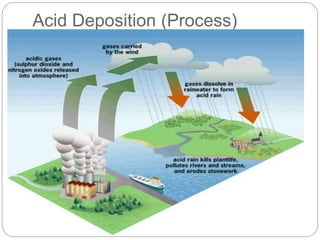
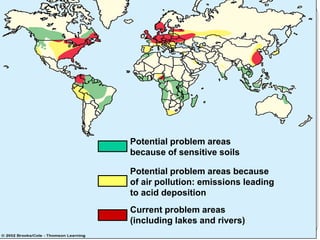
Rainwater is naturally slightly acidic due to carbon dioxide in the air. However, when sulfur and nitrogen oxides from fossil fuel combustion dissolve in rainwater, they form strong acids like sulfuric and nitric acid, making the rainwater much more acidic. This phenomenon is called acid deposition. It can occur through wet deposition as acid rain or snow, or dry deposition of acidic particles. Primary pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides directly cause acid deposition, which can damage forests and aquatic ecosystems by inhibiting growth, killing microbes and fish, and leaching nutrients from soils. International agreements have aimed to reduce acid deposition through domestic policies like installing pollution control devices on power plants and vehicles.