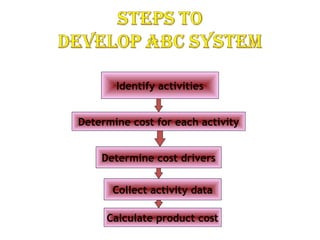
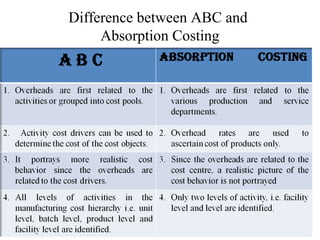
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a methodology that assigns costs to products based on the activities required to produce them and the resources consumed by those activities. ABC first traces costs to activities, then assigns costs to products based on their consumption of activities. It focuses on identifying the activities performed during production and determining the cost drivers that cause the costs of each activity. ABC provides more accurate product costs than traditional costing systems and highlights inefficient activities. However, it can be costly to implement and does not encourage changing work processes.