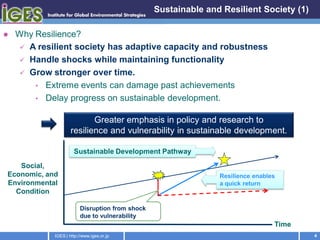
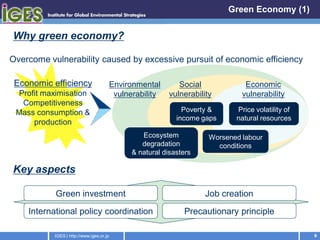
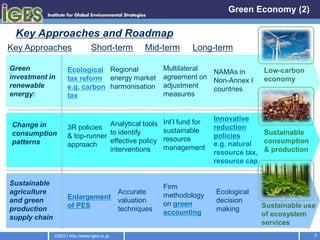
The document discusses the outcomes of the Asia-Pacific Multi-stakeholder Consultation on Rio+20, including the importance of building resilience to disasters, transitioning to a green economy, and the need to update the institutional framework for sustainable development to better integrate the social, economic, and environmental dimensions of sustainability at all levels of governance. Key recommendations include establishing a Sustainable Development Council, setting concrete sustainable development goals, and reforming multilateral environmental agreements and regional coordination on sustainability issues.