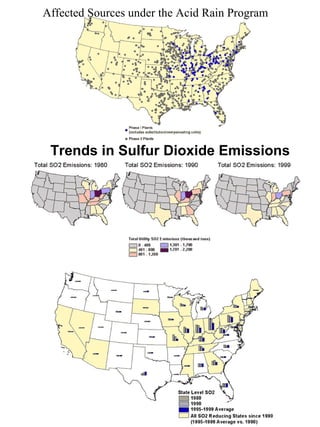
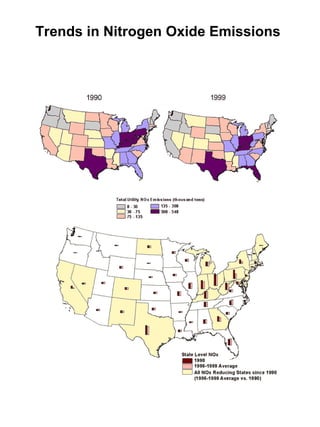
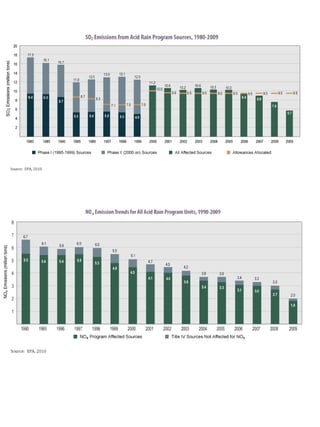
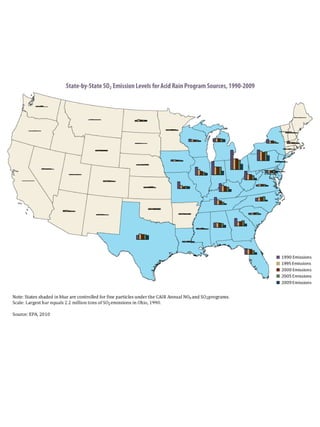
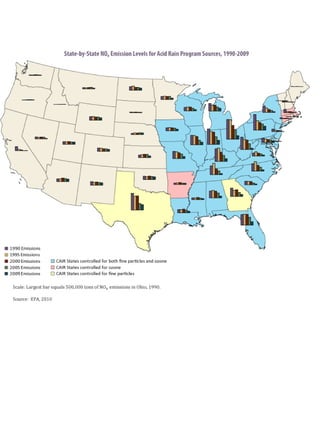
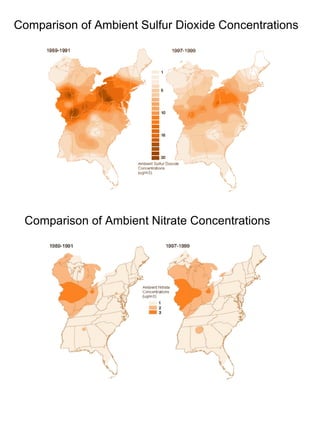
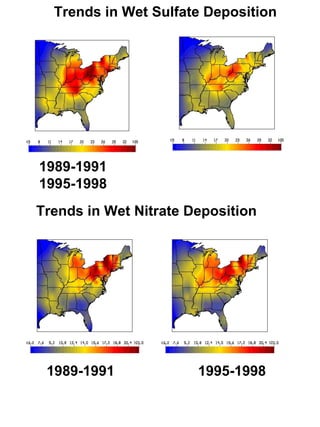
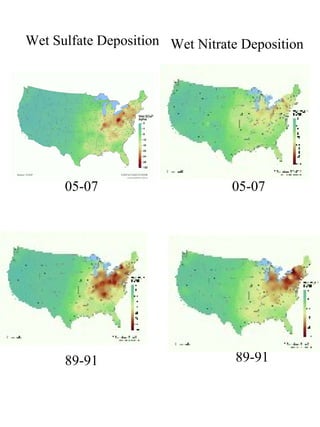
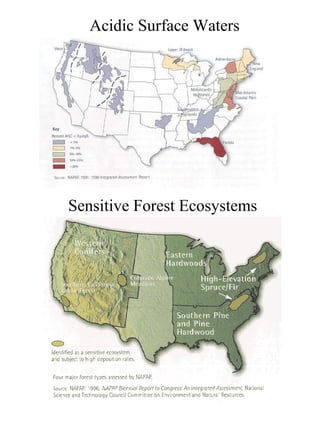
Acidic deposition, also known as acid rain, is caused by emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur oxides (SOx) which primarily come from power plant emissions. When NOx and SOx react with water, oxygen, and sunlight in the atmosphere, they form acids like sulfuric and nitric acid which fall to earth as rain, snow, or dry deposition. Acidic deposition harms ecosystems by lowering the pH of soils and surface waters outside of their normal acidic range, which can damage forests and aquatic wildlife. The EPA addresses acidic deposition through its Acid Rain Program that implements emissions trading of SOx and NOx to reduce deposition and restore damaged environments.