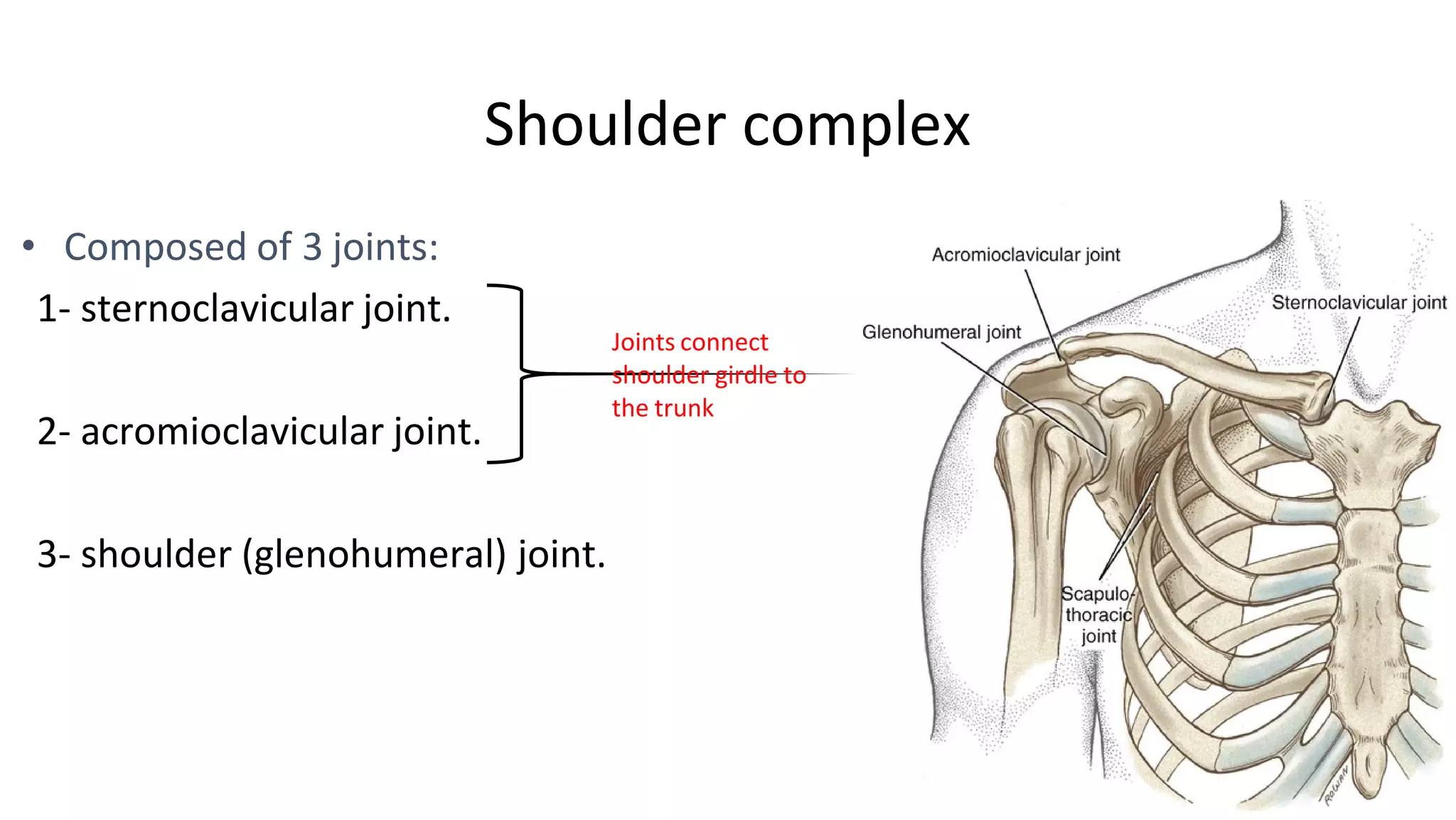
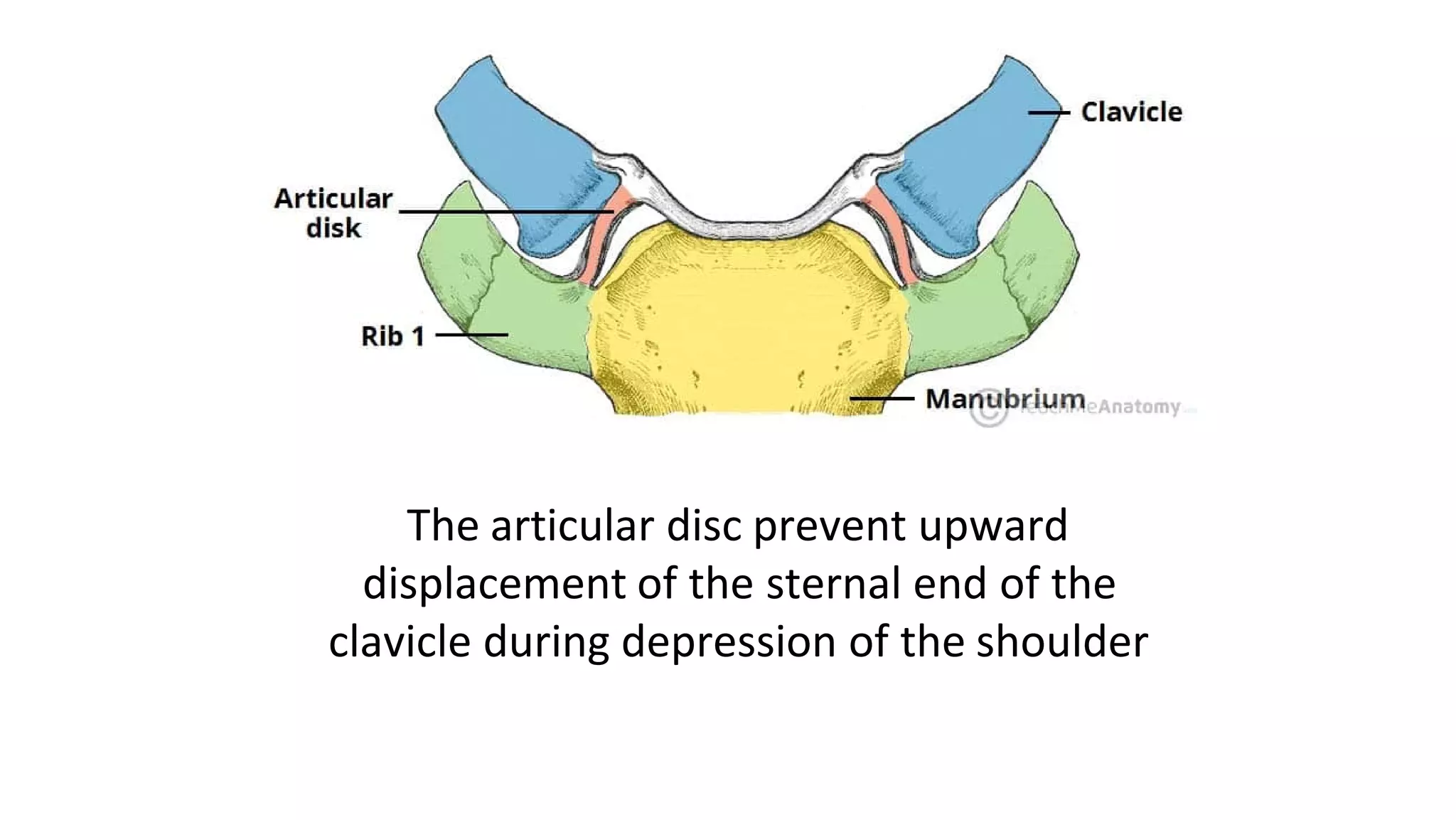
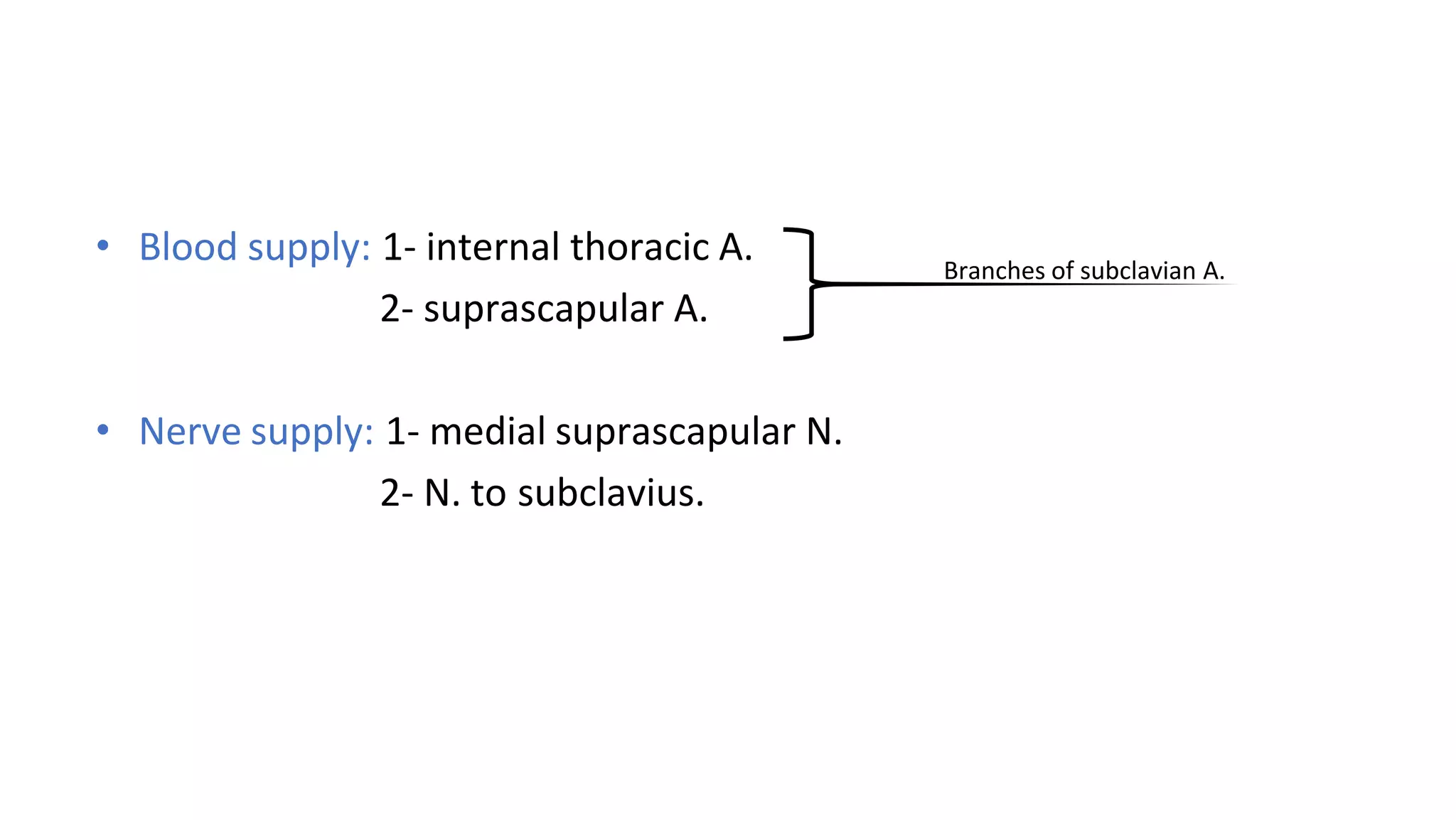
