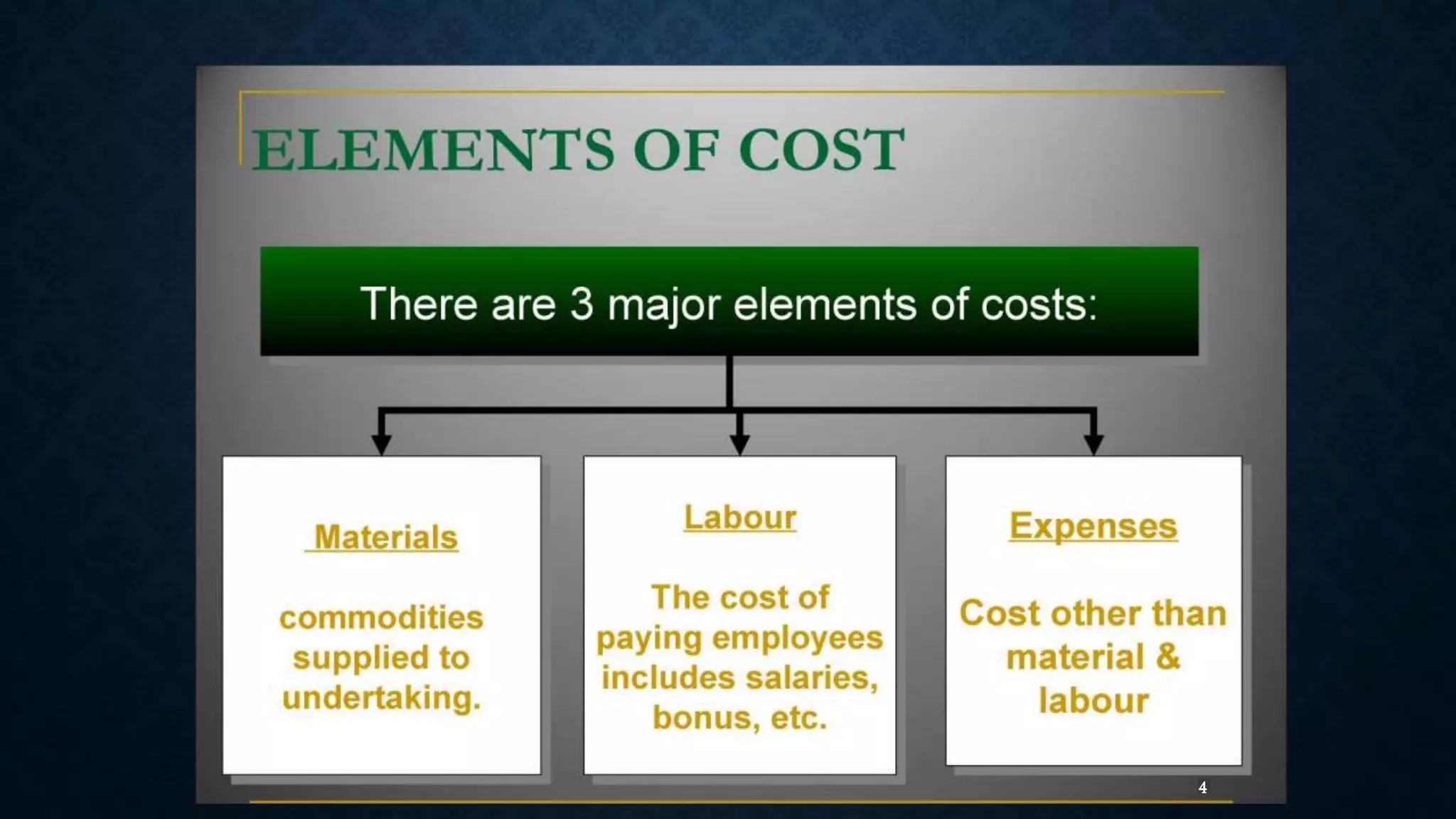
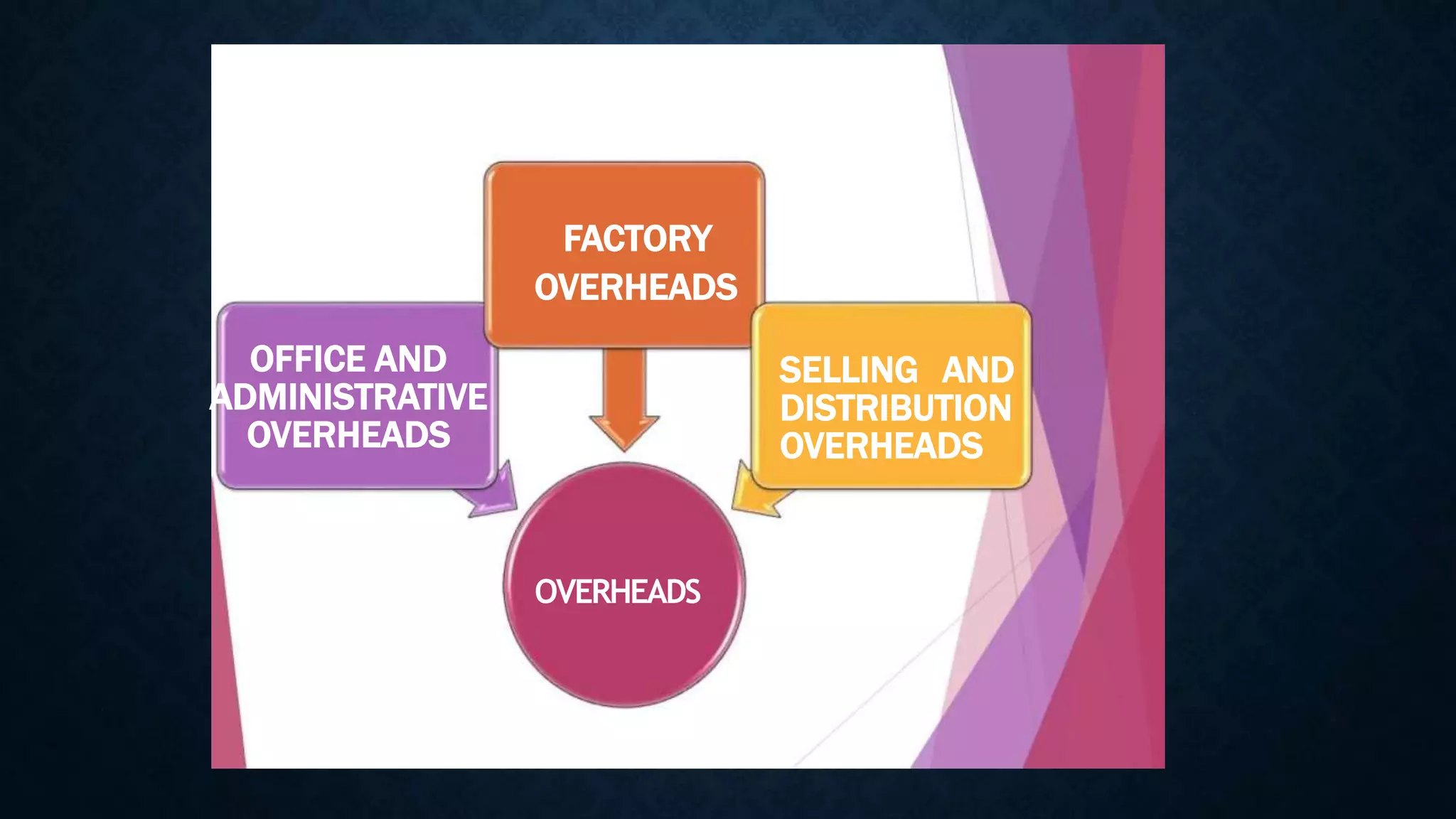
This document defines the key elements of cost - material, labor, expenses and overheads. It provides definitions for direct and indirect costs for each element. Direct costs can be directly traced to a cost object, like the cost of materials that become part of the final product. Indirect costs cannot be directly traced to a cost object, like utilities or administrative salaries. The document also categorizes overheads as factory, office/administrative, and selling/distribution overheads.