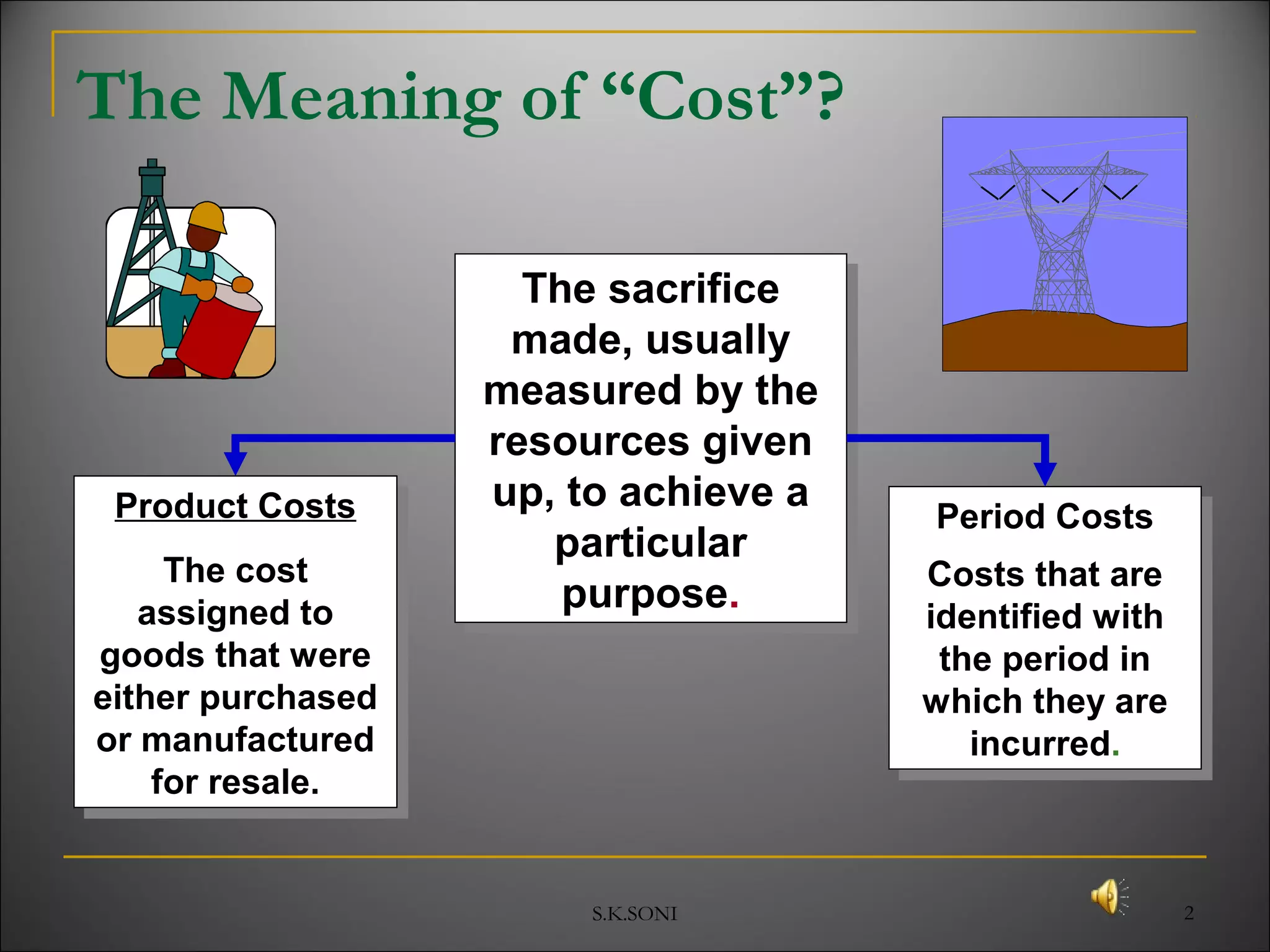