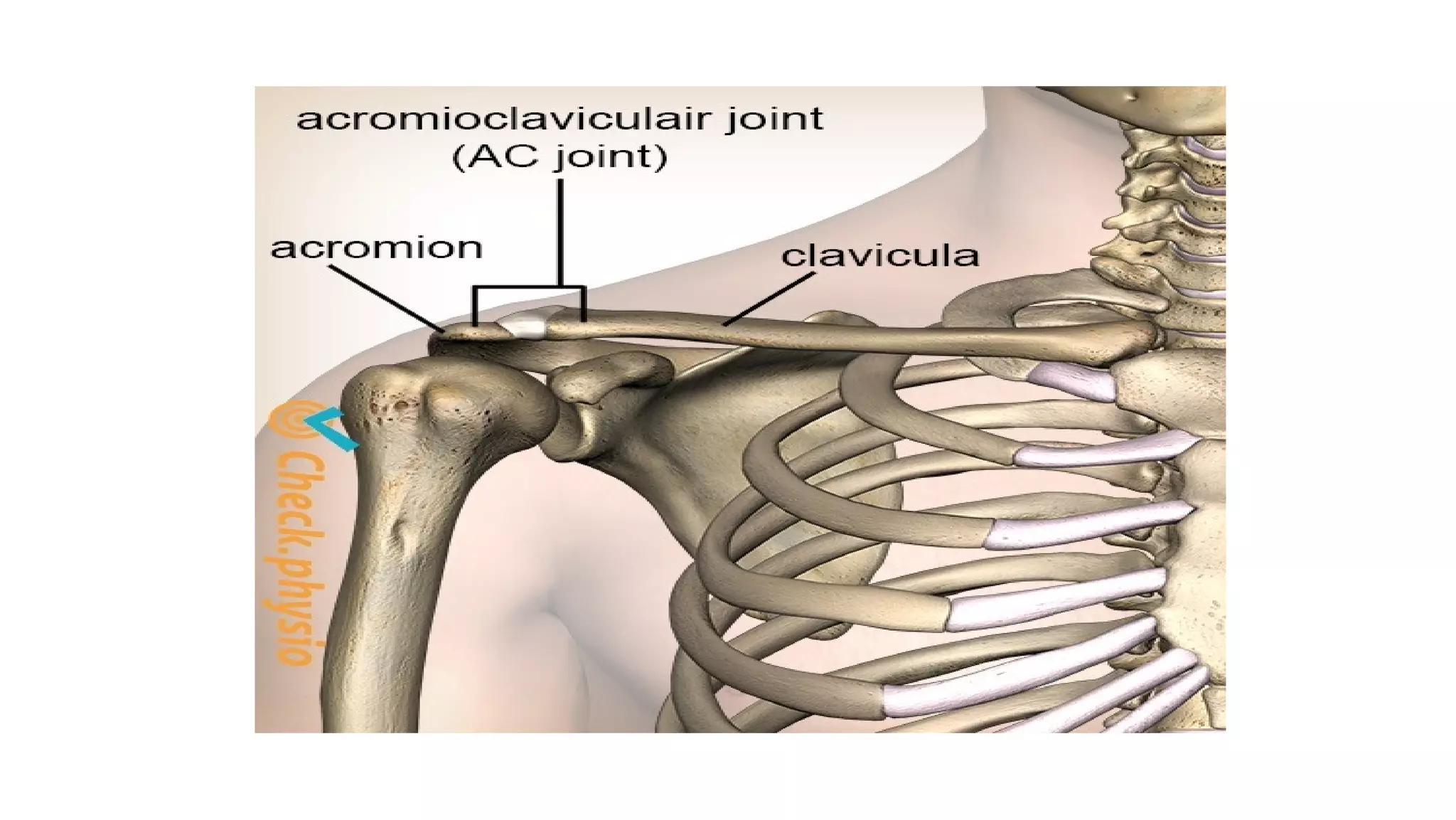
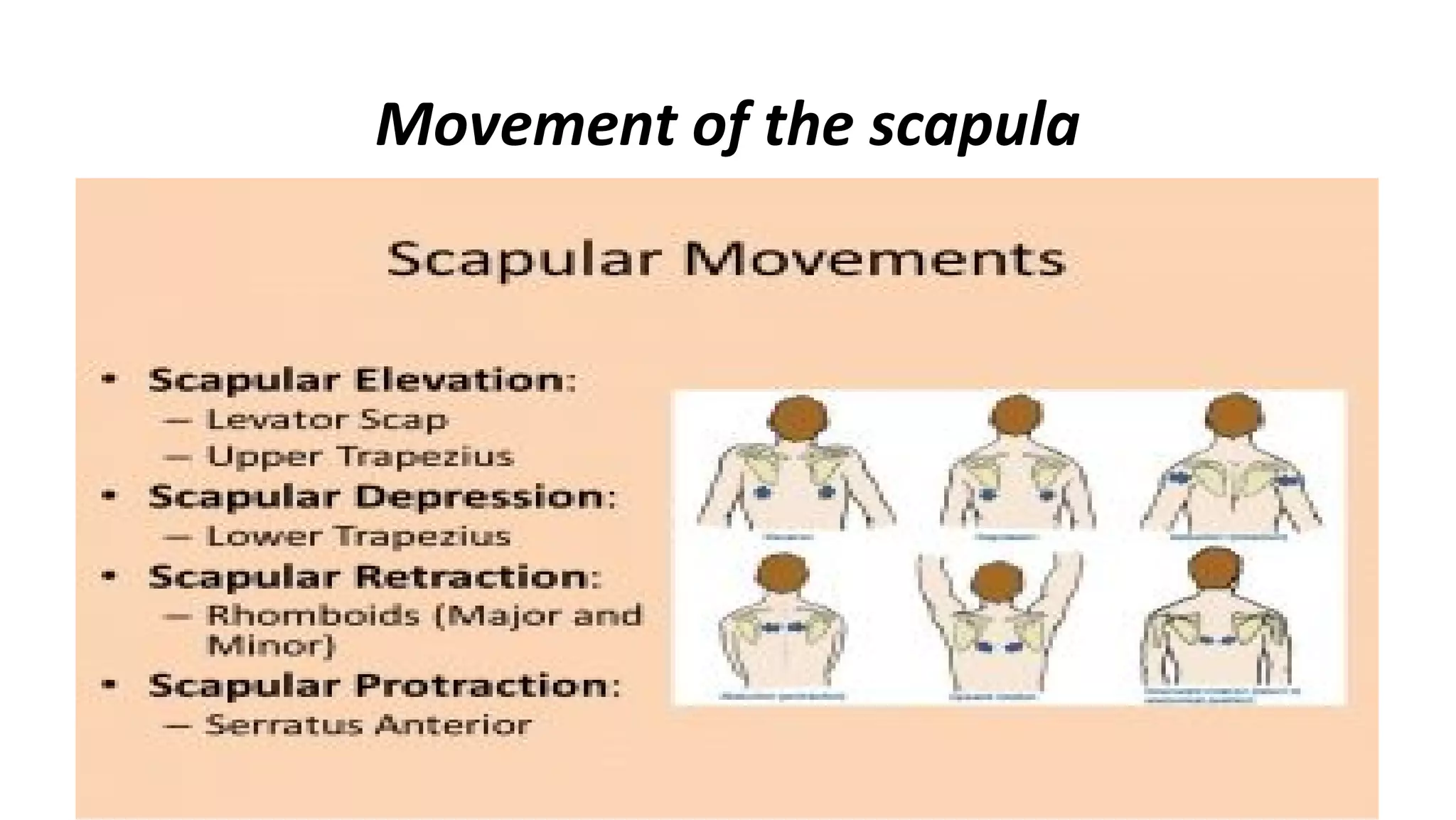
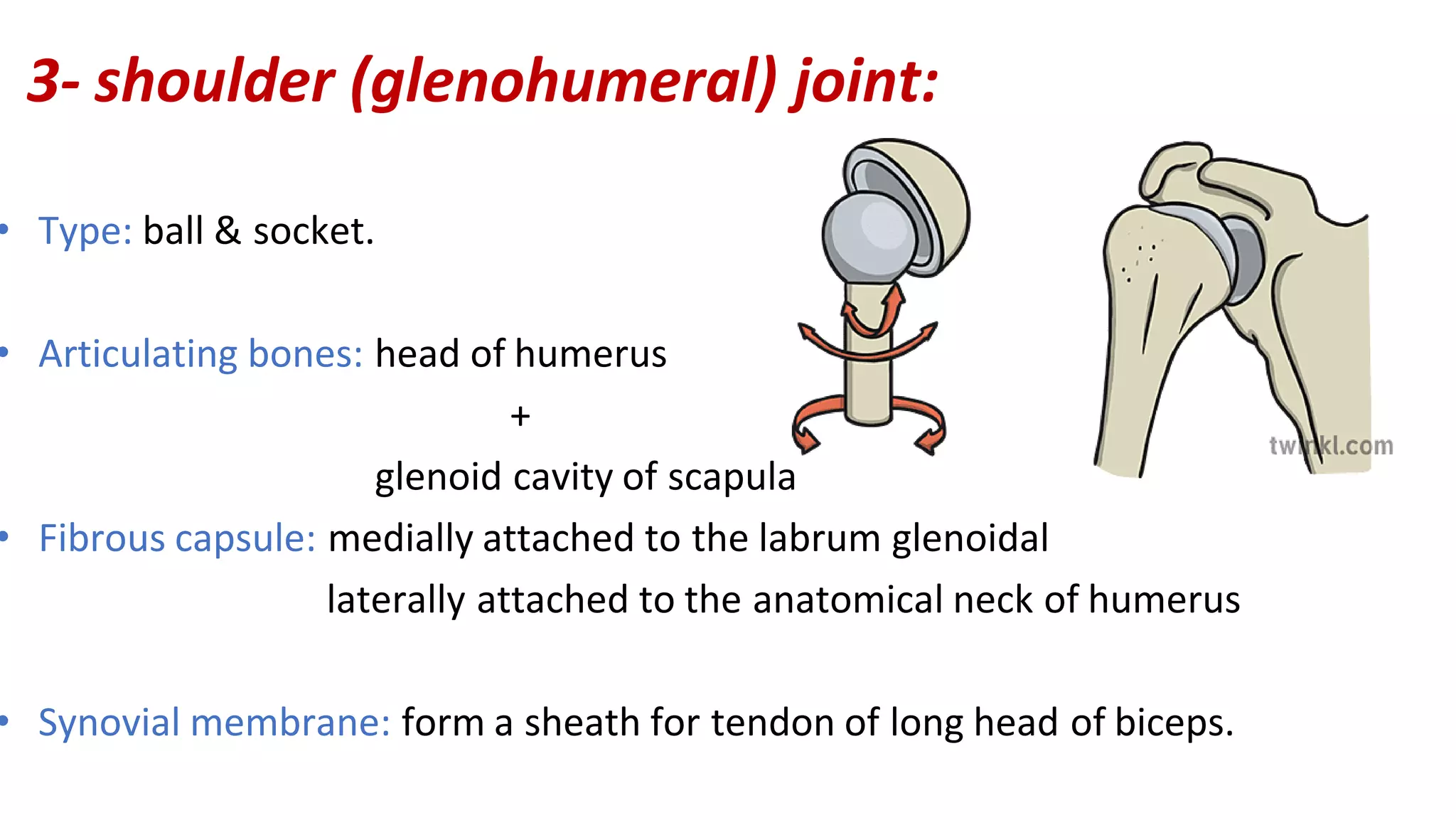
