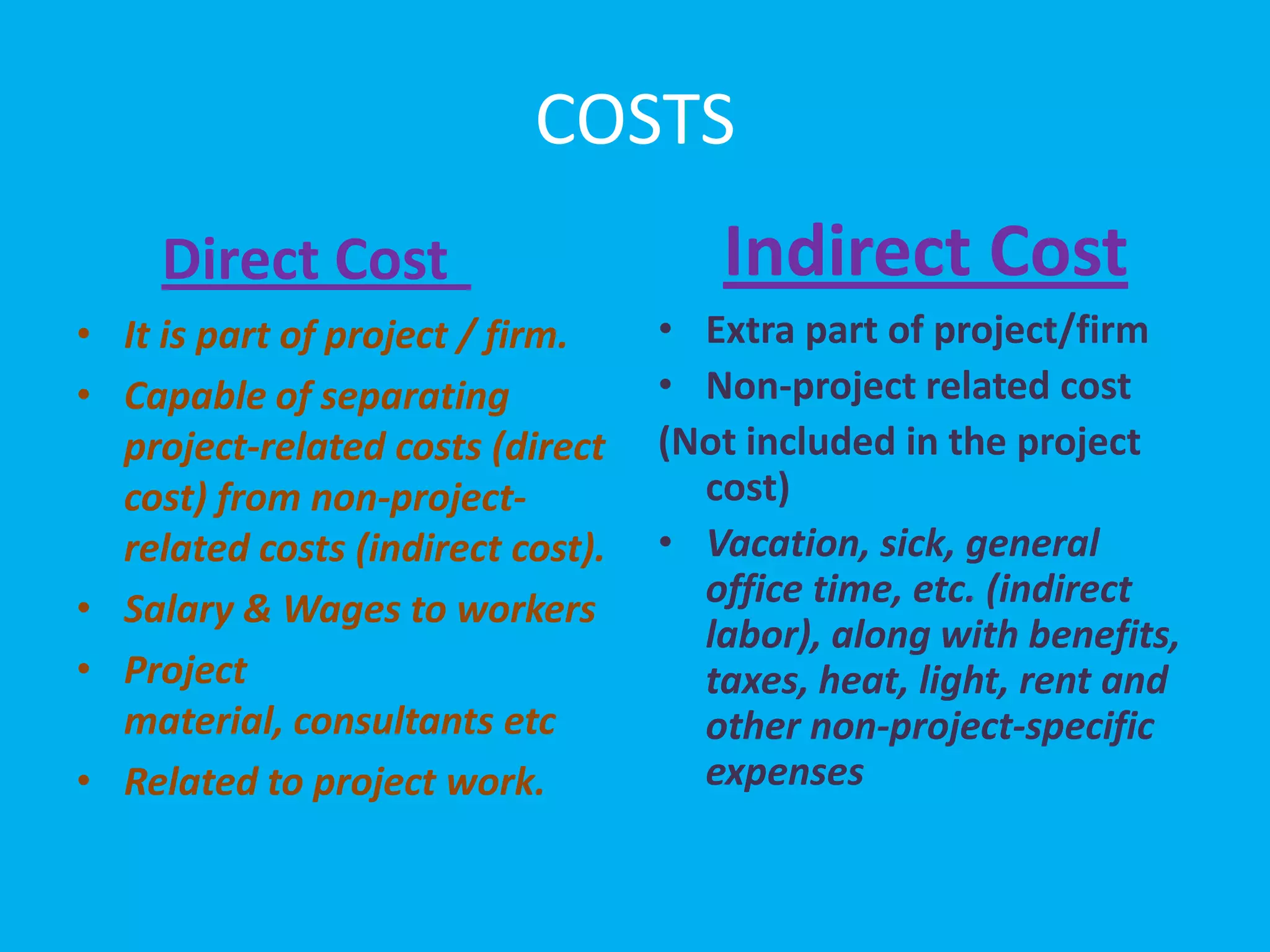
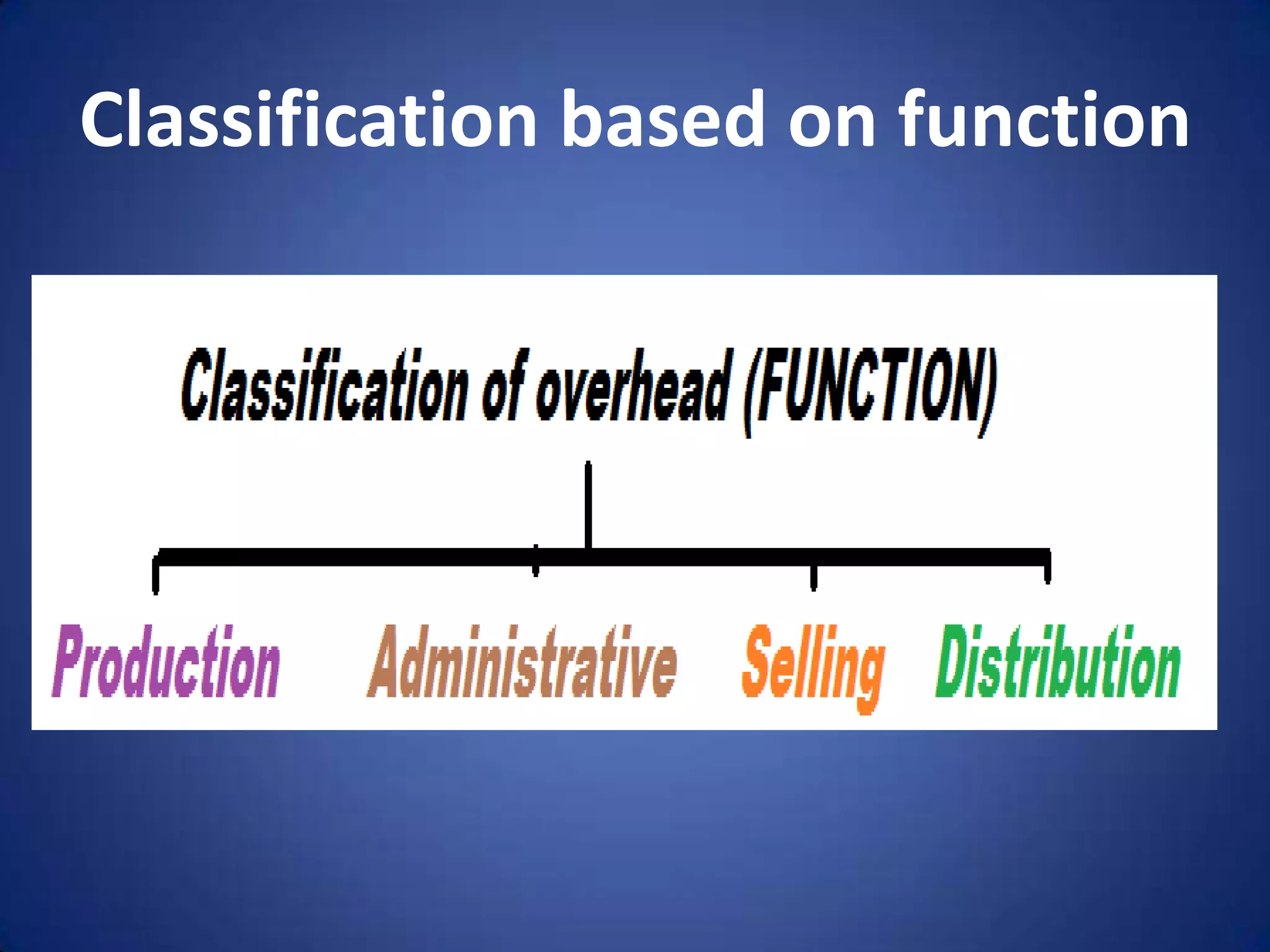
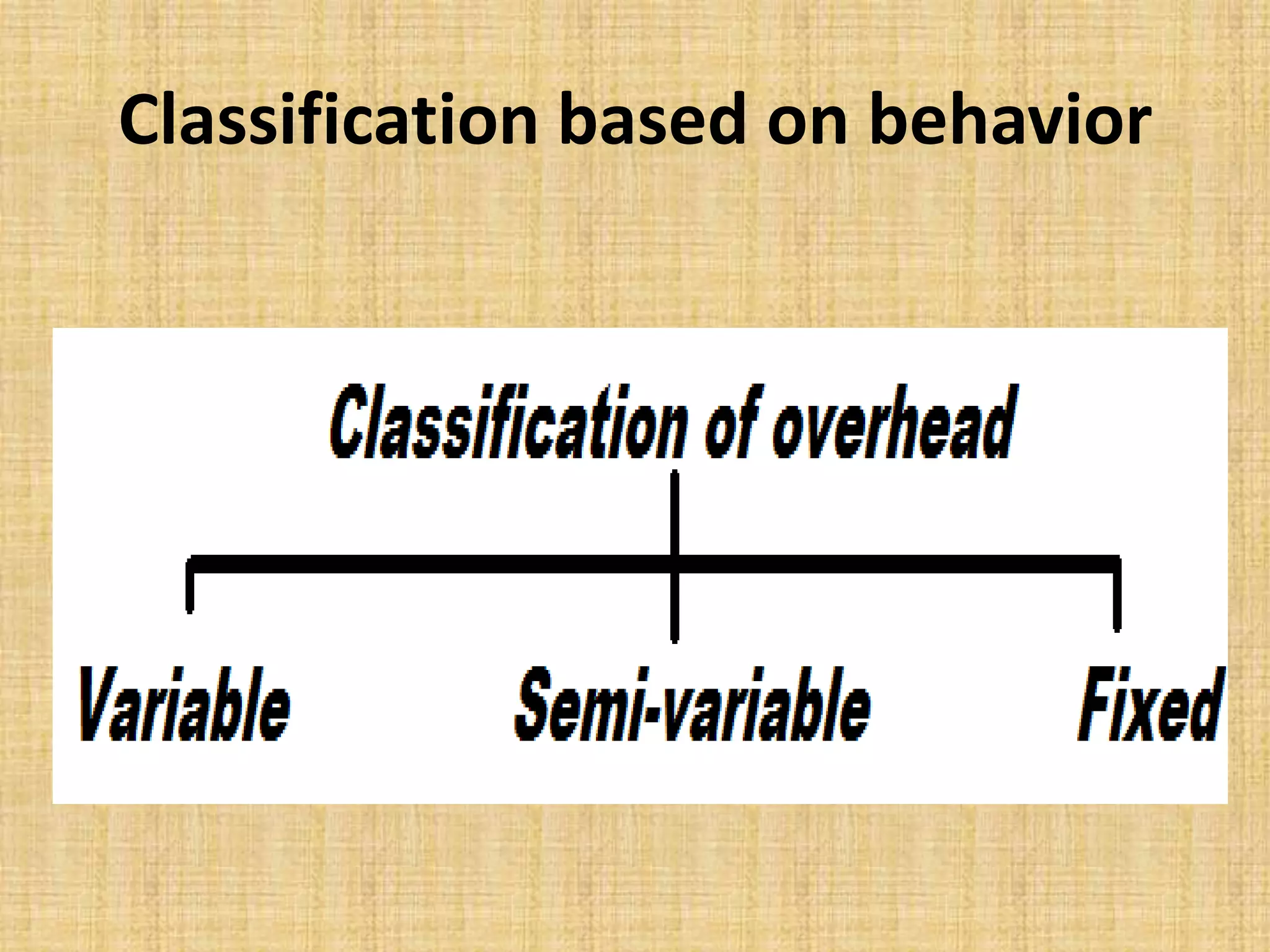
This document discusses overhead costs and their classification. It begins with an introduction of the presenter and group members. It then defines overheads as indirect costs that are not directly identifiable to a specific cost object. It provides examples of direct versus indirect costs. It also classifies overheads based on function (production, administration, selling, distribution) and behavior (variable, fixed, semi-variable). Finally, it outlines the process of allocating and apportioning overheads which involves collecting expenses, departmentalizing, and then allocating or apportioning the expenses among departments.