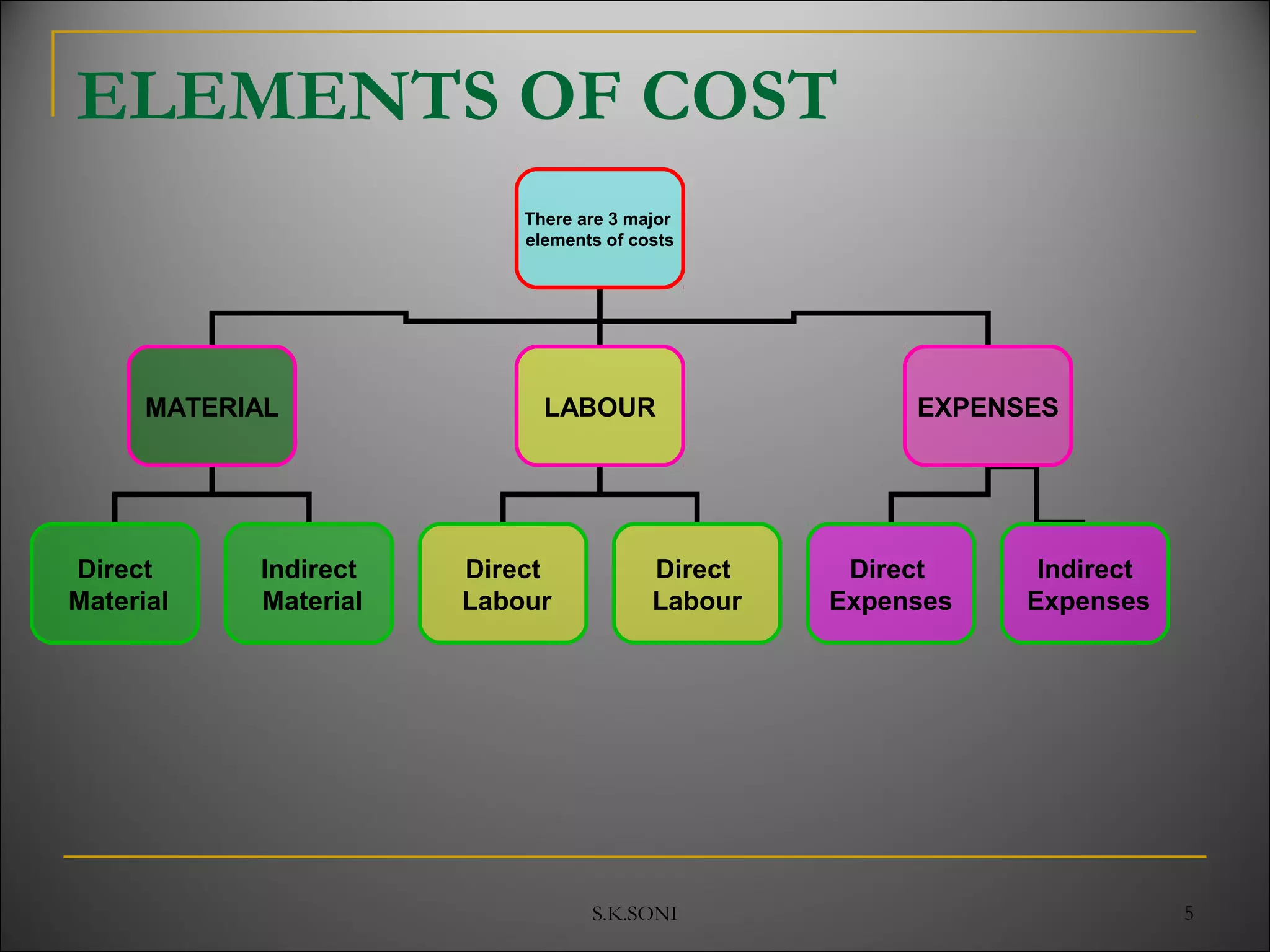
