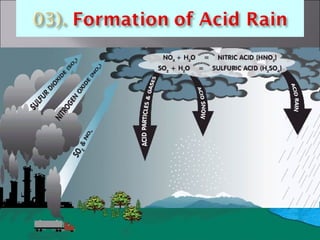
Acid rain is caused by emissions from industries, power plants, vehicles, and other sources that release sulfur and nitrogen compounds into the atmosphere. When these compounds react with water, oxygen, and other chemicals in the air, they form acids that fall to the earth as rain, snow, fog, hail or dry particles. Acid rain harms aquatic life by acidifying lakes and streams, damages trees and buildings, and can harm human health. To reduce acid rain, industries can install scrubbers to remove sulfur from smokestacks and shift to cleaner fuels, while vehicles can install converters to reduce emissions.