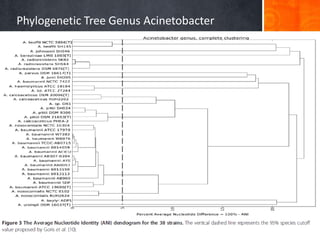
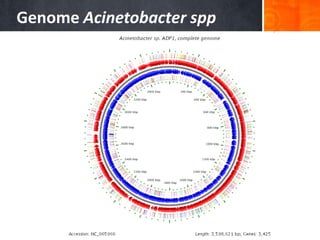
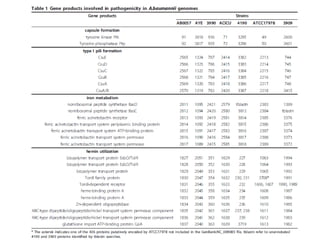
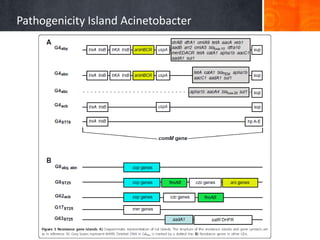
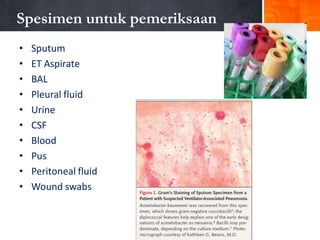
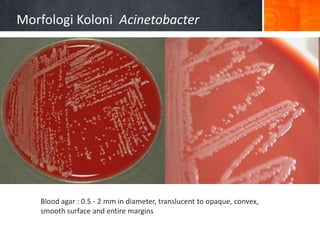
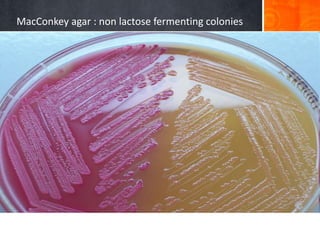
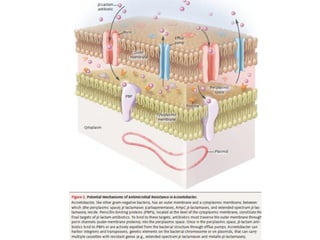
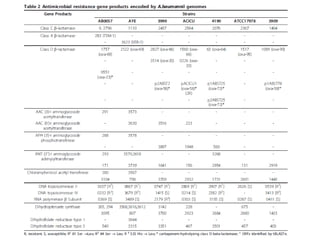
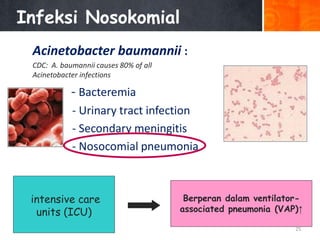
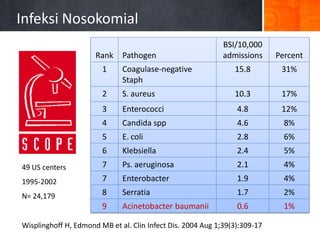
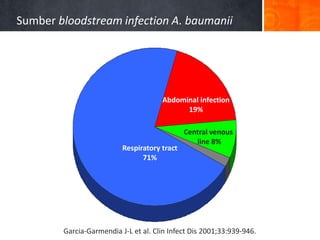
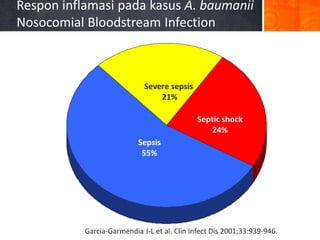
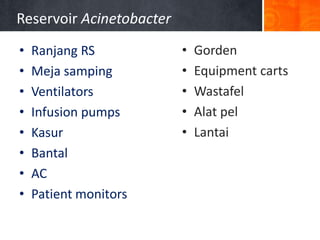
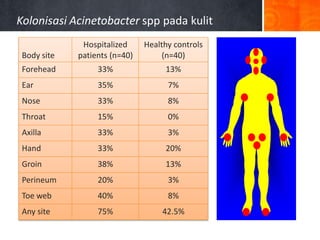
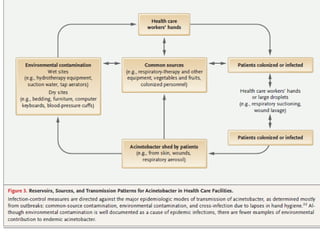
Dokumen ini menjelaskan tentang genus Acinetobacter, termasuk spesies medis penting seperti A. baumannii yang sering terkait dengan infeksi nosokomial. Dikenal dengan resistensi antibiotik tinggi, Acinetobacter dapat menginfeksi pasien di unit perawatan intensif dan memiliki berbagai mekanisme patogenitas dan transmisi. Selain itu, metode diagnosis dan karakterisasi genetik juga dibahas untuk identifikasi spesies dan analisis epidemiologi.