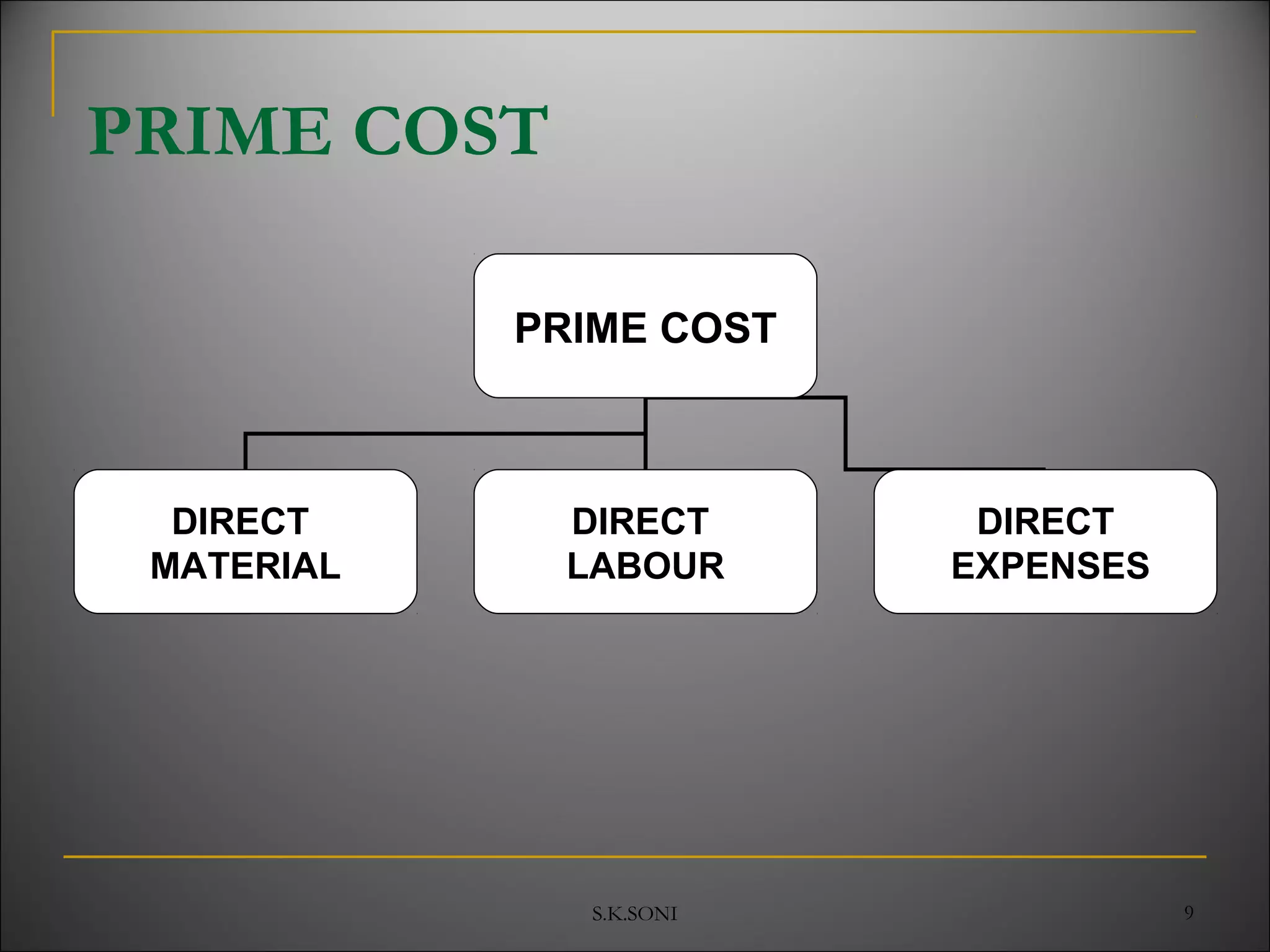
