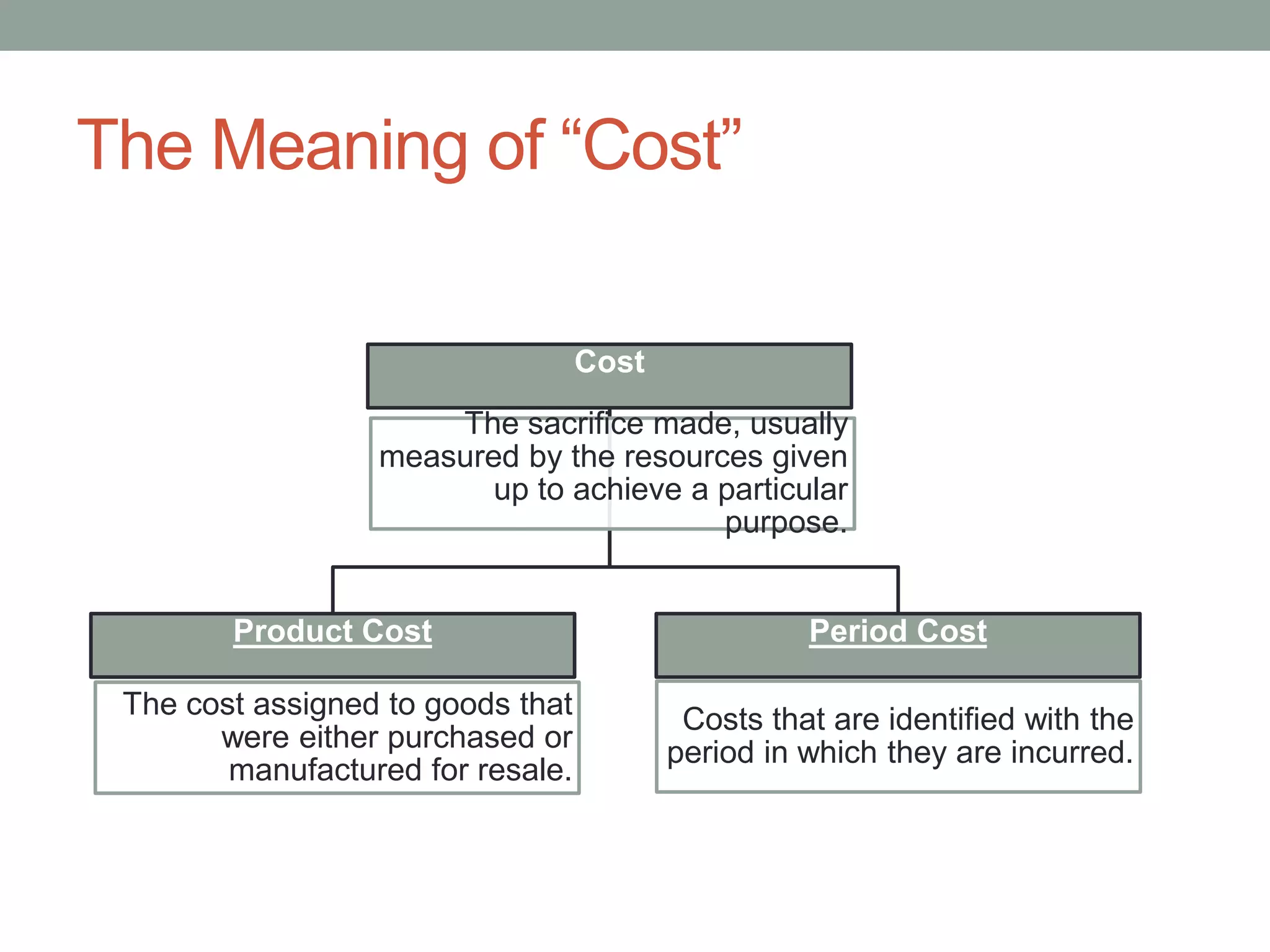
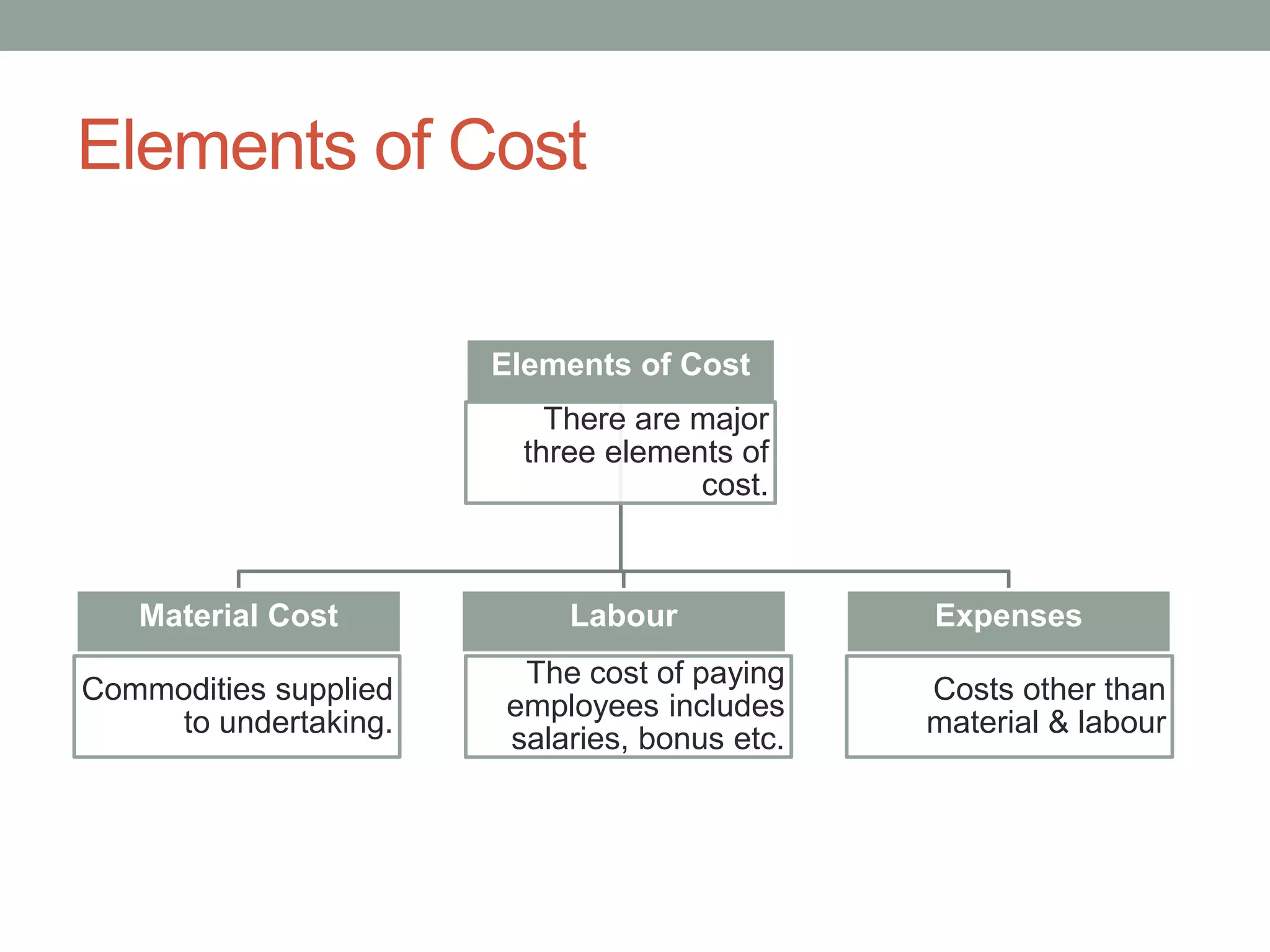
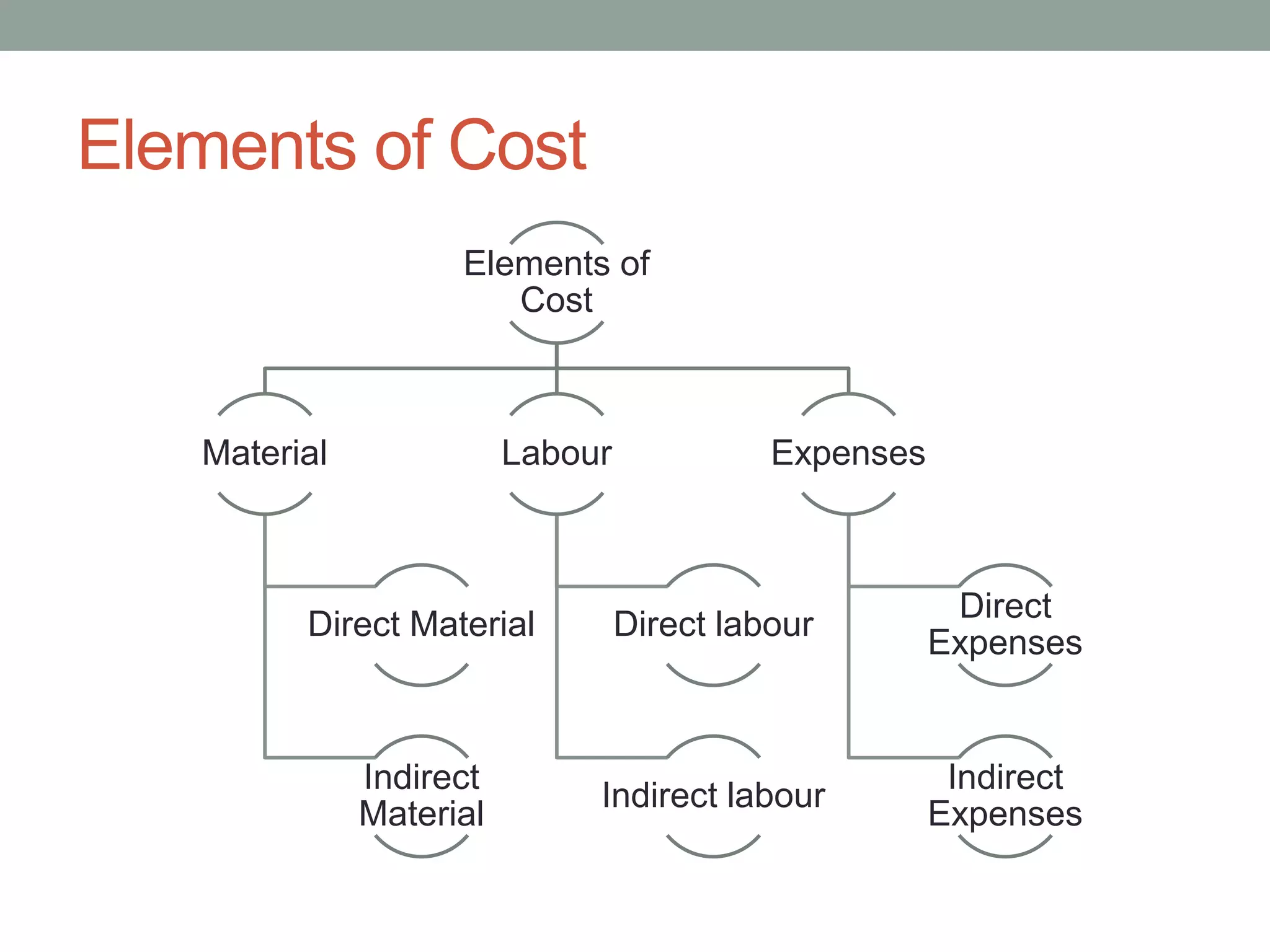
