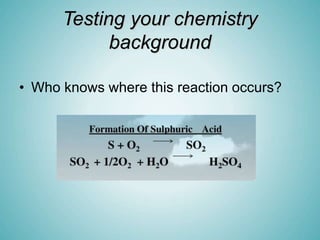
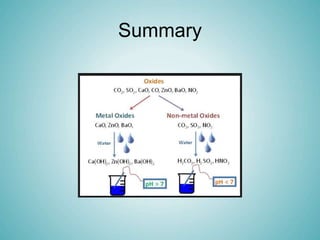
The document discusses acids and alkalis, including how they are formed, their properties, and how they react with each other. Acids are formed when certain non-metals dissolve in water, and have sour tastes and corrosive properties. Alkalis are formed when certain metal oxides dissolve in water, and feel soapy and are also corrosive. Acids and alkalis neutralize each other in a neutralization reaction, forming a salt. Common indicators like litmus paper are used to test whether a solution is acidic, alkaline, or neutral.