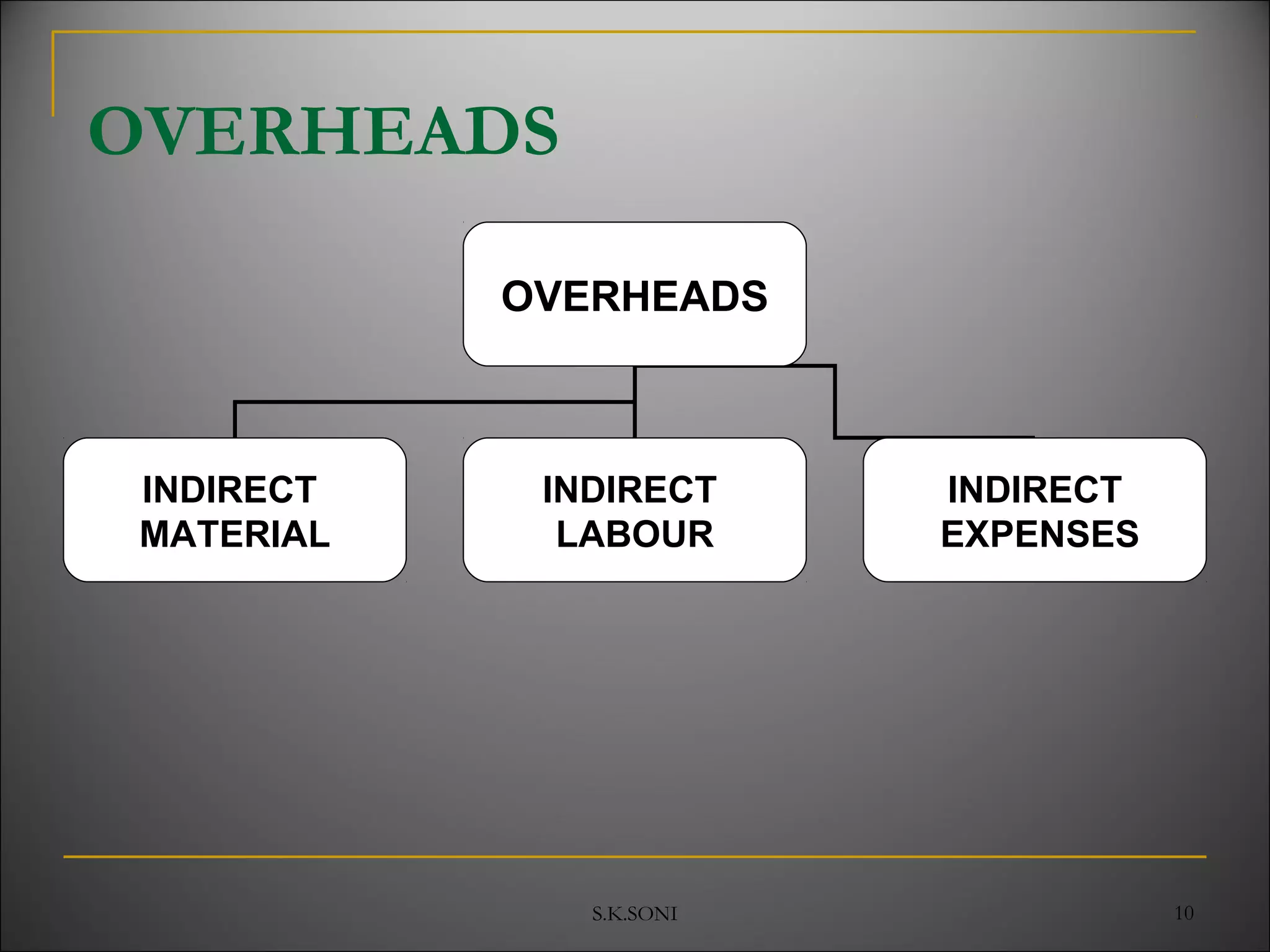