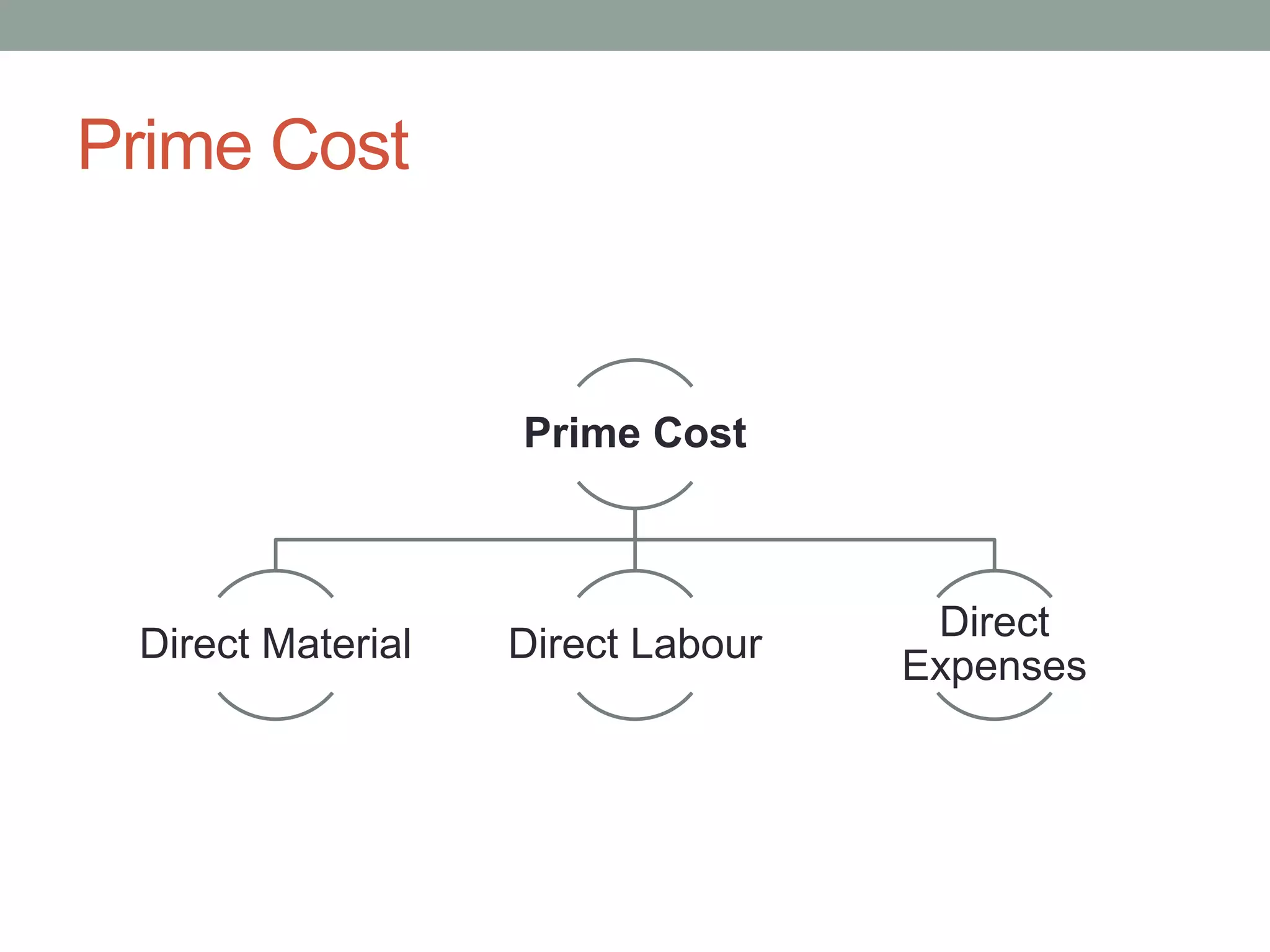
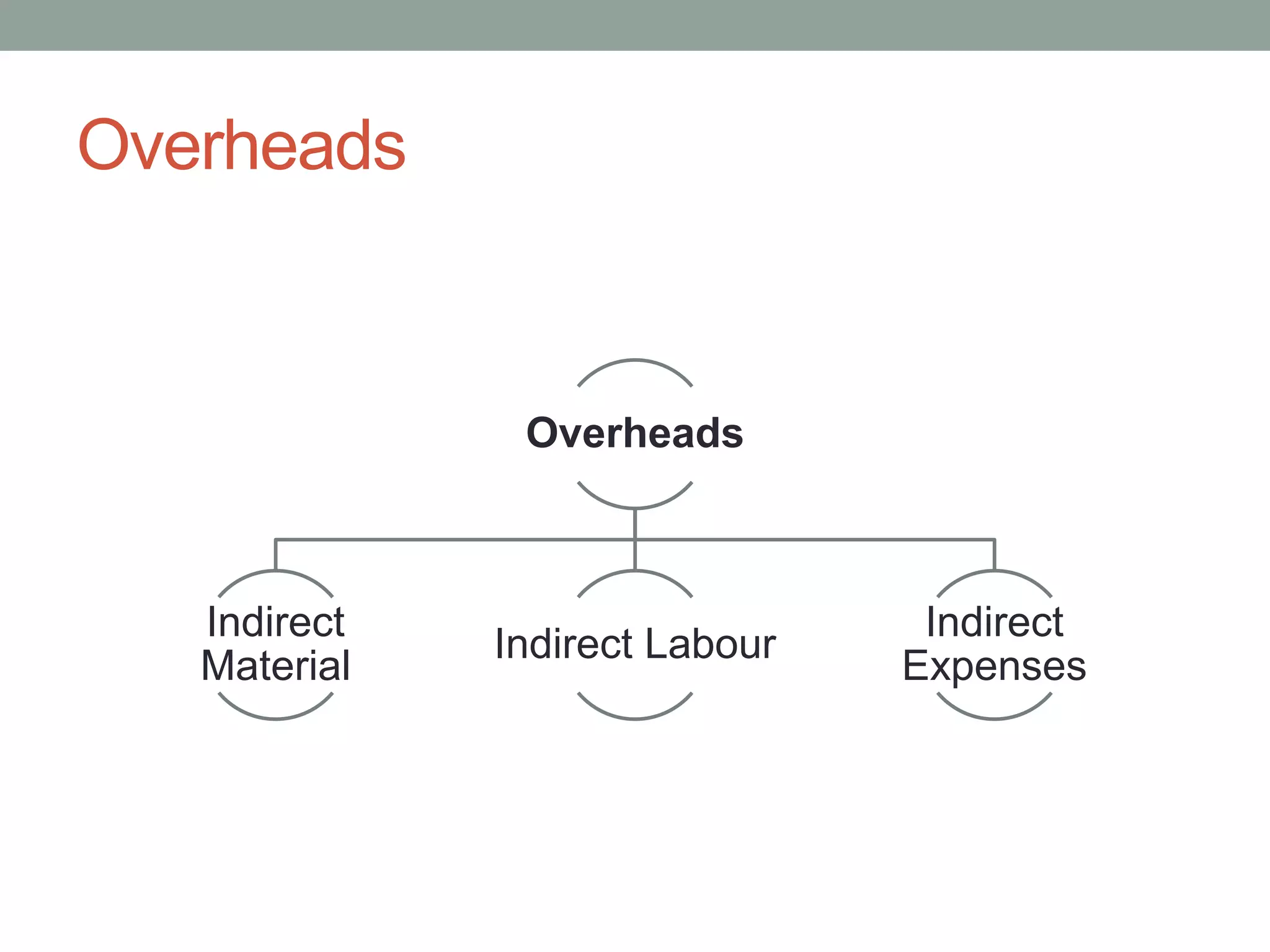
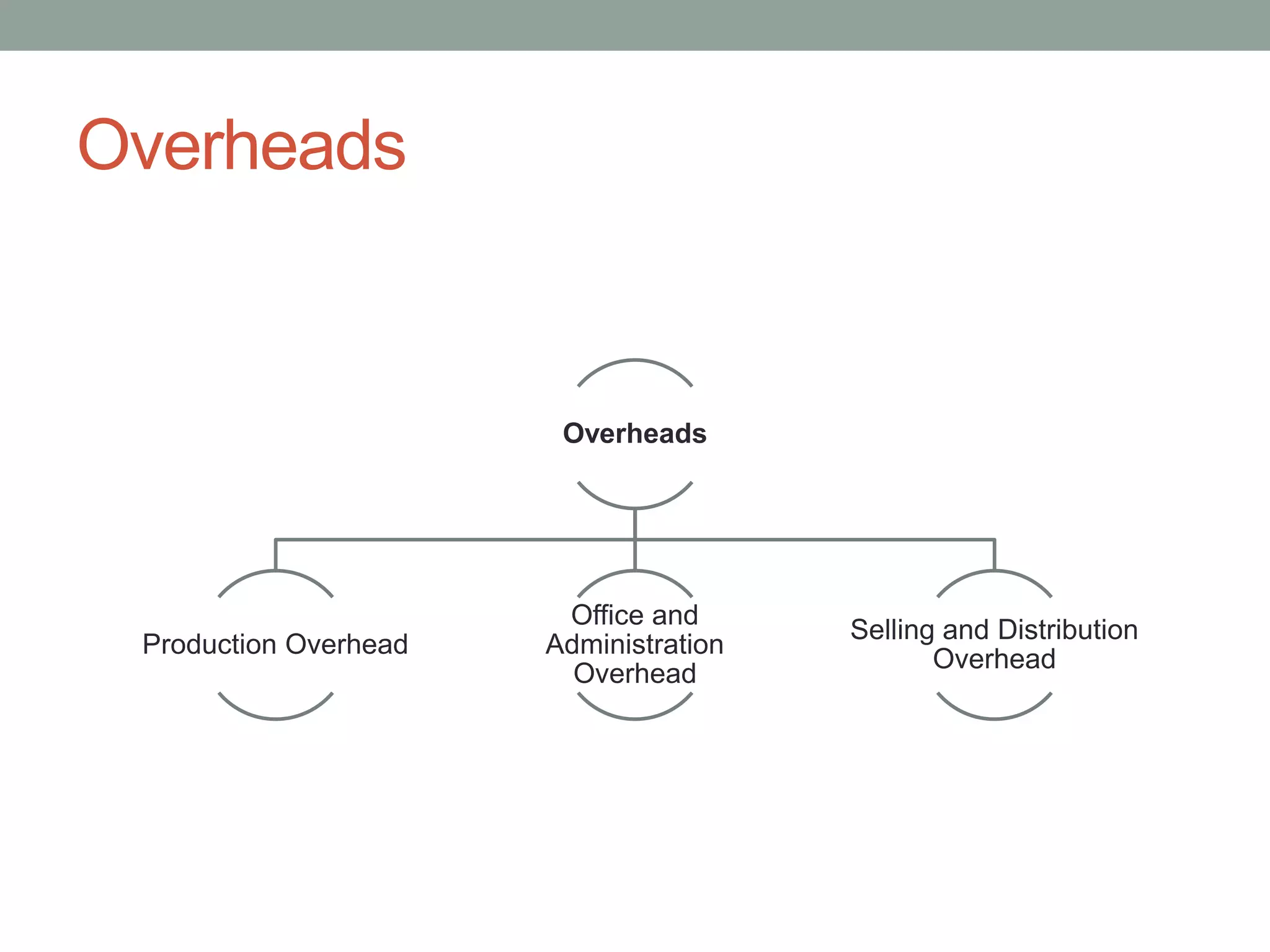
