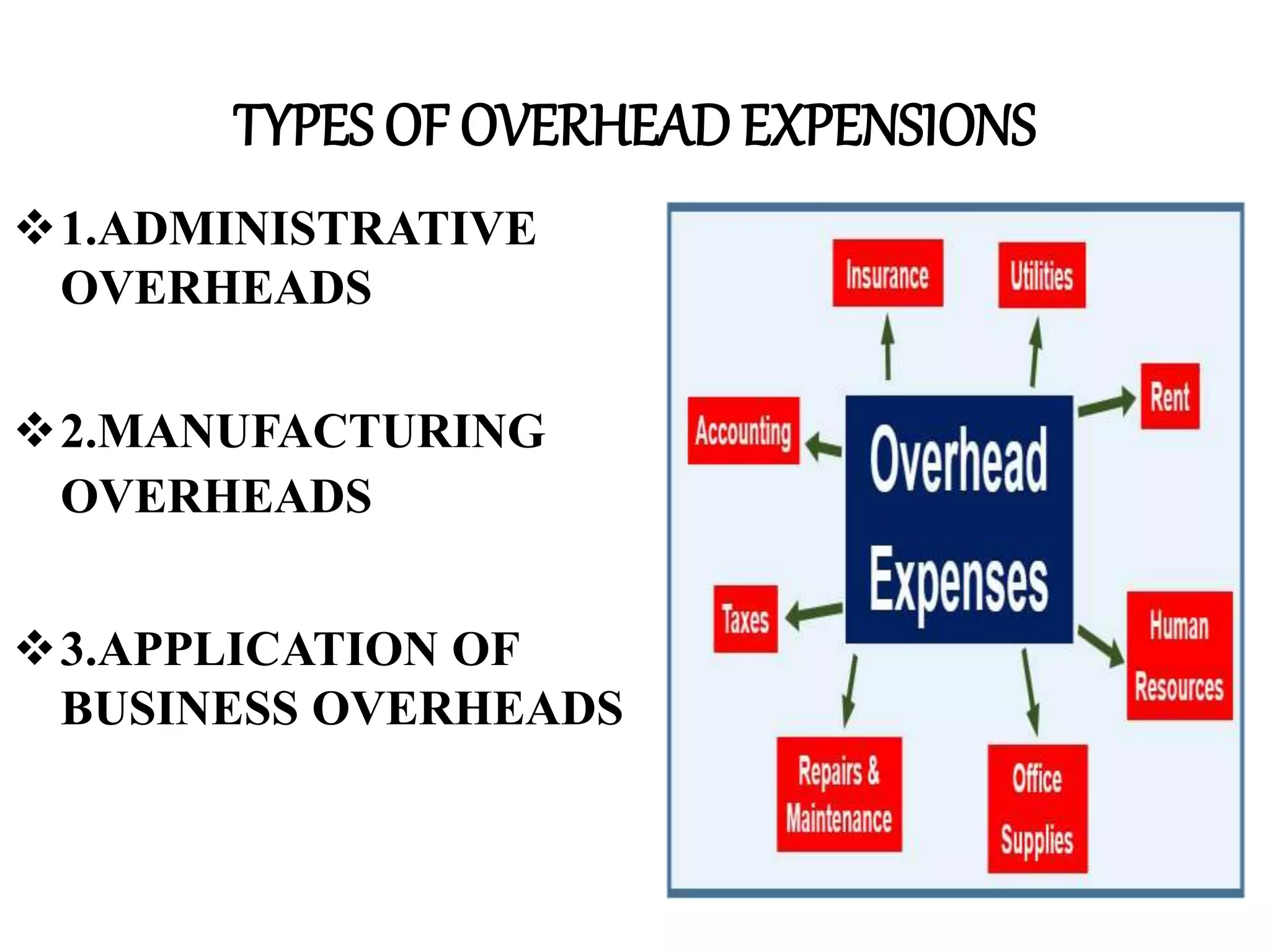
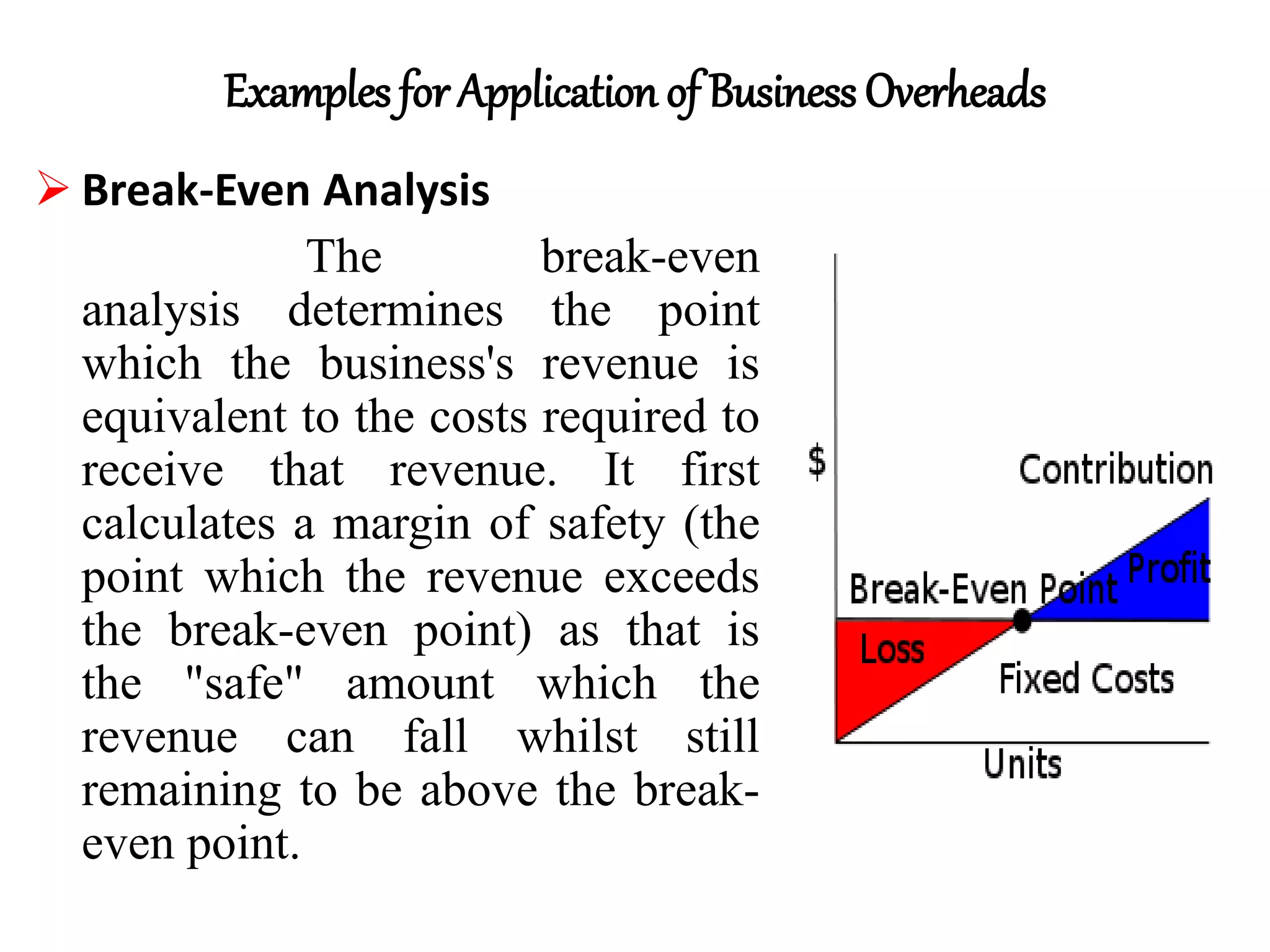
This document discusses overhead expenses in business. It defines overhead as ongoing operating expenses that cannot be directly associated with generating profits. It identifies three main types of overhead: 1) Administrative overheads like salaries and office supplies, 2) Manufacturing overheads incurred in factories like depreciation and property taxes, 3) How overheads are applied, such as in break-even analysis and shutdown graphs, to determine pricing and whether a business should continue operating. Examples are provided for each type of overhead.