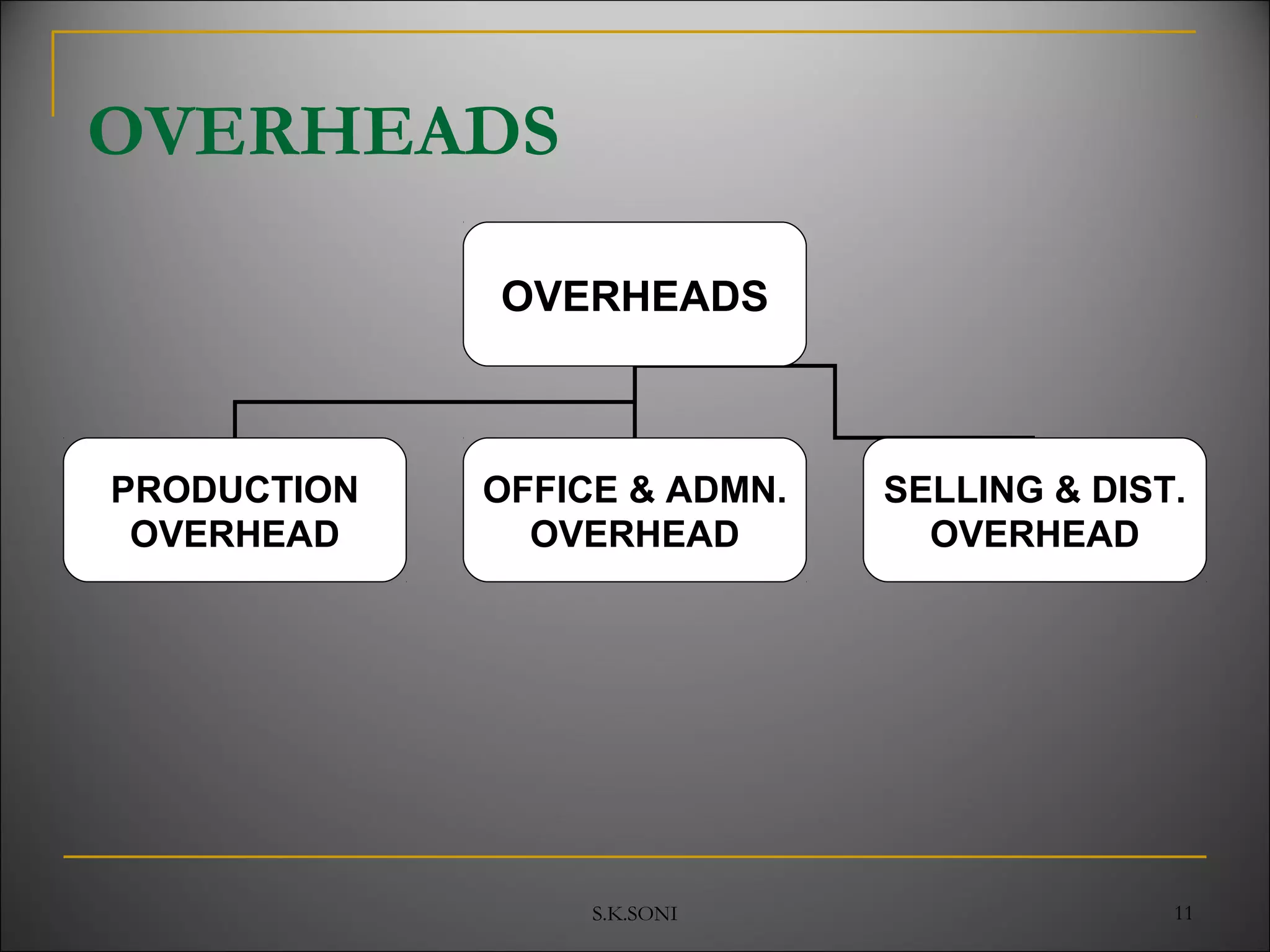