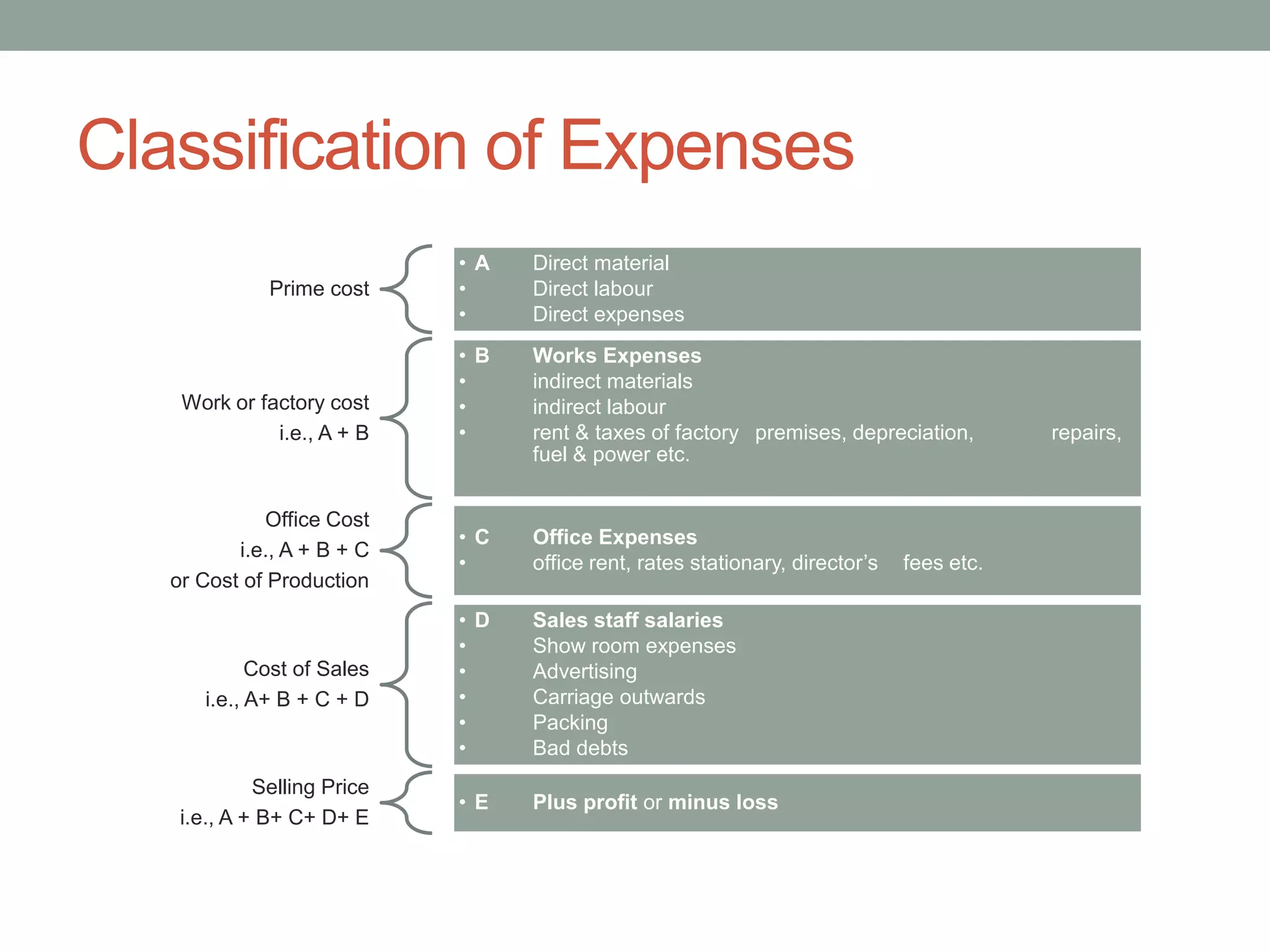
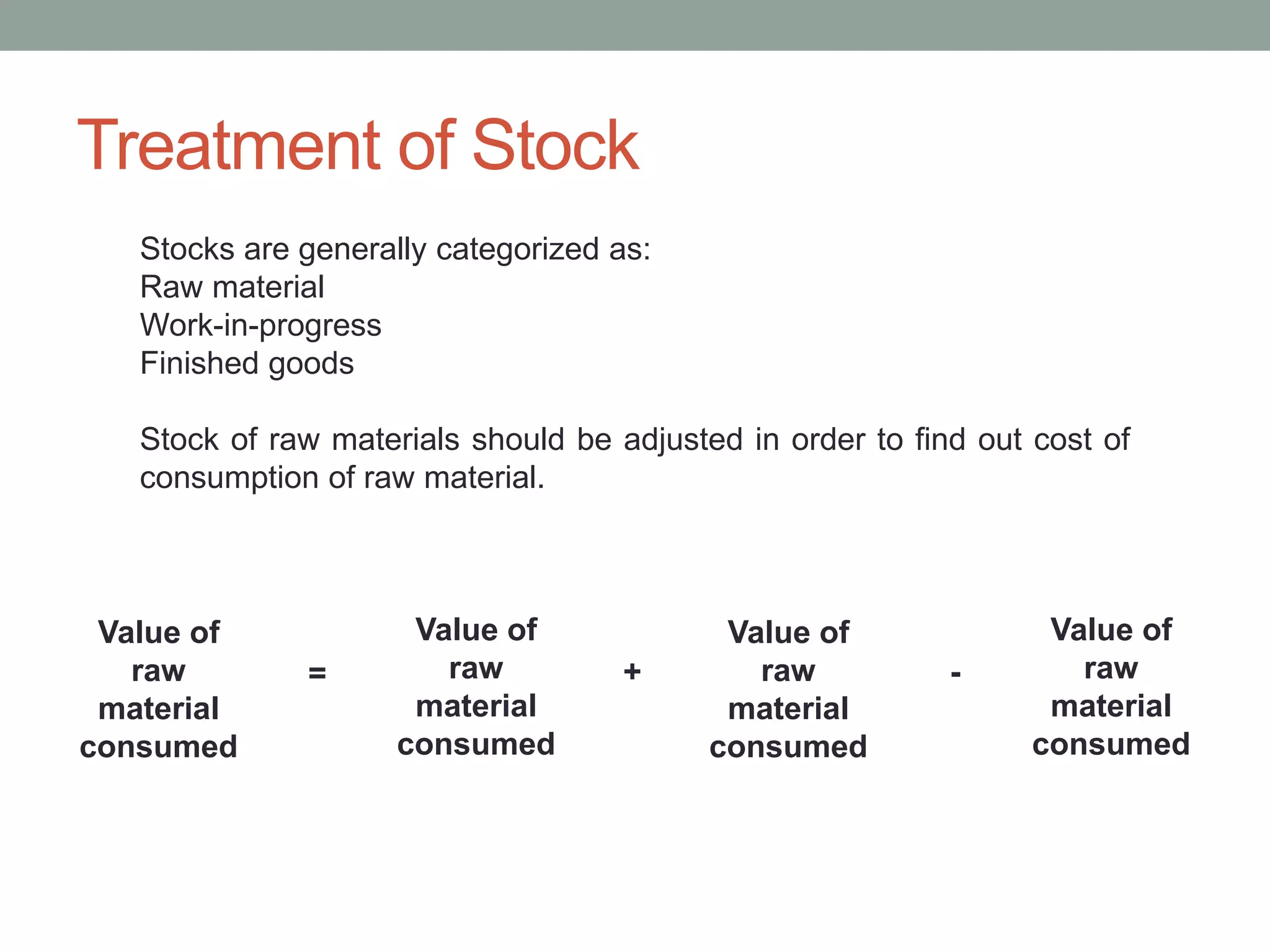
This document discusses costing concepts and elements of cost. It defines cost as the monetary value of all sacrifices made to achieve an objective. The three main elements of cost are material, labor, and expenses. Material can be direct or indirect, as can labor and expenses. Prime cost includes direct material, direct labor, and direct expenses. Overheads include indirect material, indirect labor, and indirect expenses. Stocks like raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods must be accounted for when calculating costs. Expenses excluded from costs are those related to profits like income tax and interest on capital.