This document discusses active citizenship, which refers to citizens voluntarily working directly or through representatives to exercise power towards shared goals. It outlines several key points:
- Active citizenship involves both rights and responsibilities in civic issues.
- It concerns everyone and depends on partnerships between various groups in society.
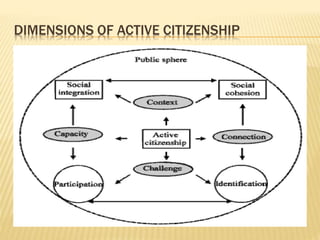
- There are four dimensions: capacity to act, relationships with others, desire to be involved, and awareness of social contexts.
- Sociological theories focus on socializing individuals for new roles, while psychological theories emphasize personal development.
- Barriers to active citizenship include lack of time, work/leisure patterns, and changing values.
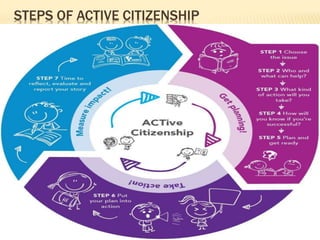
- Ways to be an active citizen include joining community groups, volunteering, and