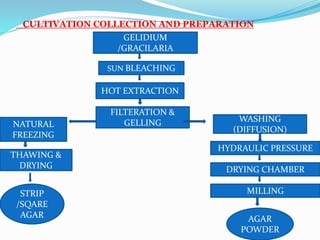
The document provides a comprehensive profile of agar, highlighting its biological source from red algae, geographical locations for collection, and its preparation process. It details the chemical constituents, including agarose and agaropectin, and includes various chemical tests for identification and quality assessment of agar. Additionally, the document discusses common adulterants and diverse applications of agar in fields such as pharmaceuticals, microbiology, and food industry.