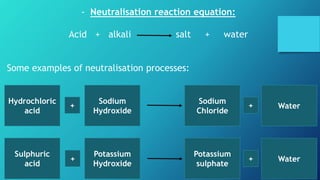
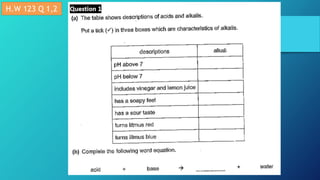
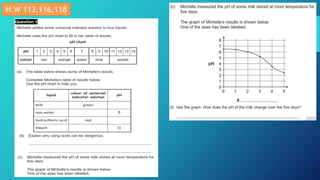
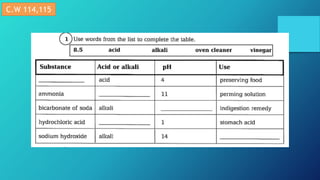
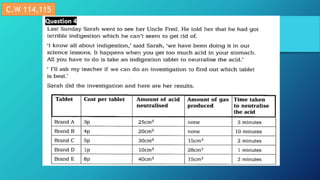
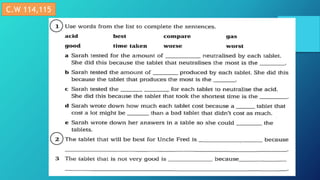
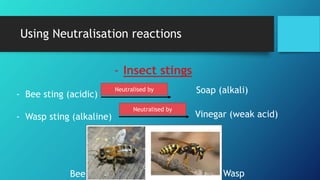
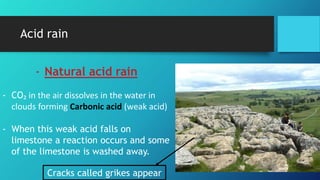
This document discusses neutralization reactions between acids and bases. It provides examples of common acids like hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric acid reacting with bases like sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide to form salts and water. Additional examples are given for using neutralization reactions to cure bee stings, treat indigestion, make baking powder rise in cakes, improve acidic soil for crop growth, and reduce the effects of acid rain by neutralizing it. The document also covers how neutralization can be used to clean teeth and dissolve mineral scales from kettles.