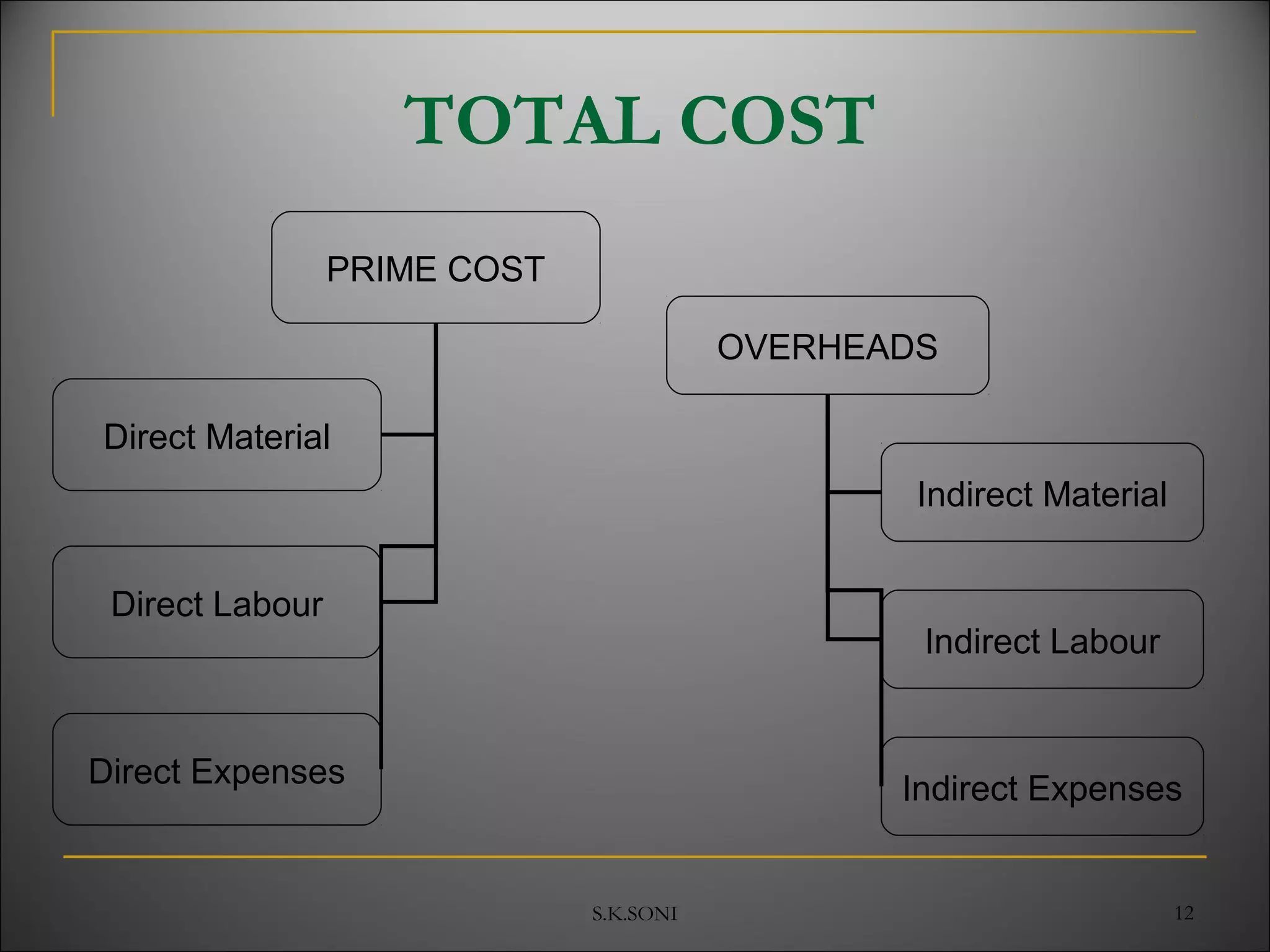
