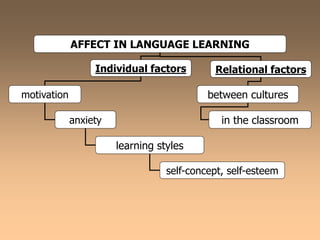
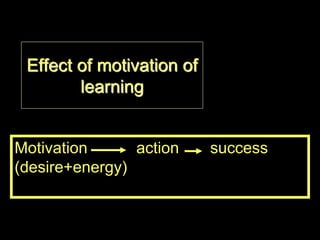
The document discusses how to motivate language learners by making language learning more affective and effective. It argues that the attitudinal climate of the classroom and consideration of affective factors can promote learning by helping students miss fewer classes, improve self-concept, achieve more academically, and cause fewer behavioral issues. Success depends more on the relationships between people in the classroom than on materials alone. Both individual learner factors like motivation, anxiety and learning styles, and relational dynamics between learners impact the learning process. Teachers can enhance motivation and learning by displaying confirming behaviors that build learner confidence and identity.