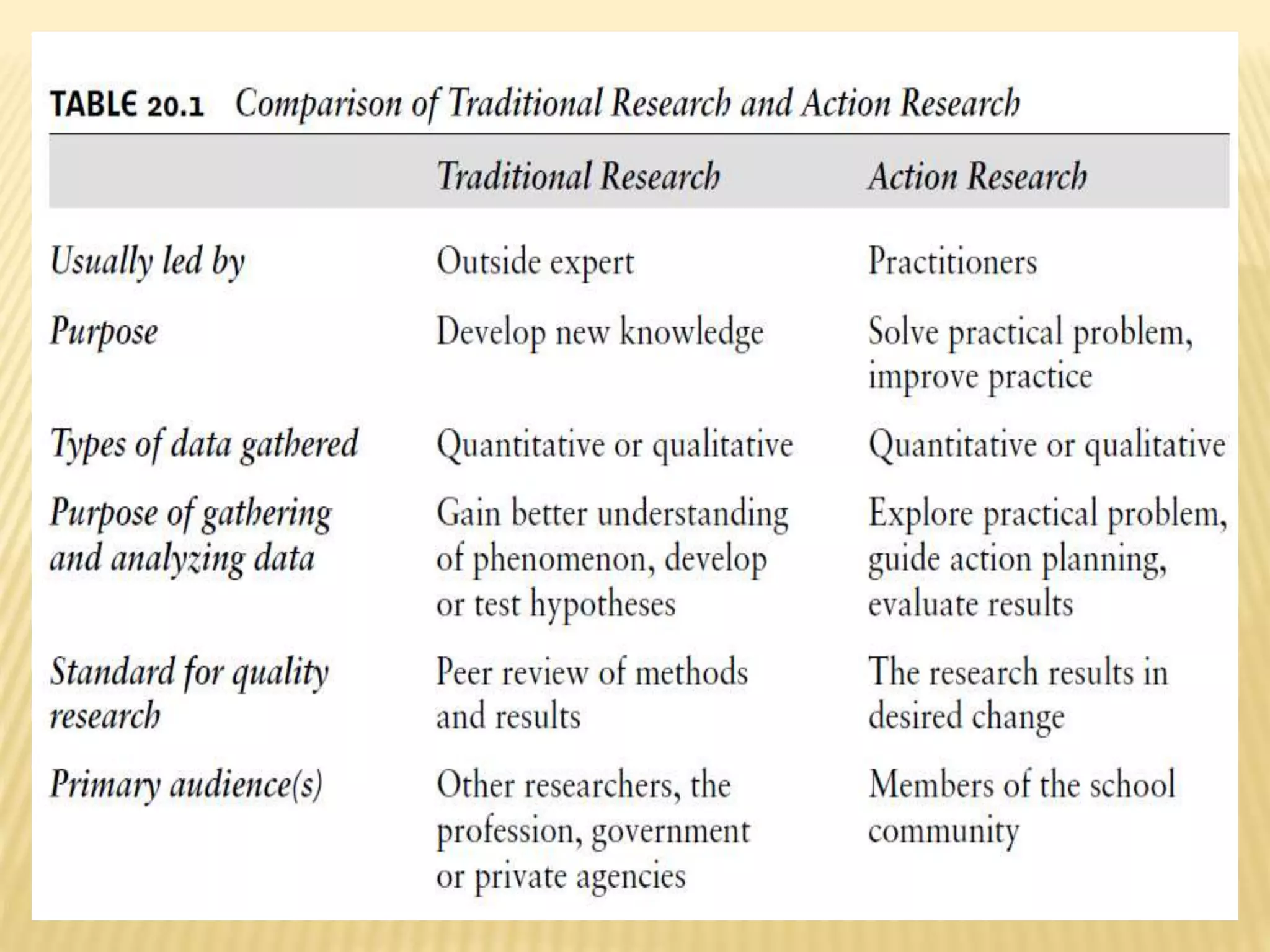
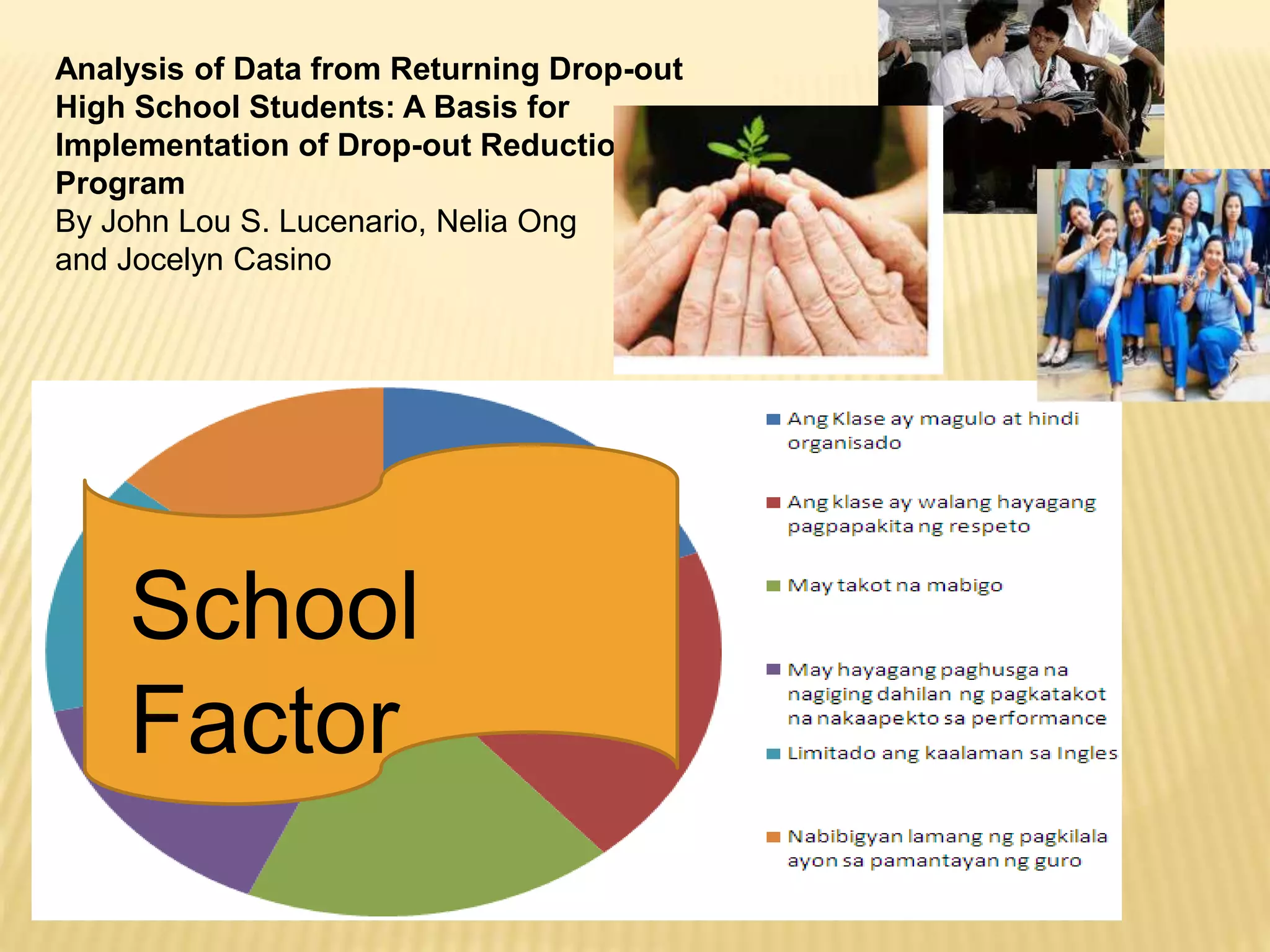
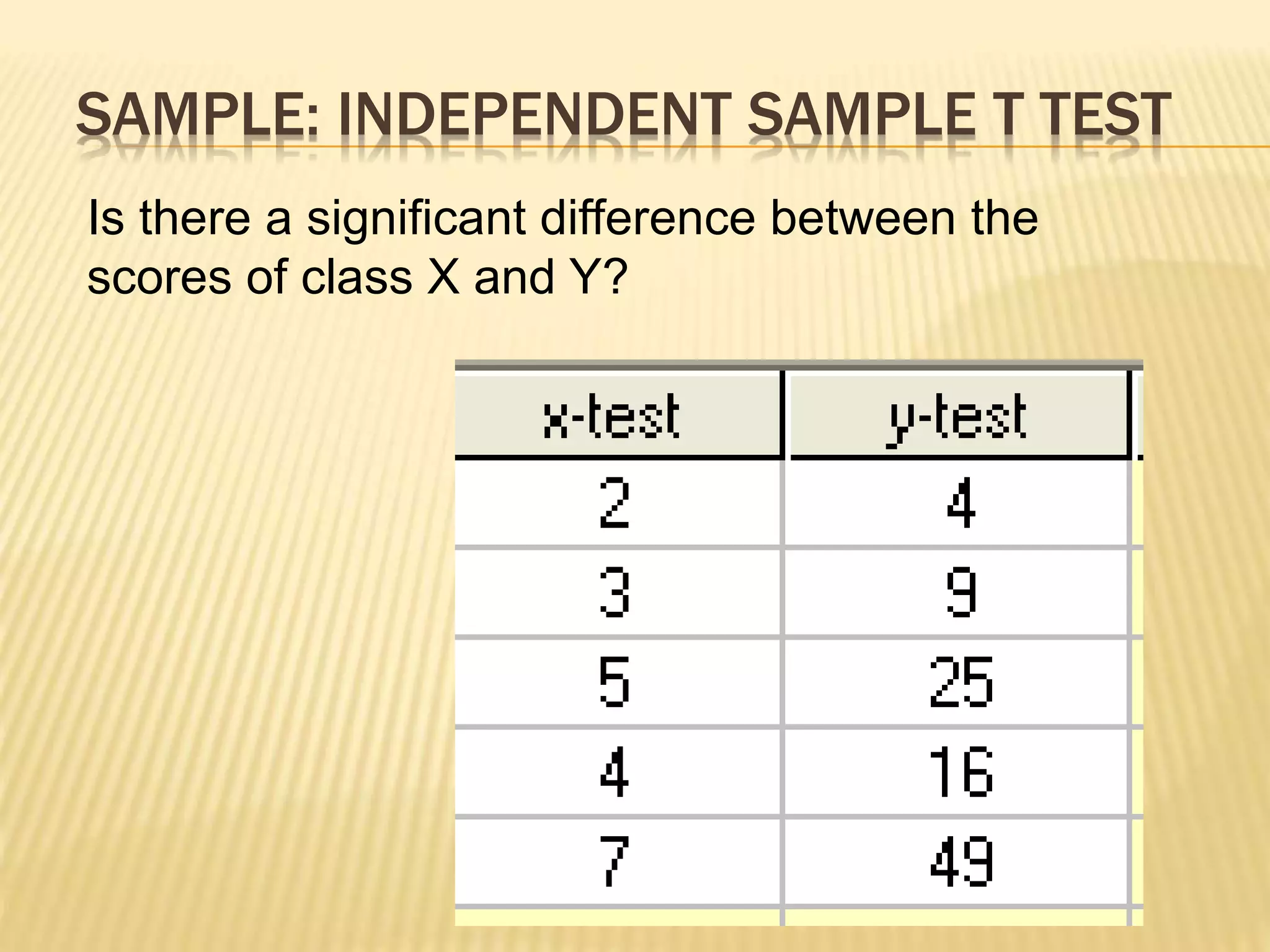
