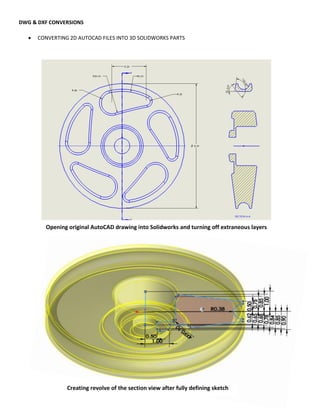
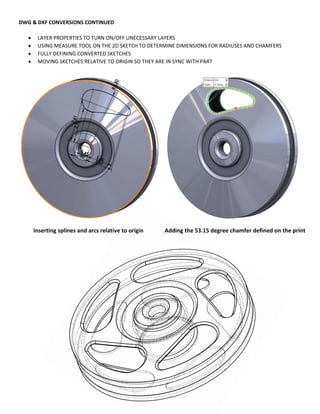
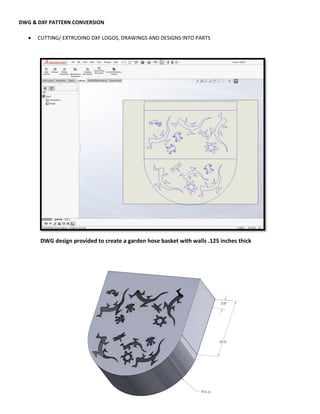
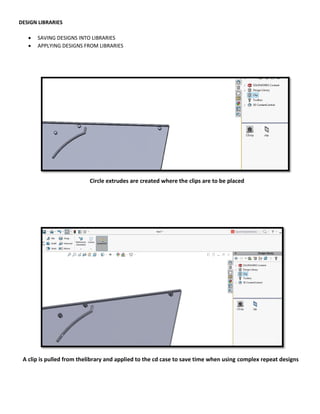
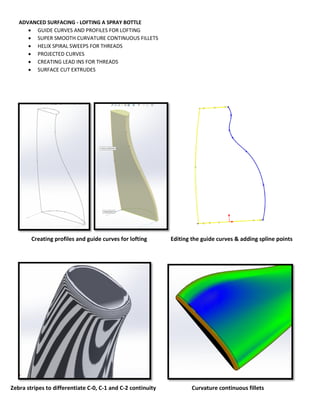
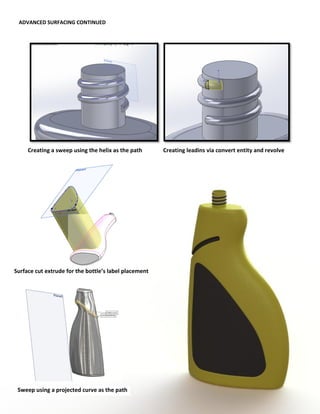
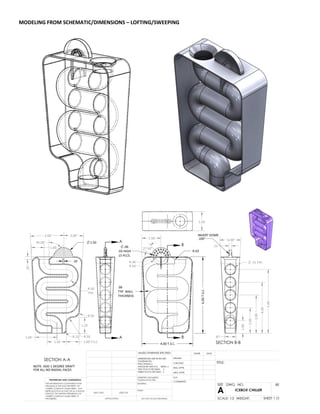
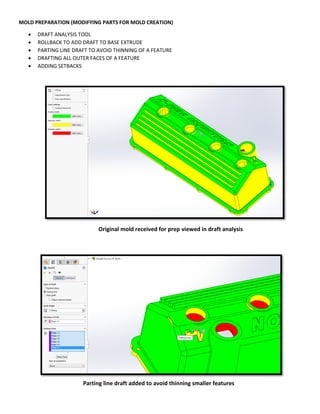
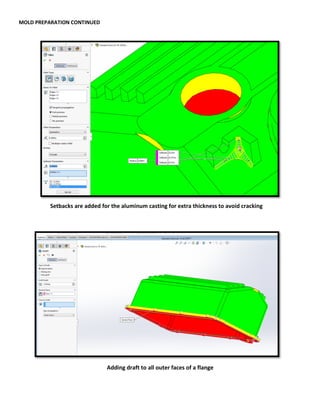
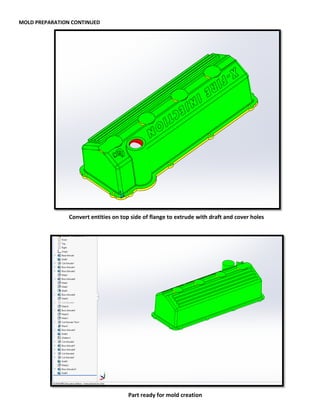
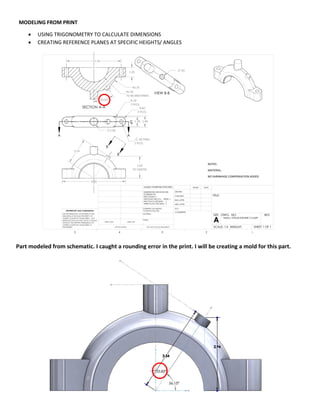
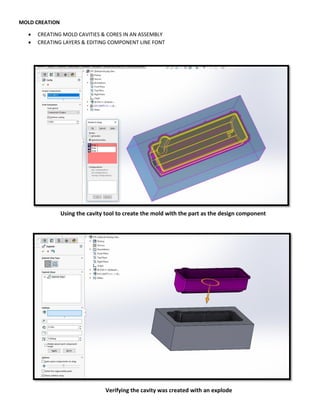
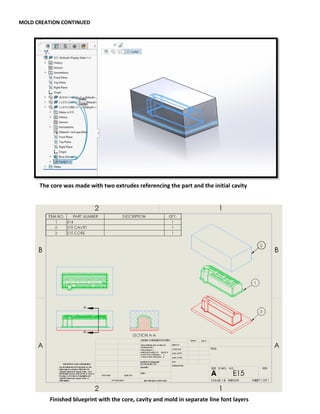
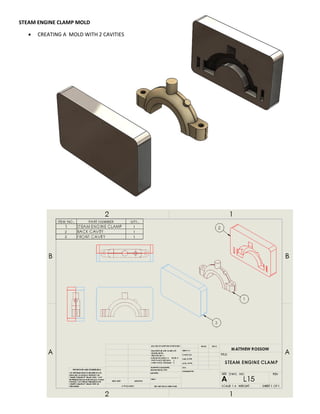