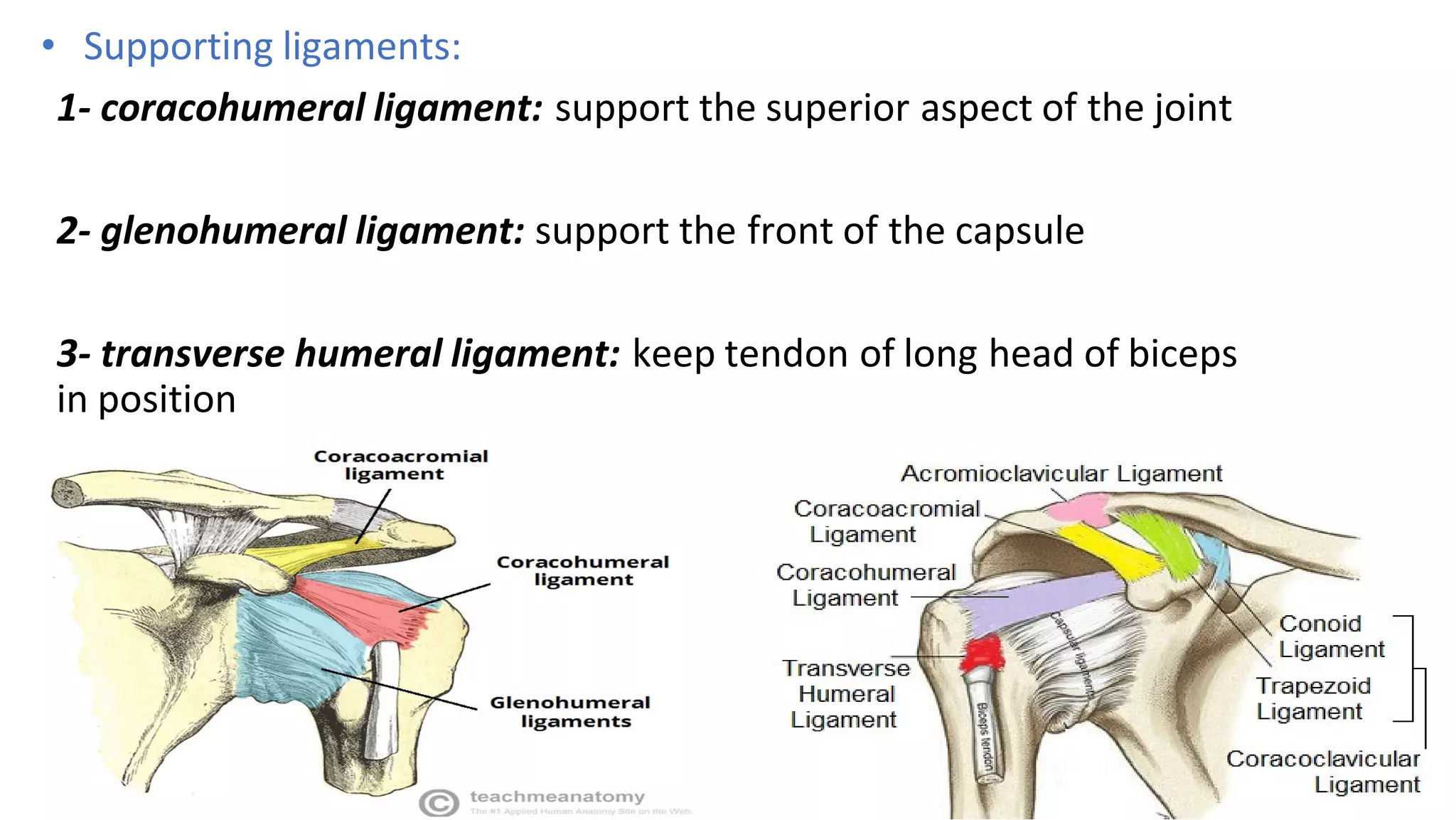
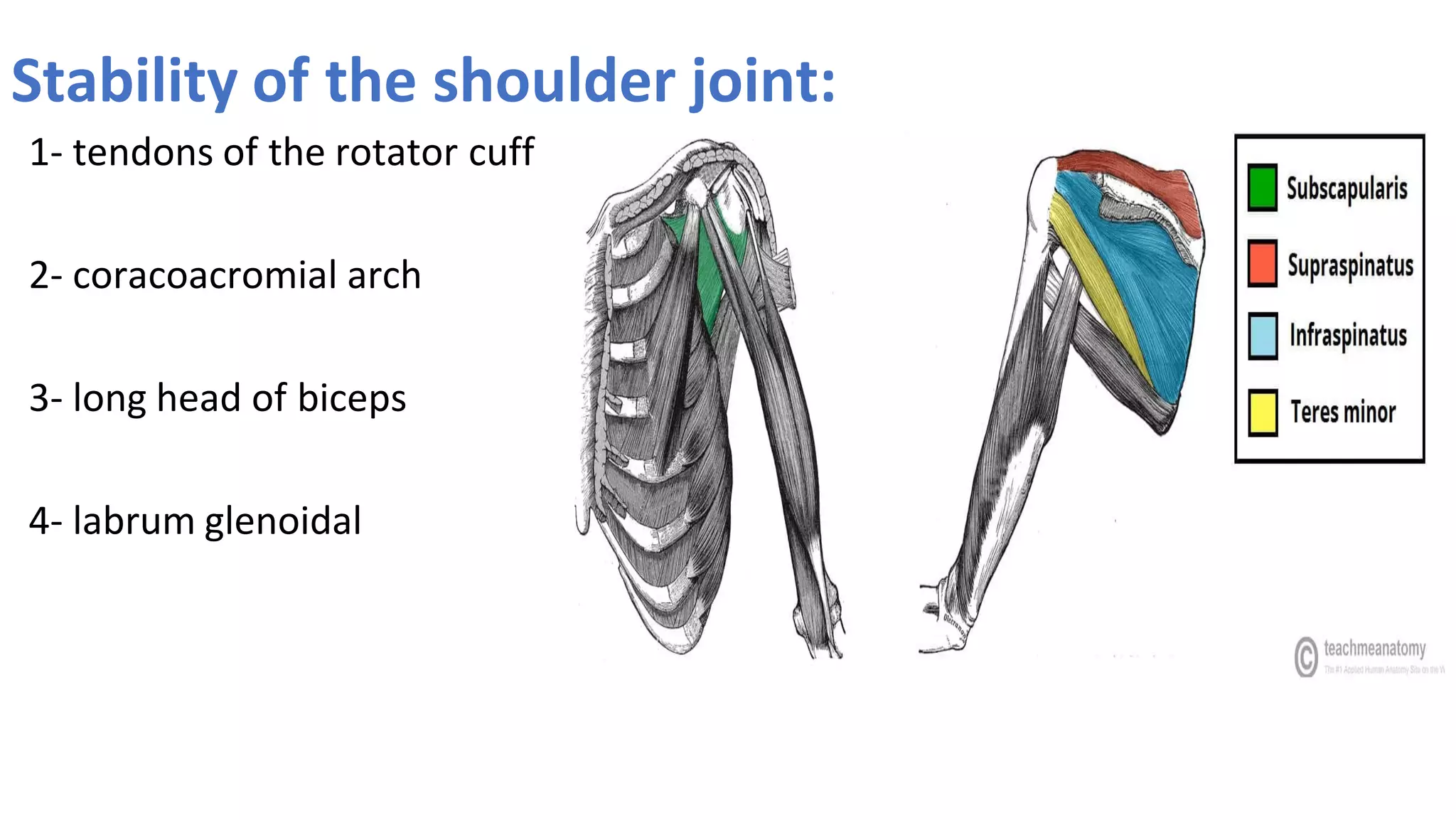
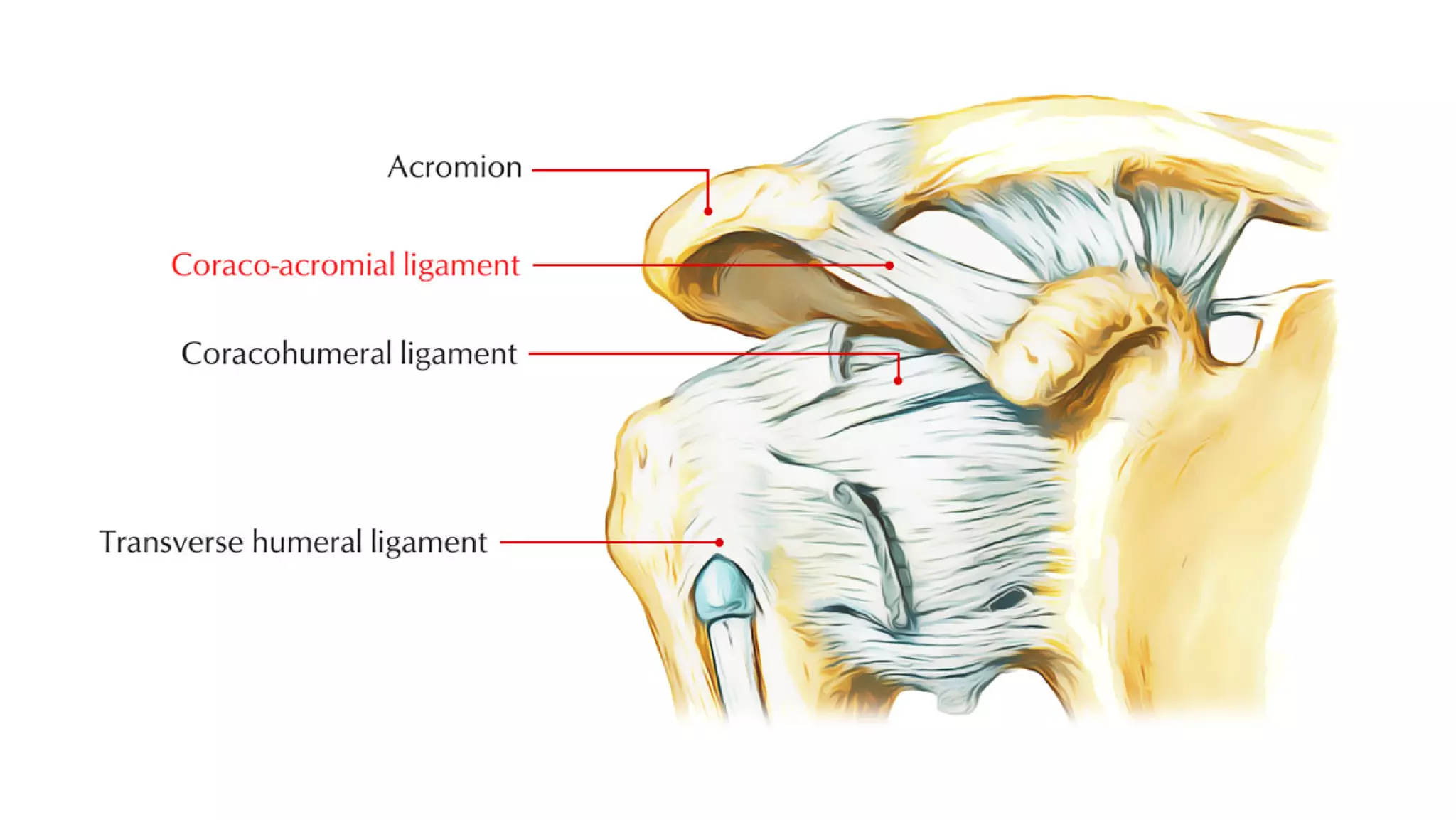