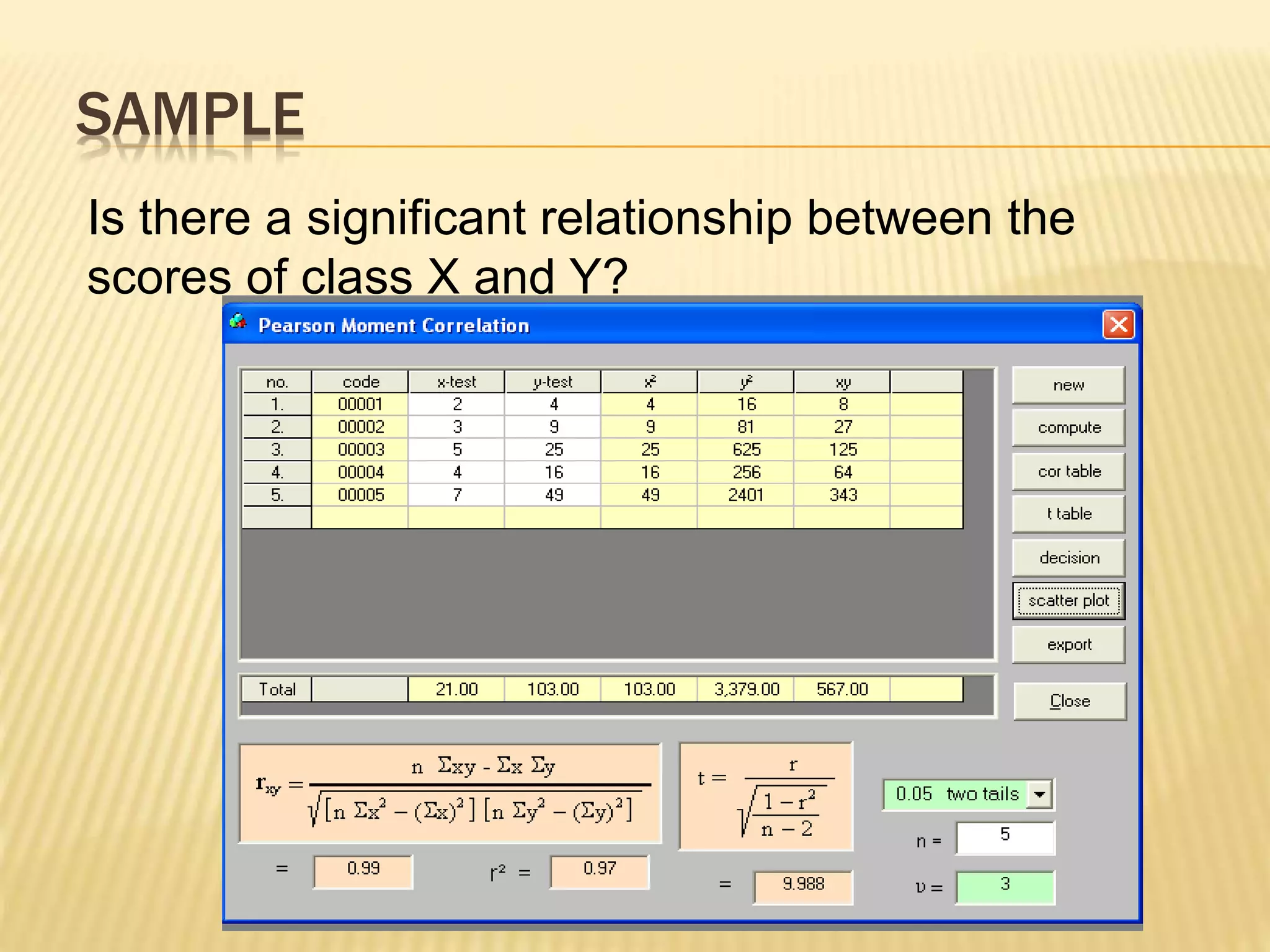
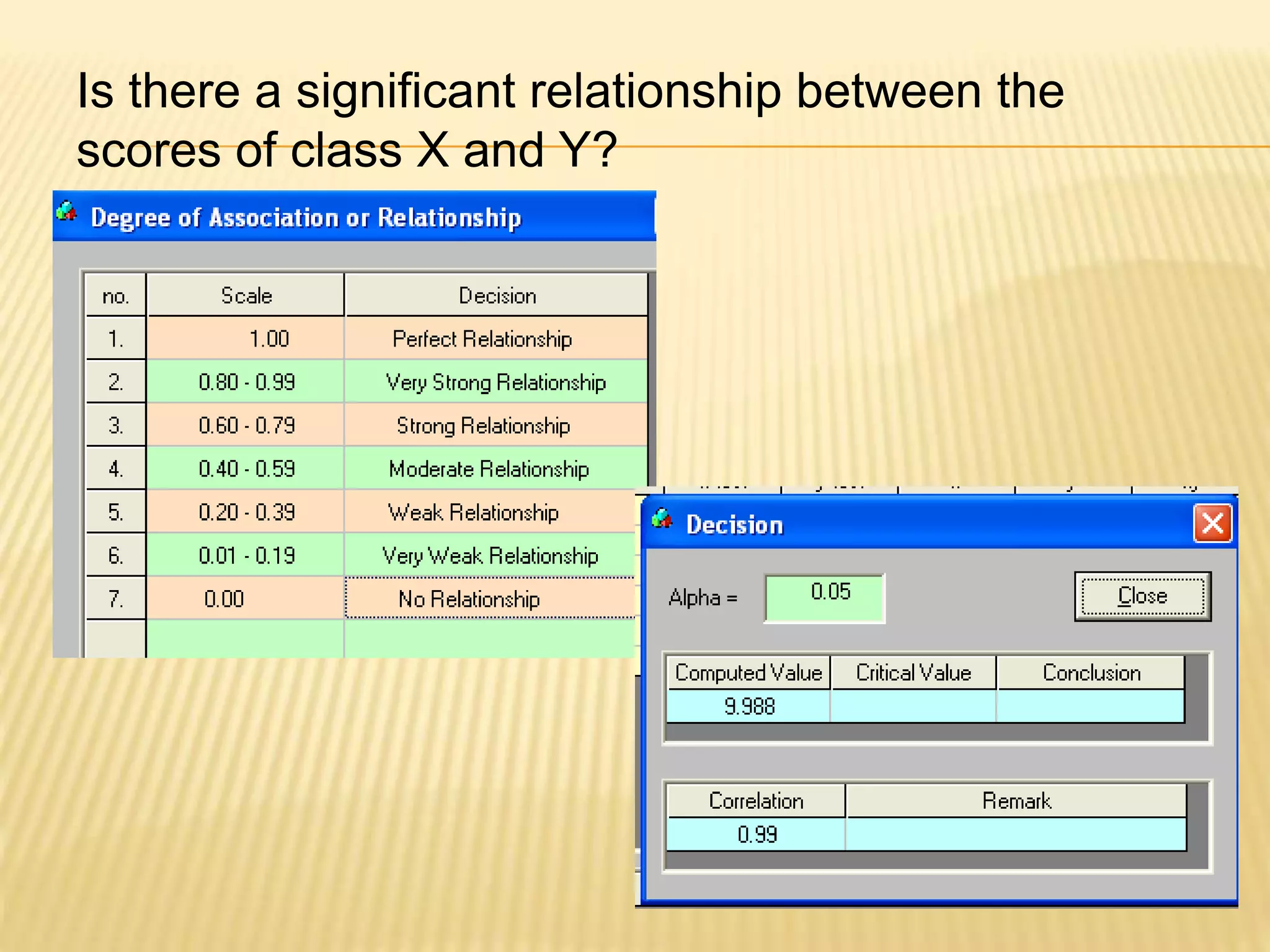
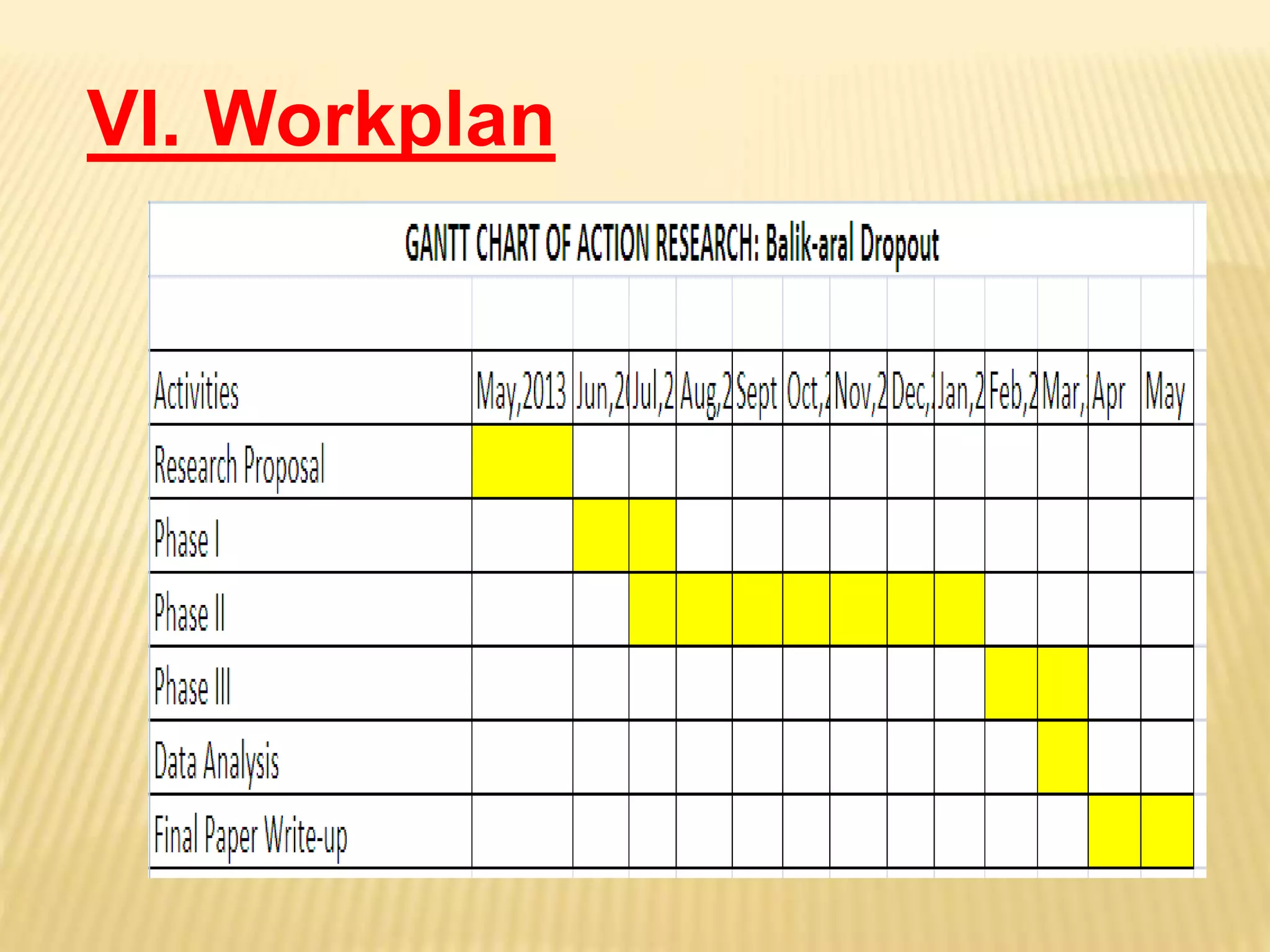
This document discusses action research and provides guidance on conducting action research. It defines action research as a process of systematic inquiry to improve educational practices or resolve problems in classrooms and schools. It provides the bases and rationale for undertaking action research, including relevant Department of Education orders. It also outlines the typical components and steps in a research process, including developing research questions, reviewing literature, determining methodology, analyzing data, developing an action plan, and establishing a workplan and budget.