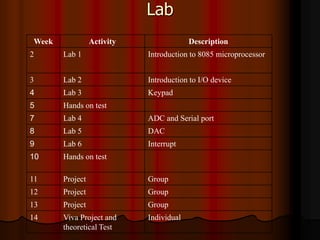
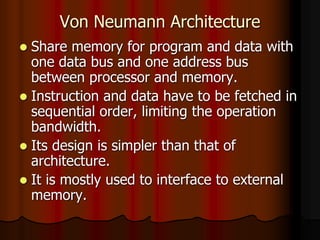
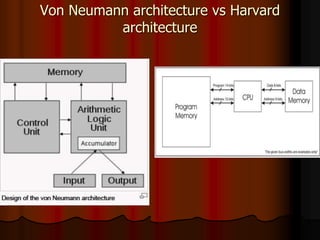
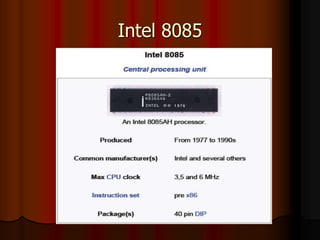
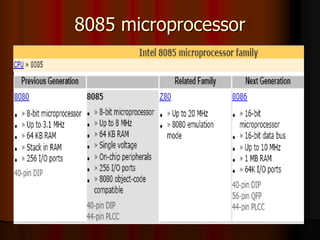
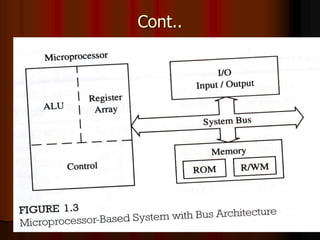
This document outlines the course content for EEE226 Microprocessor course taught by Dr. Zaini Abdul Halim. The course aims to help students understand microprocessor architecture, assembly language programming, and interfacing microprocessors to external devices. It will be evaluated based on hands-on tests, theoretical tests, lab reports, and a final project. Topics covered include the 8085 microprocessor architecture, programming, and applications. The syllabus lists weekly labs and activities covering concepts like I/O devices, ADCs, DACs, and interrupts.