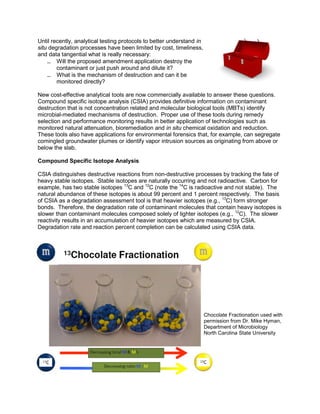
This document discusses optimizing in situ remediation of groundwater contamination using advanced diagnostic tools. It describes compound specific isotope analysis (CSIA) and molecular biological tools (MBT) that can definitively identify contaminant destruction and the microbial mechanisms involved. CSIA tracks stable isotopes to determine if degradation occurred, while MBTs quantify microbial populations and activity. These tools provide better information for selecting and applying in situ remediation technologies like bioremediation and chemical oxidation. When used during remedy selection and performance monitoring, they result in more successful application of in situ groundwater treatment.