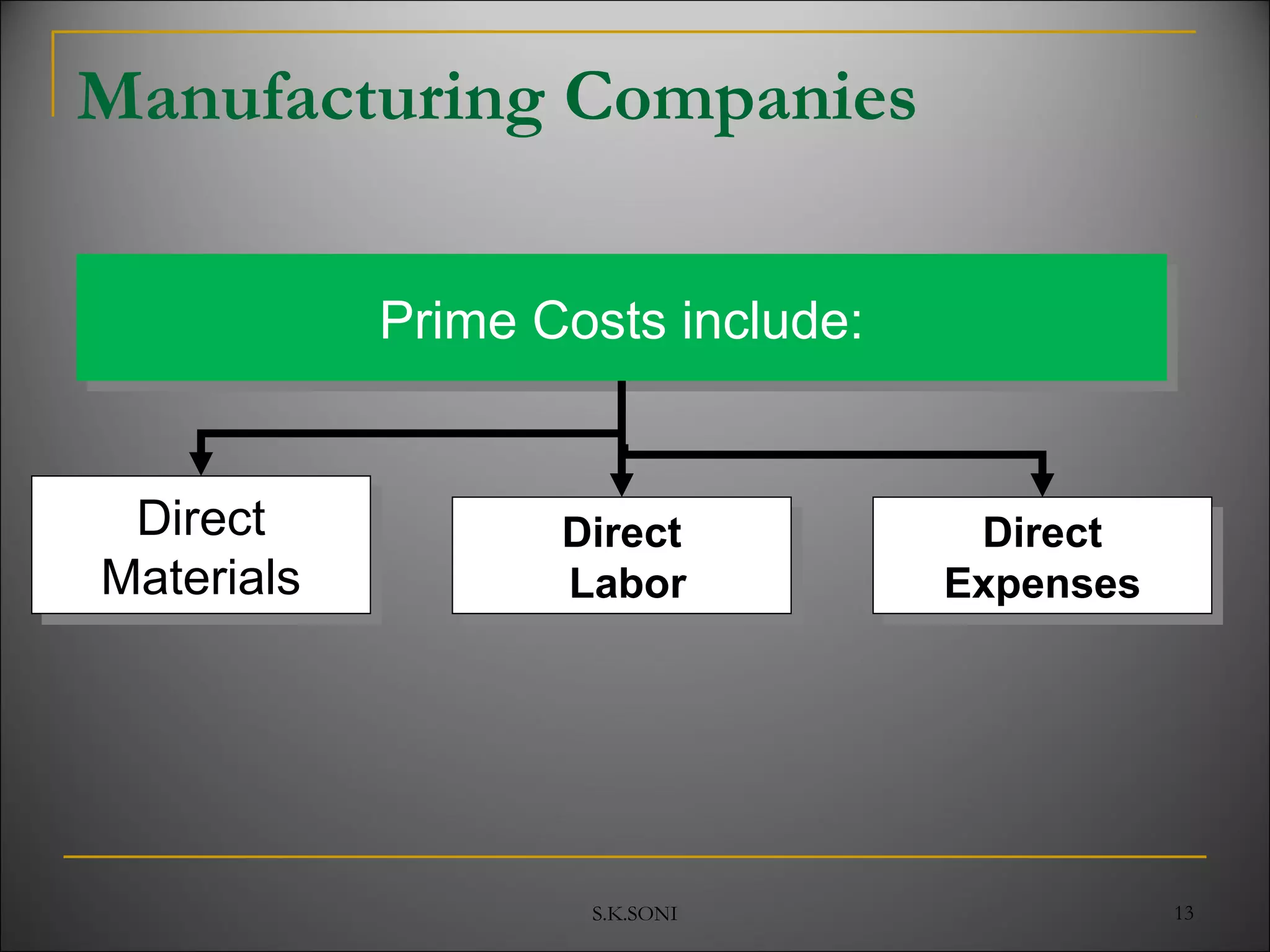