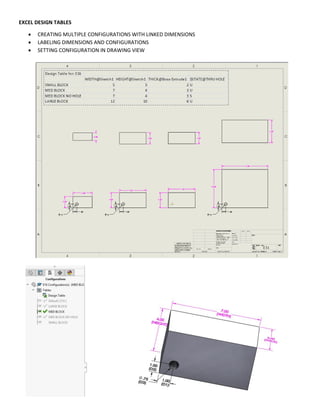
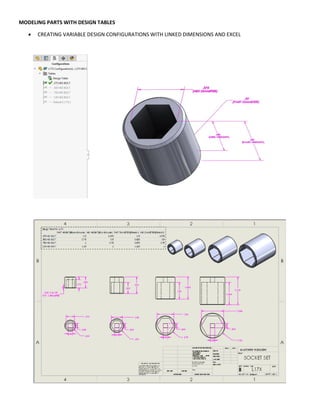
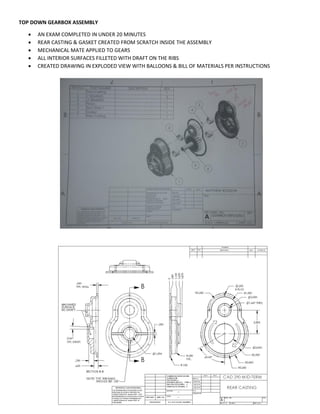
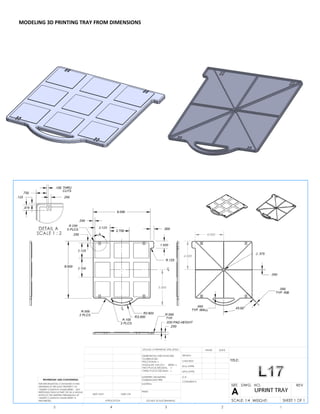
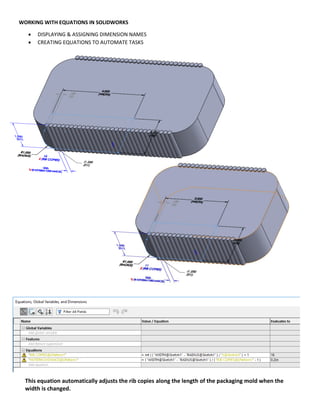
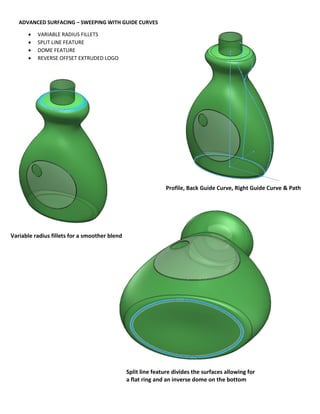
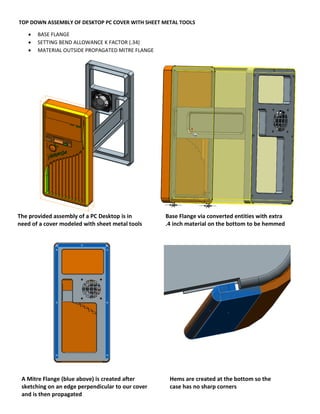
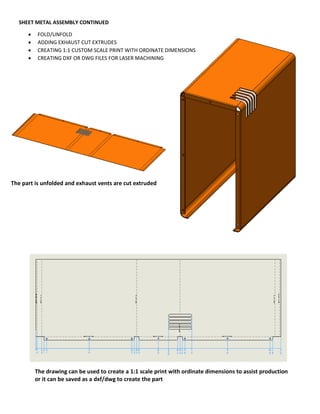
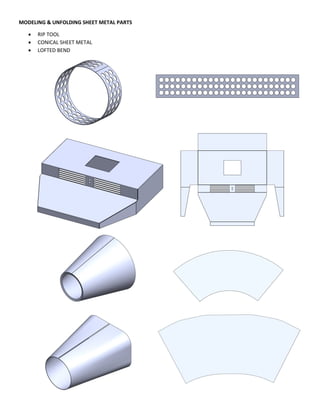
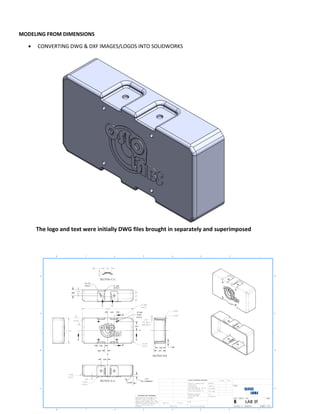
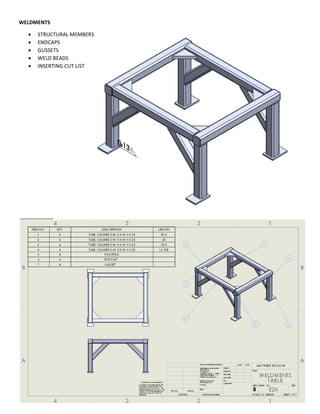
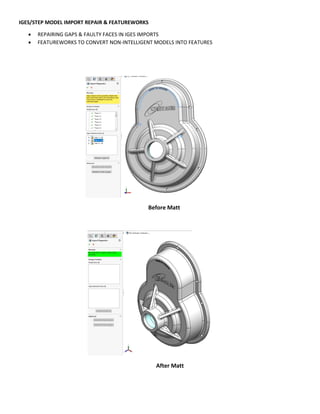
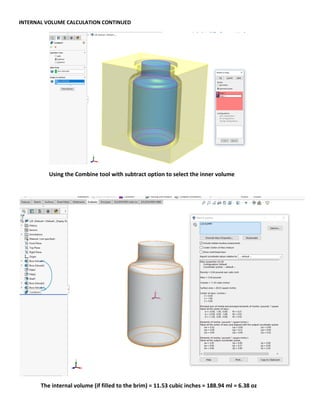
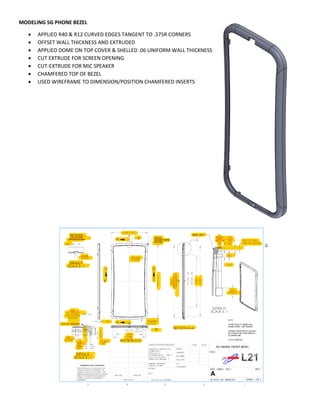
This document provides an overview of topics covered in Matt Rossow's Advanced SolidWorks portfolio, including converting 2D drawings to 3D parts, design libraries, advanced surfacing techniques like lofting and sweeping, preparing parts for molds, mold creation, using design tables, top-down assemblies, working with equations, sheet metal modeling, weldments, and more. The portfolio contains examples of parts and assemblies modeled using these techniques, from simple to complex geometries, demonstrating Matt's proficiency with advanced SolidWorks tools and modeling methods.