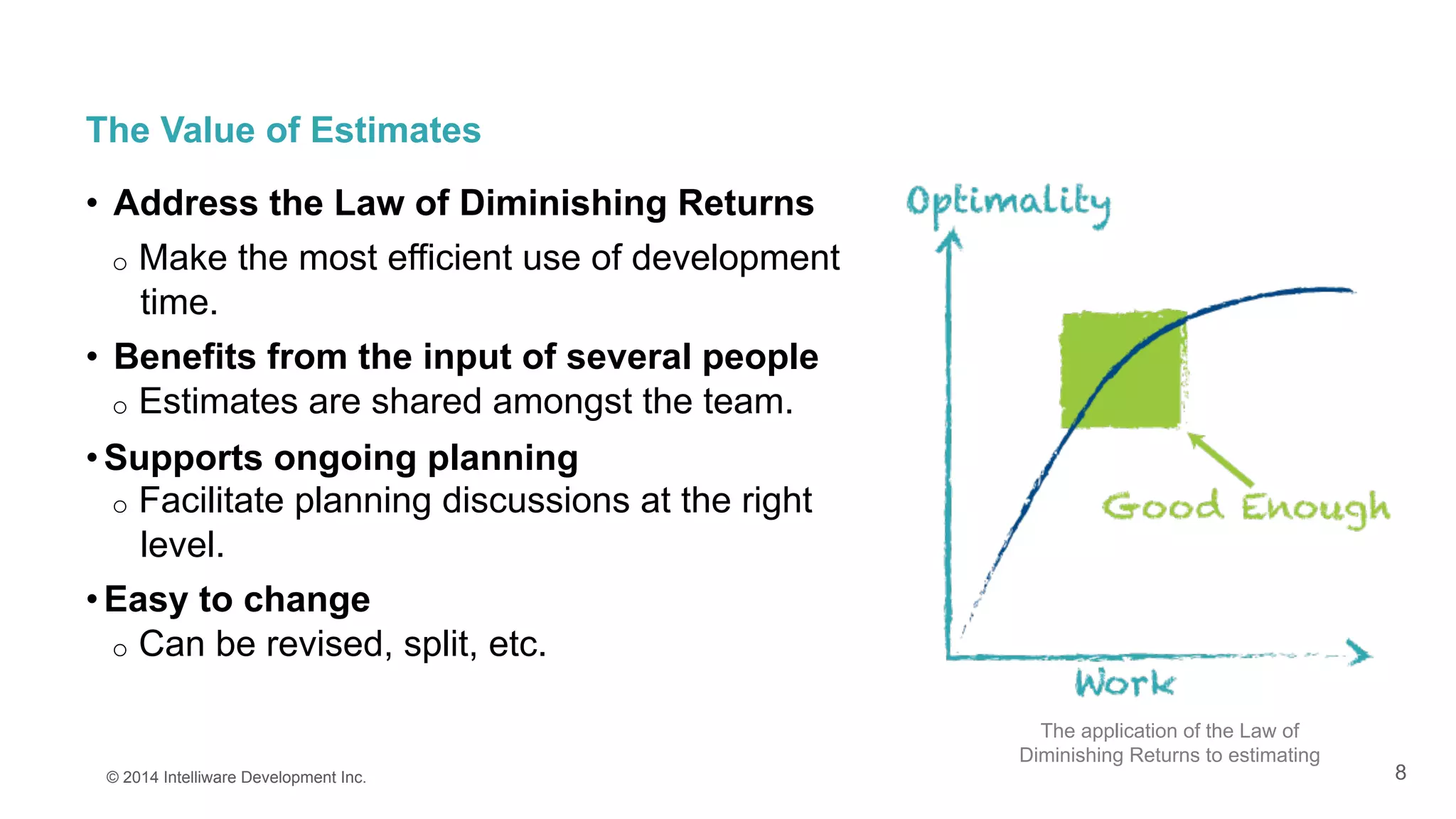
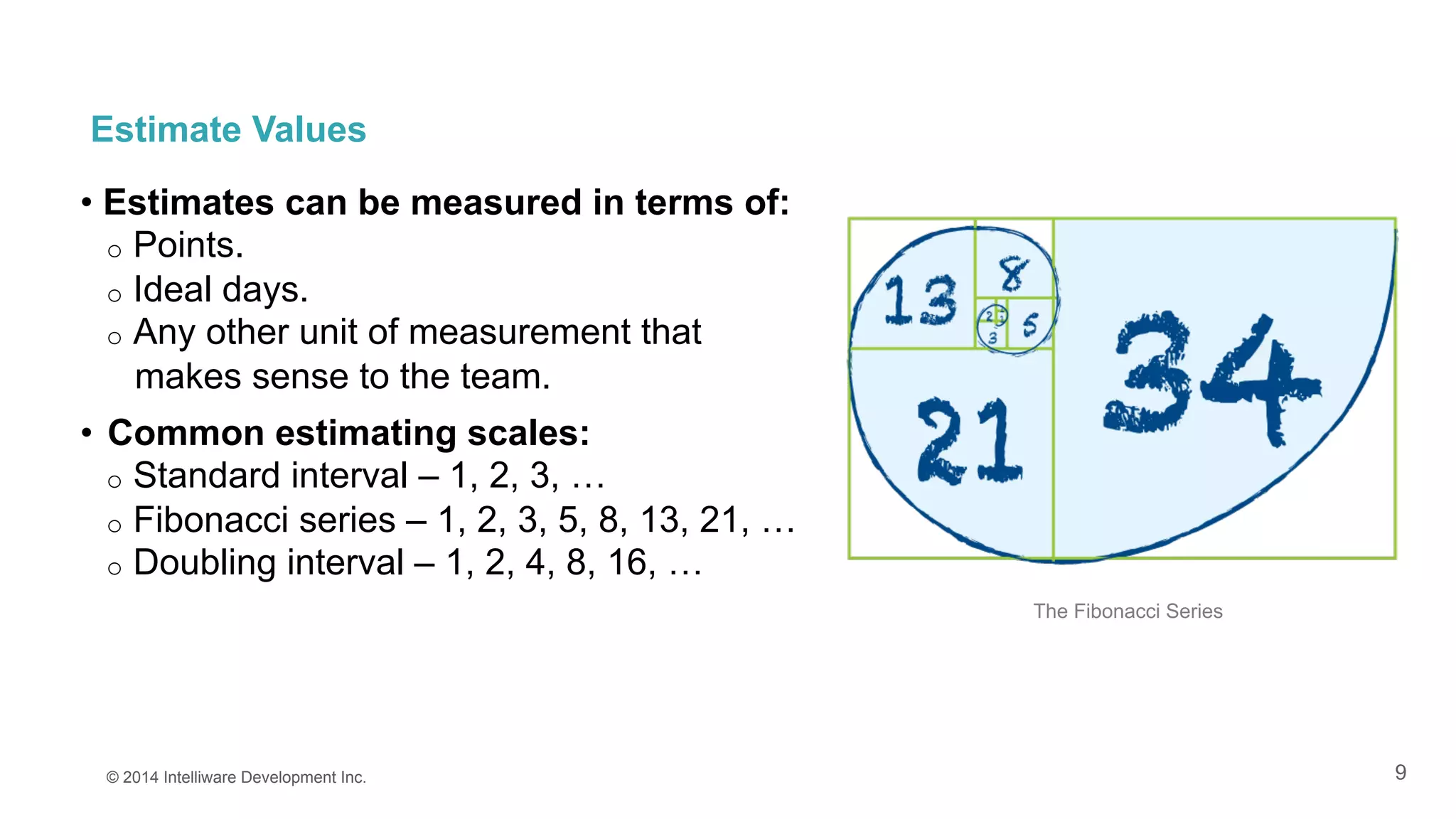
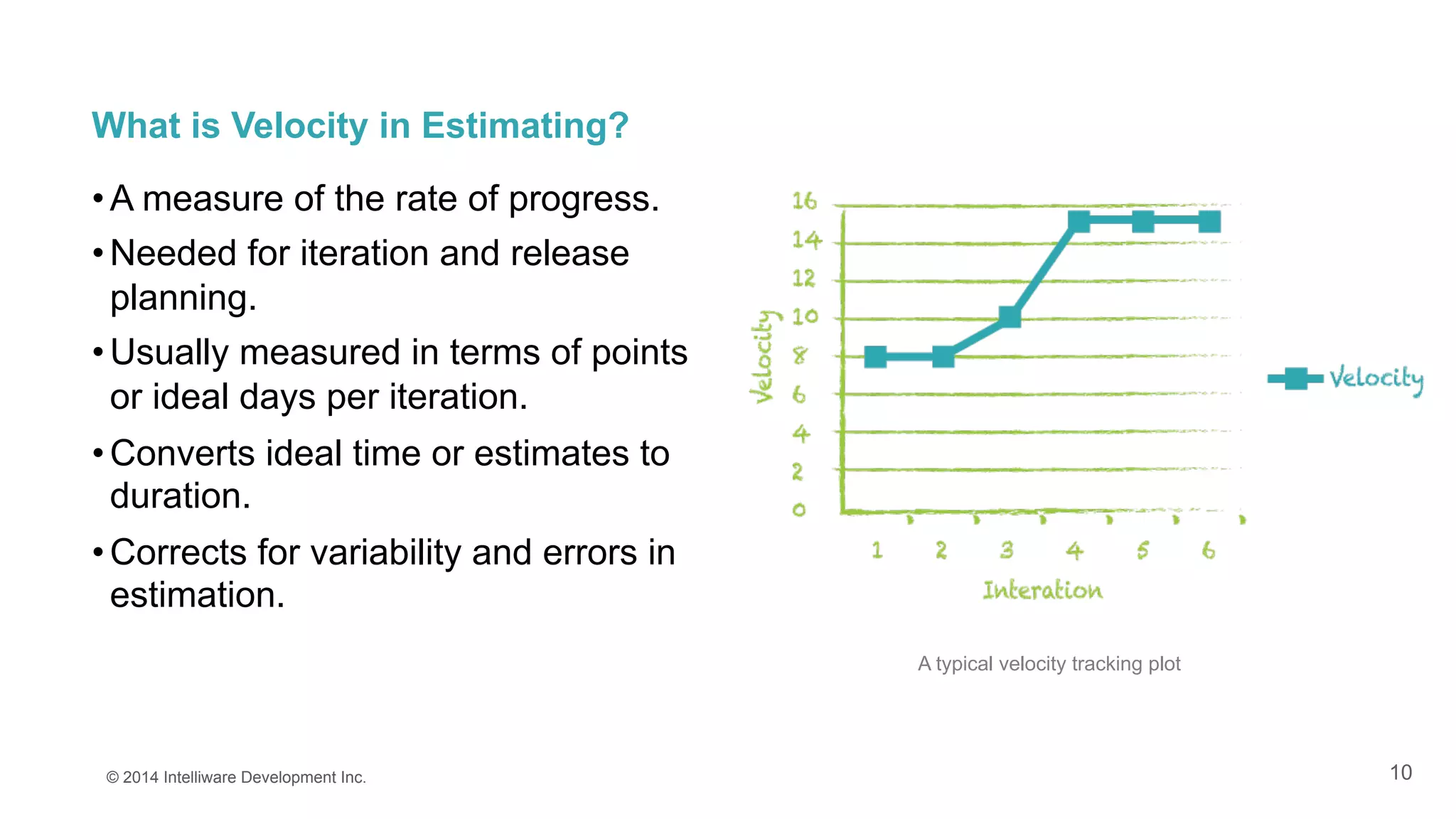
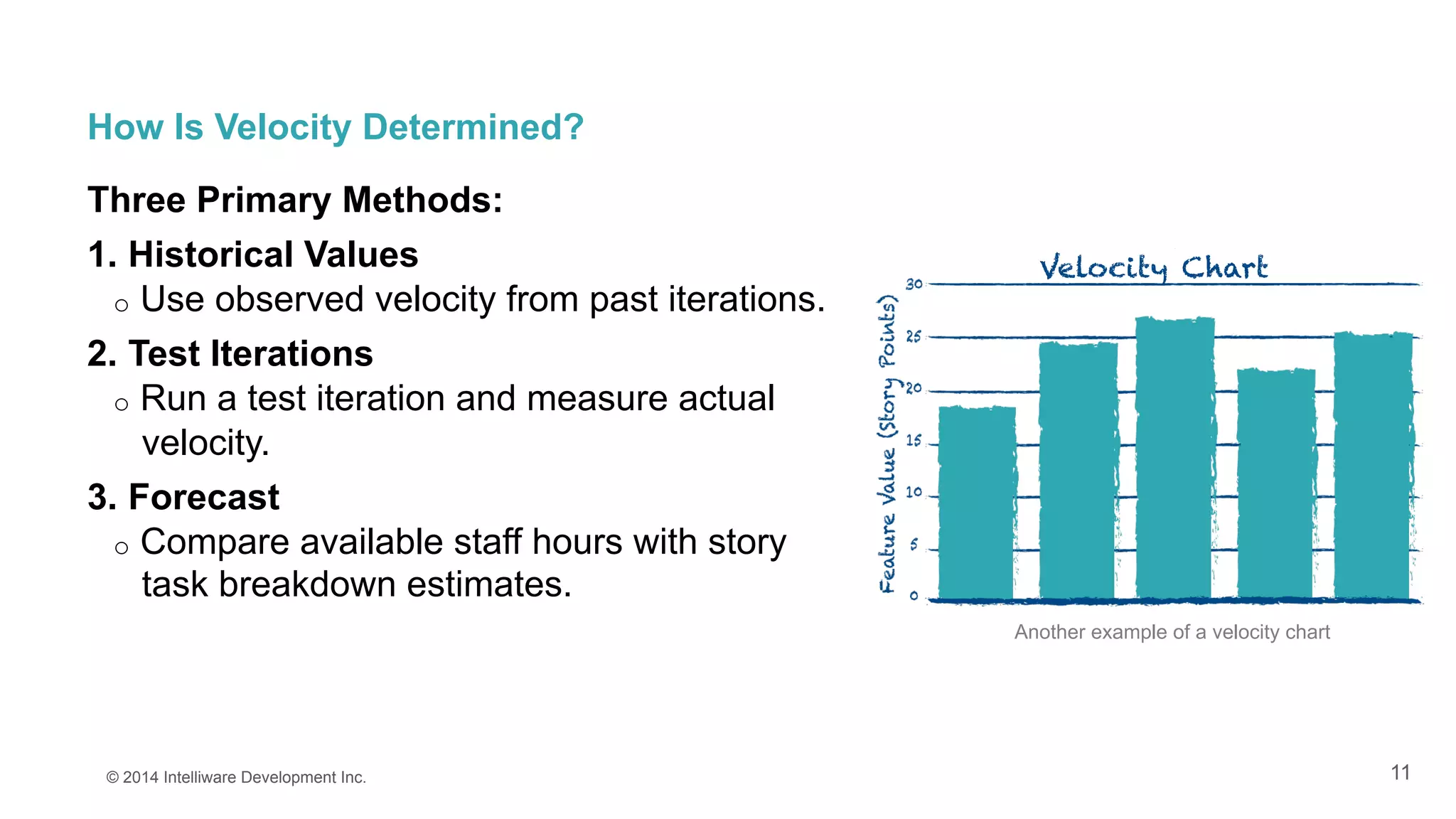
