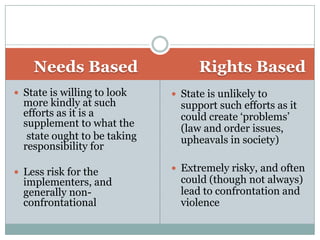
This document discusses strategies for effective advocacy to implement women-friendly laws. It defines advocacy as a set of democratic actions seeking social change and empowering marginalized groups. Advocacy can occur at local, state, national, and international levels and can include people-centered, policy, legislative, and media advocacy. Effective advocacy requires organizing actions like rallies and campaigns, building coalitions, conducting research, and advocating for rights-based rather than just need-based policies and laws. Success requires developing evidence, briefing advocacy partners, and using a combination of advocacy techniques and building synergies between different approaches.