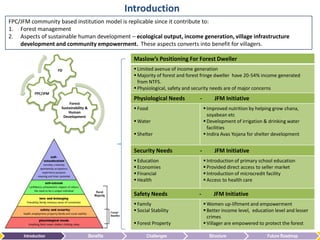
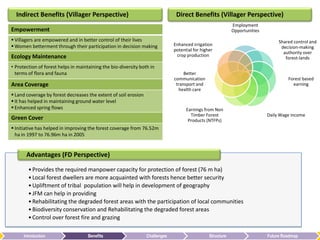
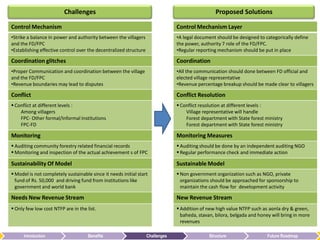
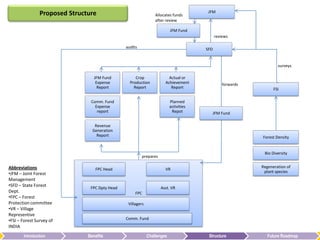
The document summarizes the benefits of the Forest Protection Committee/Joint Forest Management (FPC/JFM) community-based forest management model. It contributes to forest management, sustainable human development through income generation, infrastructure development, and community empowerment. These benefits help fulfill forest dwellers' basic needs like food, water, and shelter according to Maslow's hierarchy of needs. The FPC/JFM model also provides indirect benefits like empowerment, ecology maintenance, and increased forest cover. However, it faces challenges like balancing power between villagers and forest departments, coordination issues, conflicts, monitoring, and sustainability. The document proposes solutions like clarifying roles, independent auditing, and generating new revenue streams from additional forest products to