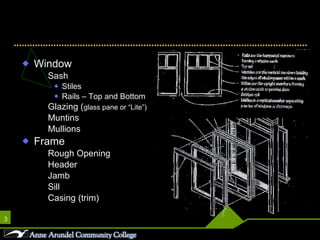
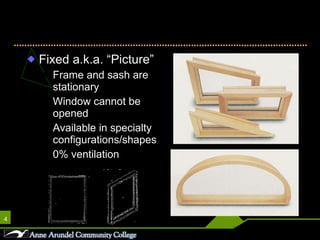
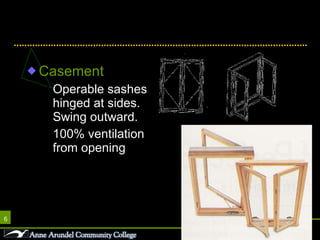
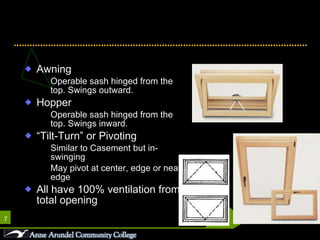
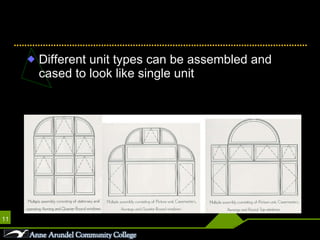
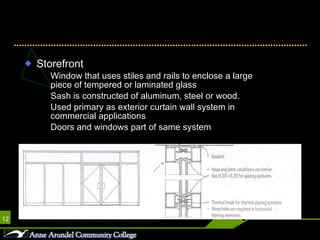
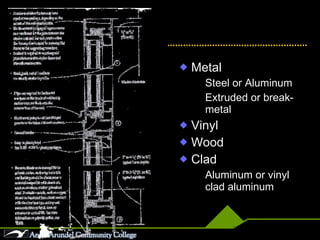
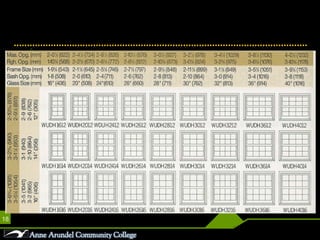
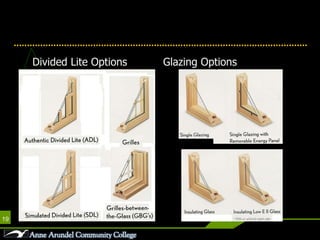
This document discusses different parts, materials, and types of windows. It describes the frame, sash, glazing, muntins, mullions, jamb, sill, and casing that make up windows. It also outlines various window operations such as fixed, casement, awning, hopper, tilt-turn, glider, double-hung, and jalousie. Finally, it mentions common window materials like metal, vinyl, wood, and discusses specifying dividers and glazing as well as types of skylights.