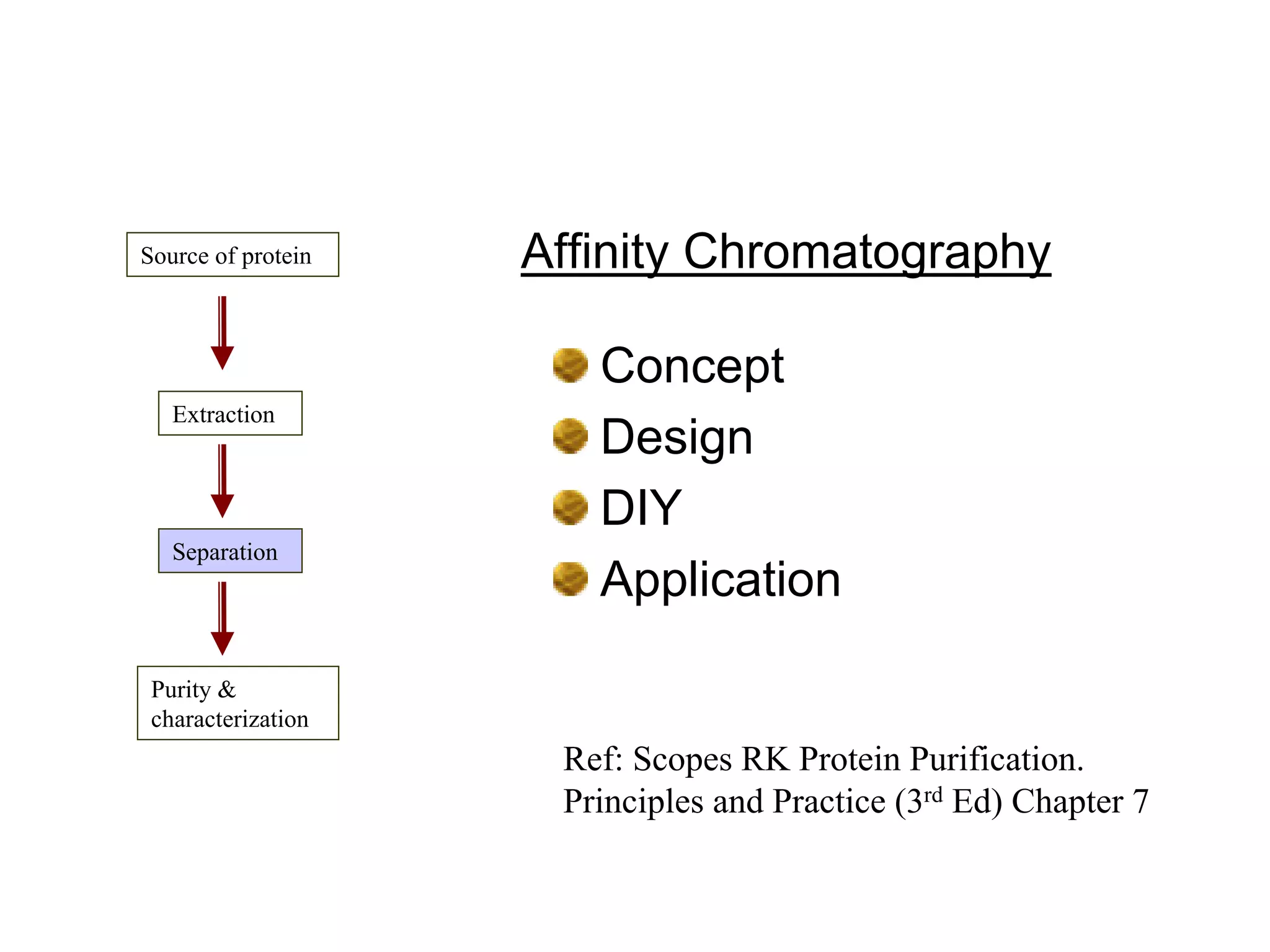
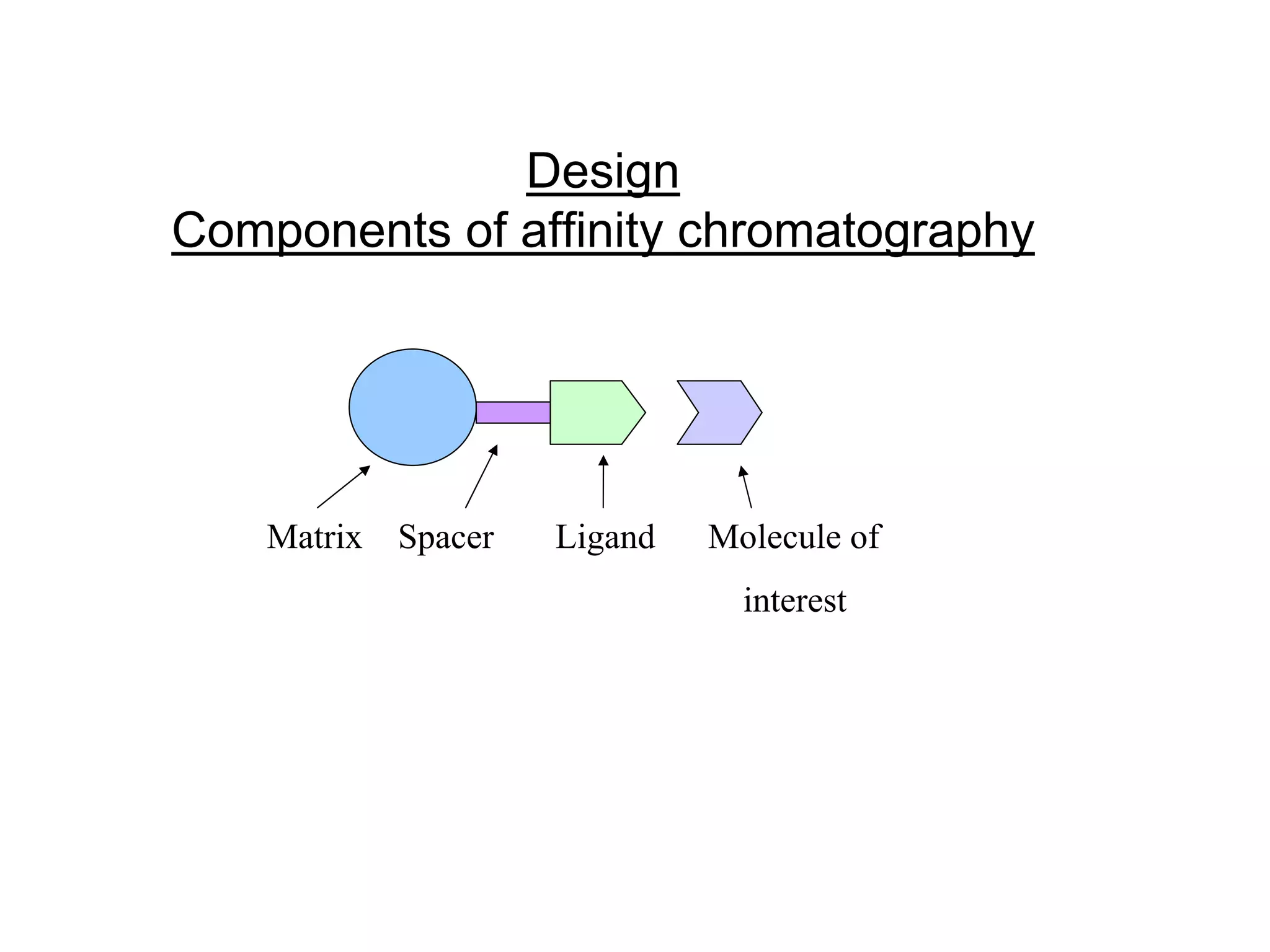
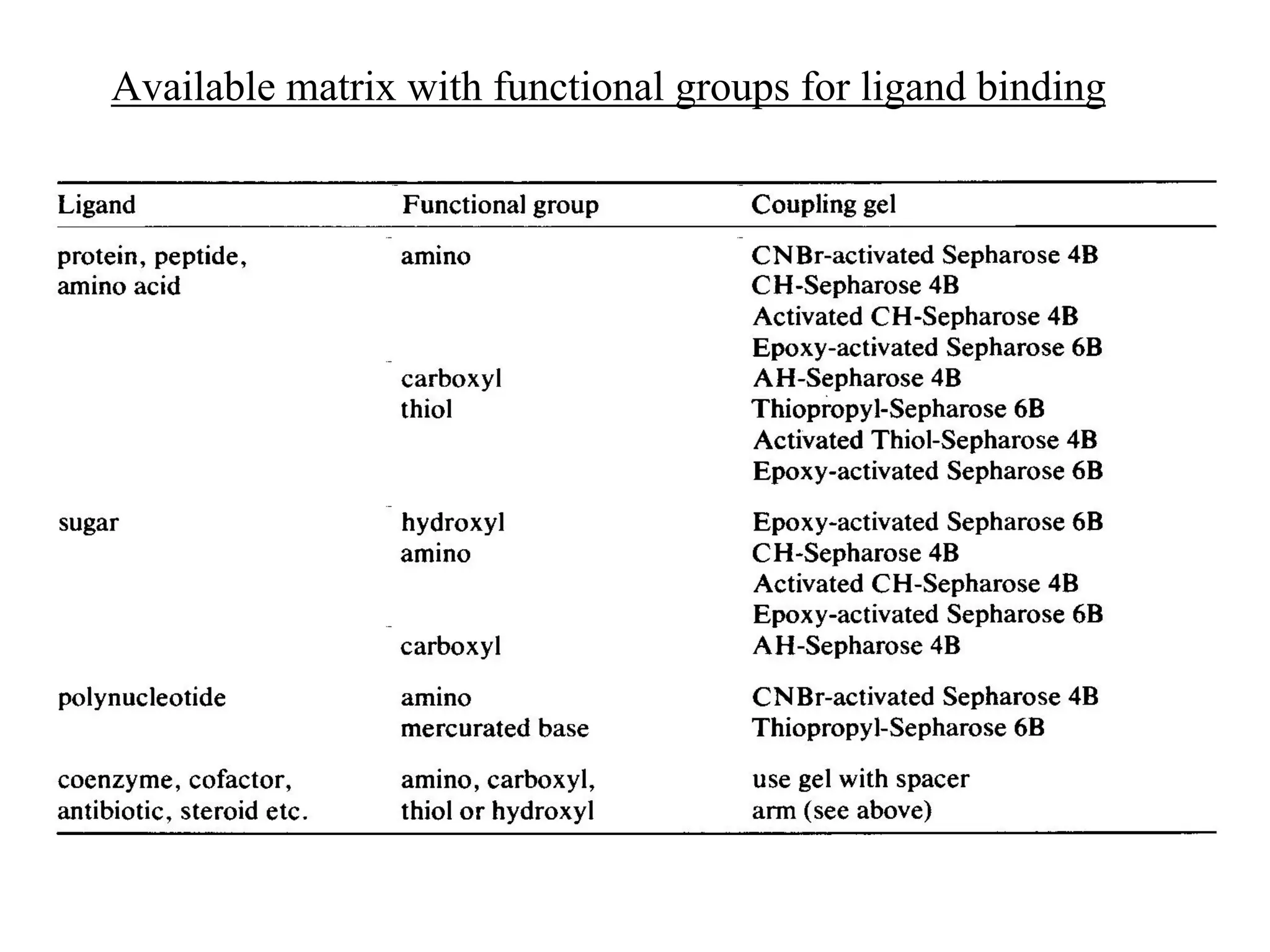
Affinity chromatography is a technique that uses the specific binding between a ligand and target molecule to separate a target from a complex sample. It works by immobilizing a ligand with specific binding affinity for the target molecule on an insoluble support. The sample is passed through the column, and the target molecule binds reversibly to the ligand. The bound target can then be eluted selectively under appropriate conditions. Key components of an affinity gel include the matrix, spacer, and ligand. Researchers can also design their own affinity gels by raising antibodies or choosing a suitable ligand to isolate a protein of interest, such as using an agarose gel with immobilized antibodies to purify the Rubisco enzyme from plant extracts.