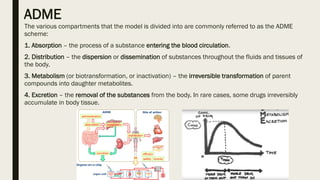
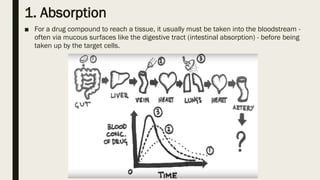
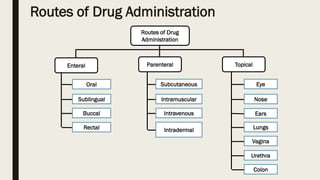
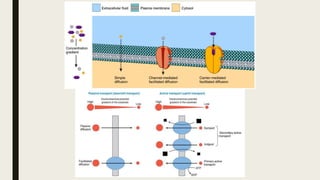
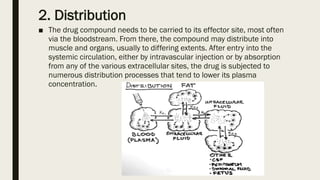
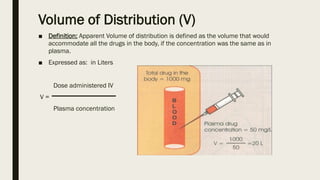
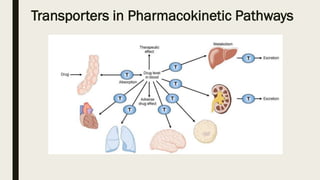
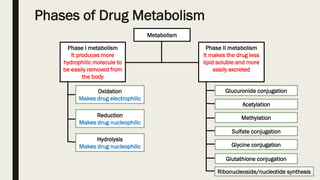
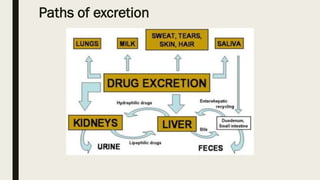
ADME stands for absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, which are critical factors in pharmacokinetics that determine how drugs behave in the body. Absorption involves the entry of drugs into the bloodstream, distribution refers to how drugs spread through body tissues, metabolism is the conversion of drugs into metabolites, and excretion is the removal of drugs from the body. Understanding these processes is essential for determining optimal drug dosing, effects, and potential adverse reactions.