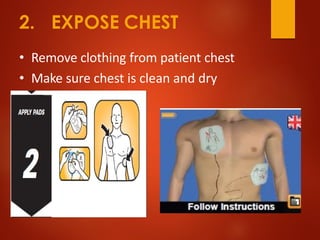
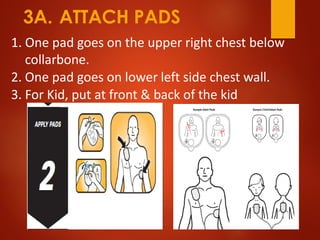
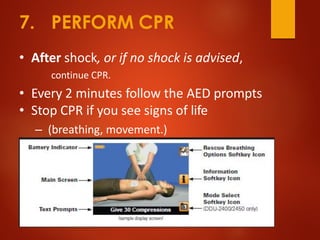
The document outlines the anatomy and physiology of the heart, detailing the various valves and blood circulation pathways. It includes instructions for the use of an automated external defibrillator (AED), such as how to prepare the patient and administer shocks safely. The document emphasizes the importance of troubleshooting heartbeats with an AED during emergencies.