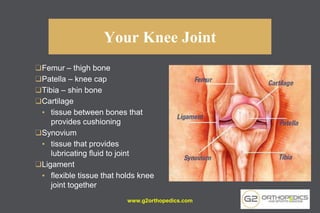
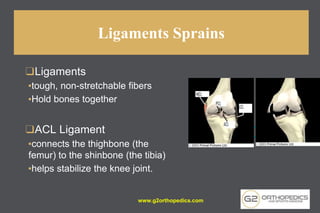
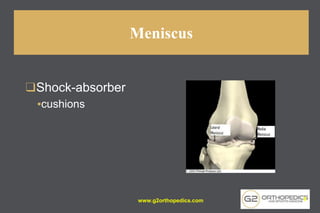
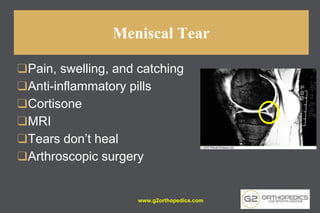
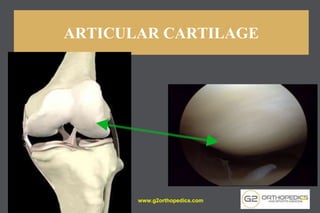
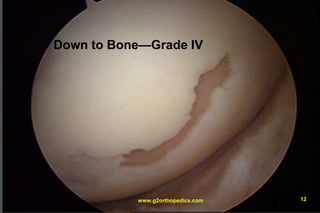
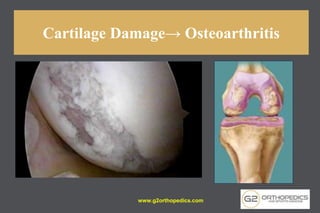
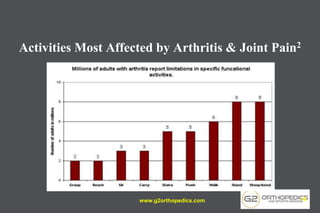
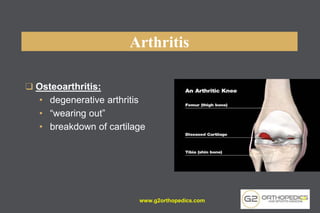
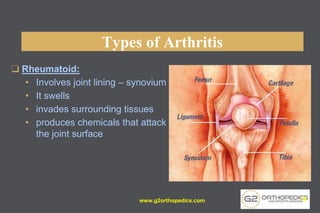
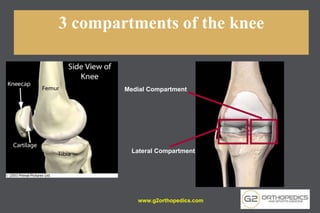
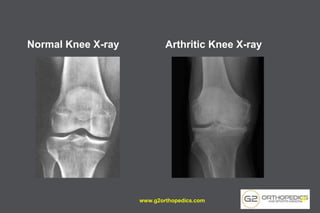
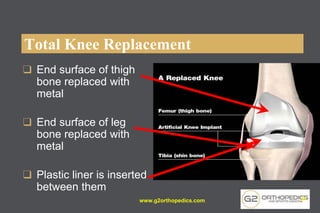
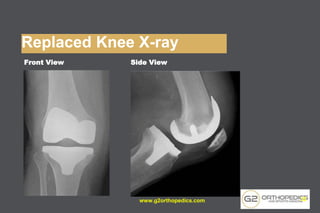
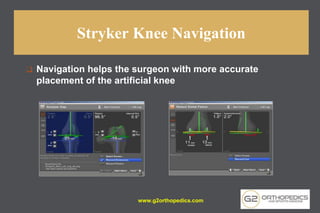
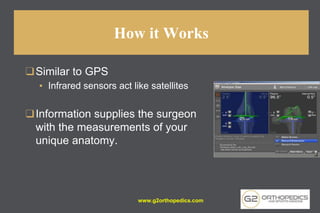
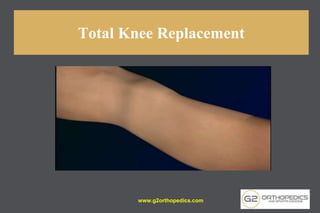
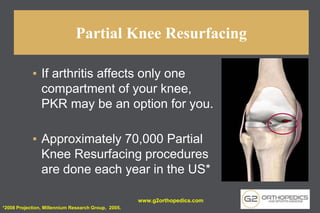
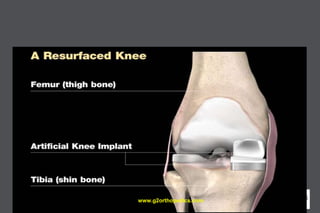
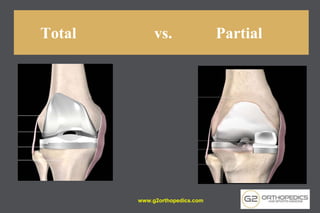
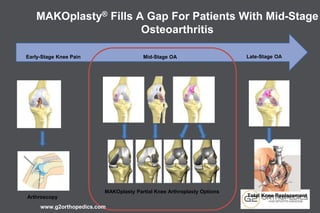
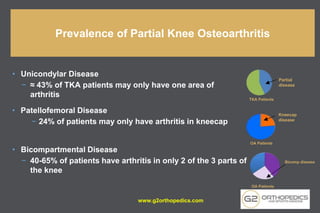
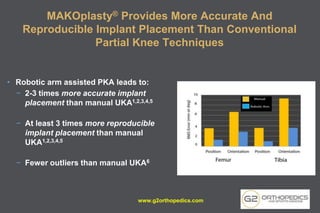
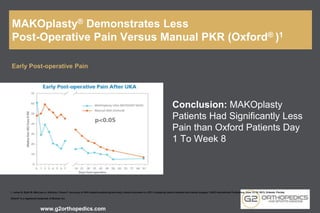
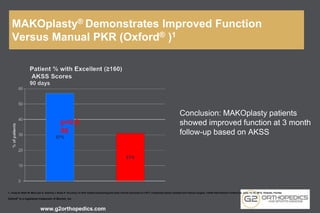
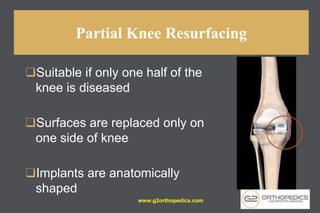
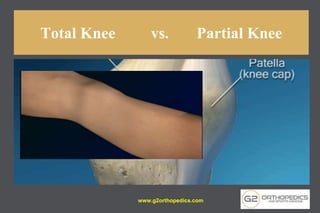
The document discusses potential causes and treatment options for knee pain, focusing on various injuries, types of arthritis, and surgical solutions like total and partial knee replacements. It explains the anatomy of the knee, common injuries such as ACL tears and meniscal tears, and the benefits of robotic surgery technology in improving surgical outcomes. The document emphasizes the importance of personalized care and rehabilitation in treating knee pain.