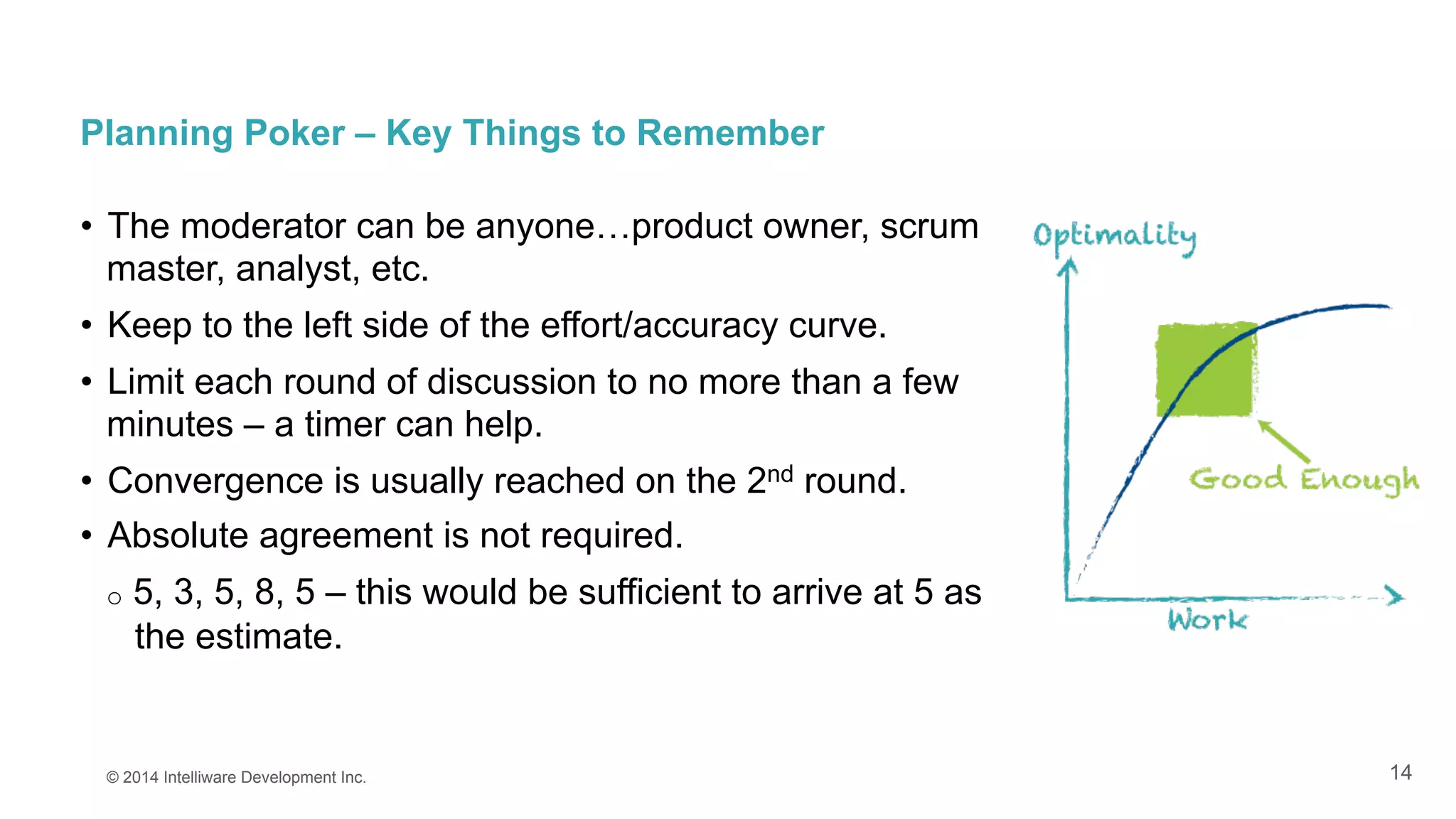
The document discusses the importance of estimates in agile project planning, detailing how they support ongoing planning and help teams determine the number of user stories that can be completed in iterations. It introduces the concept of planning poker, an interactive method for teams to reach consensus on estimates, and emphasizes the distinction between effort and duration in estimation processes. Furthermore, it explains the value of estimates in maximizing development efficiency and provides various methods for determining velocity in project management.