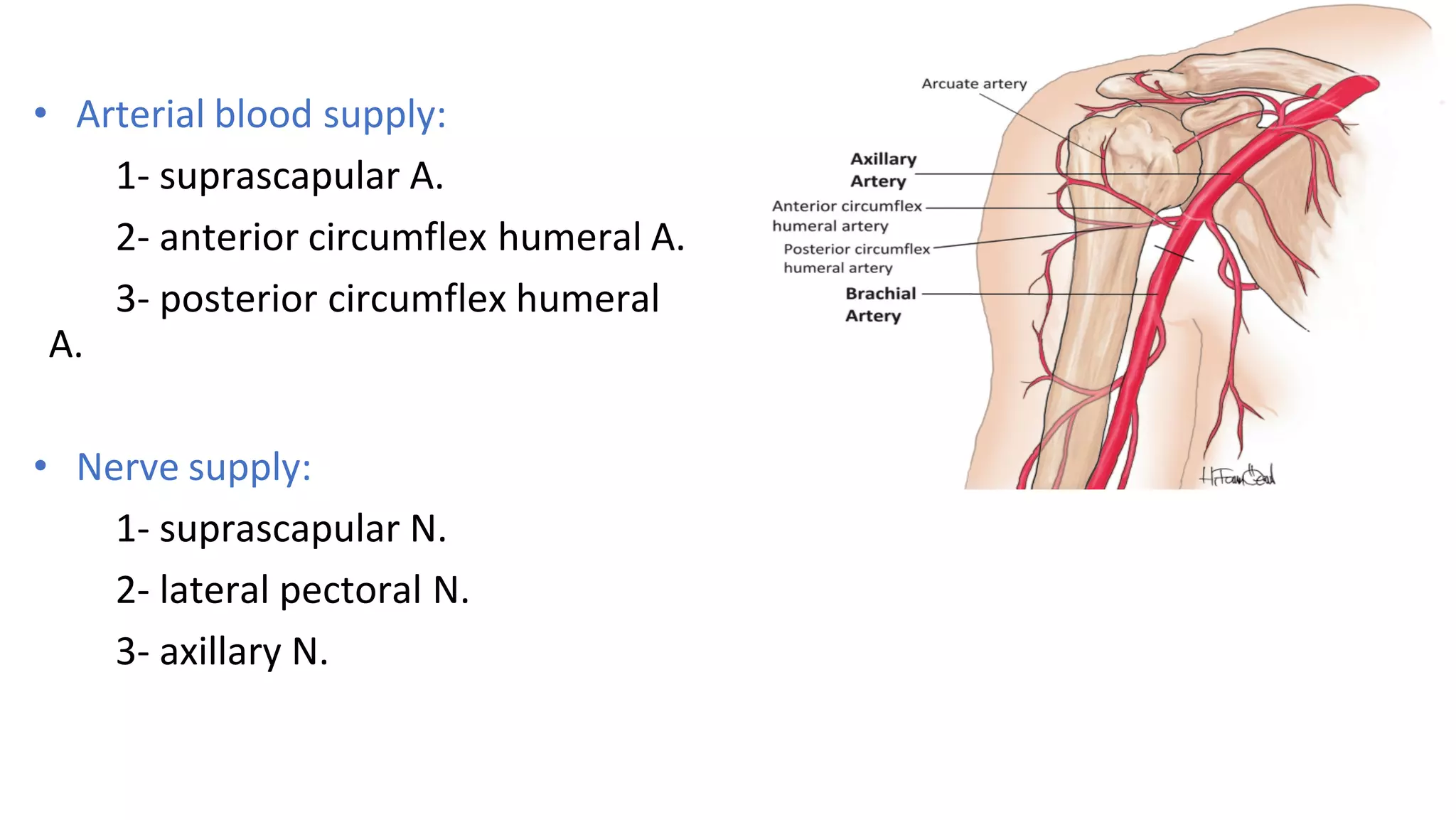
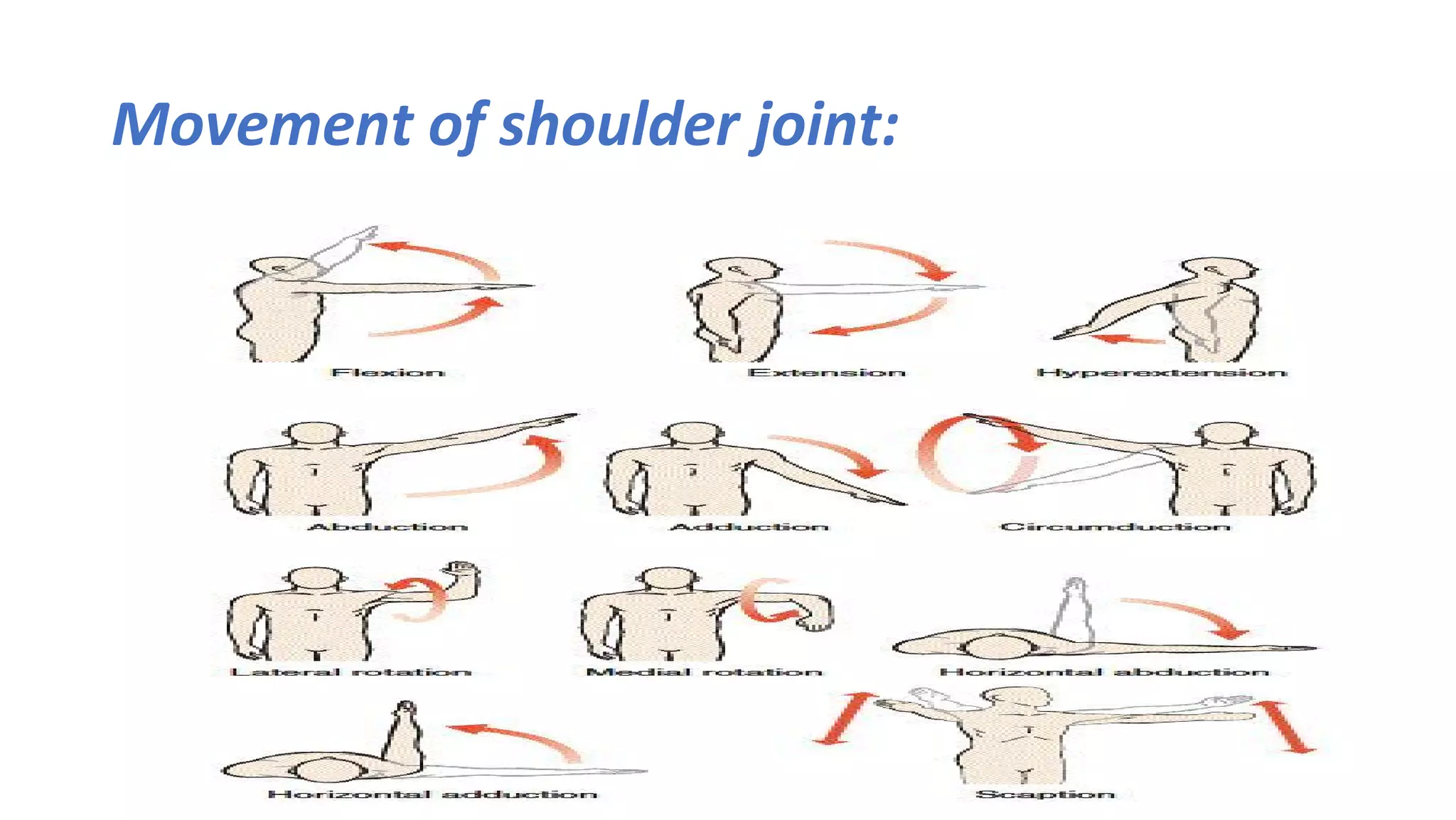
The document discusses the three joints that make up the shoulder complex: the sternoclavicular joint, acromioclavicular joint, and glenohumeral joint. It describes the type, articulating bones, ligaments, blood supply, and nerves of each joint. The sternoclavicular joint has a saddle shape and prevents upward displacement of the clavicle. The acromioclavicular joint is plane-shaped and stabilized by acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligaments. The glenohumeral joint is a ball and socket joint responsible for shoulder movement.