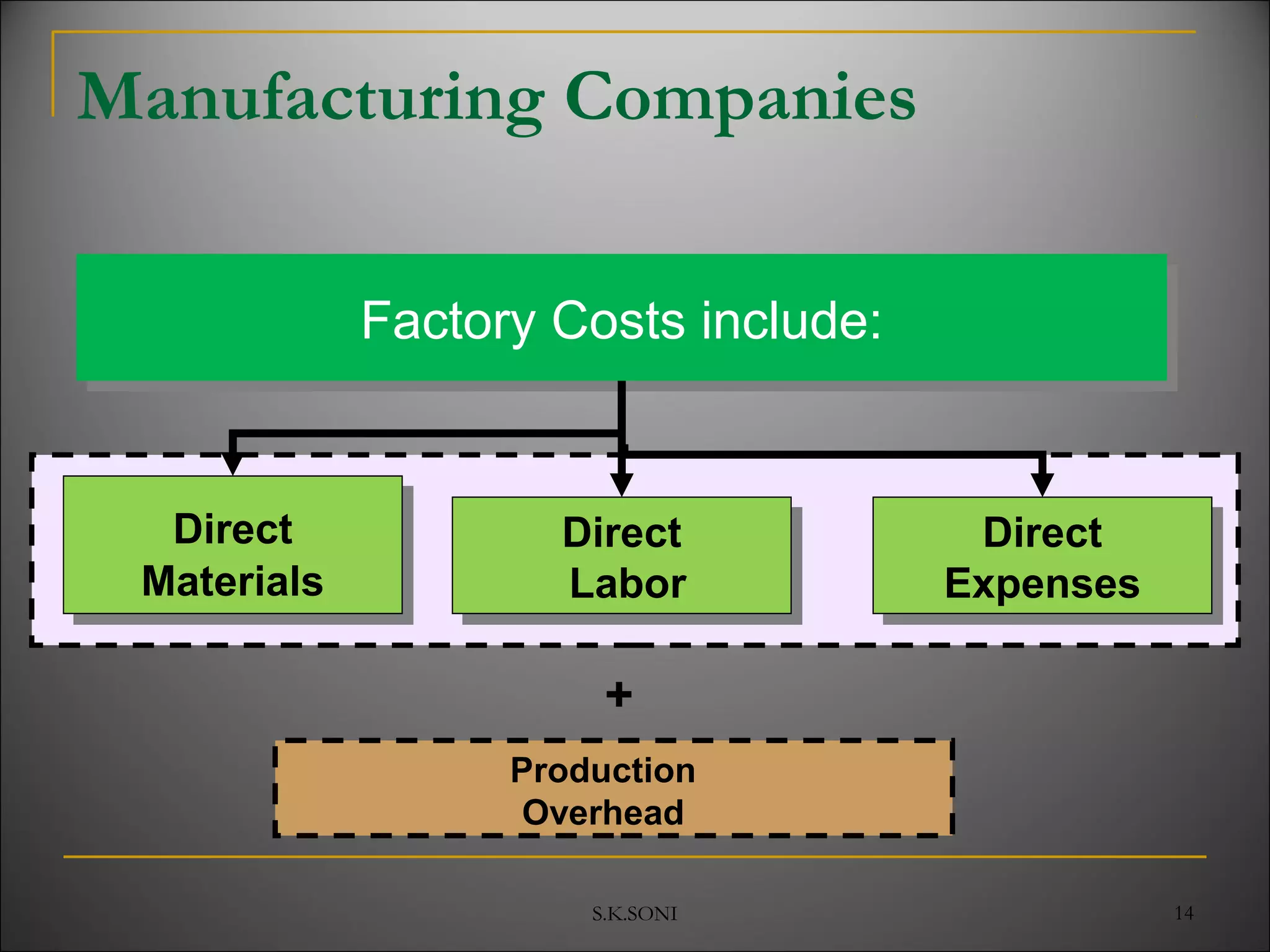
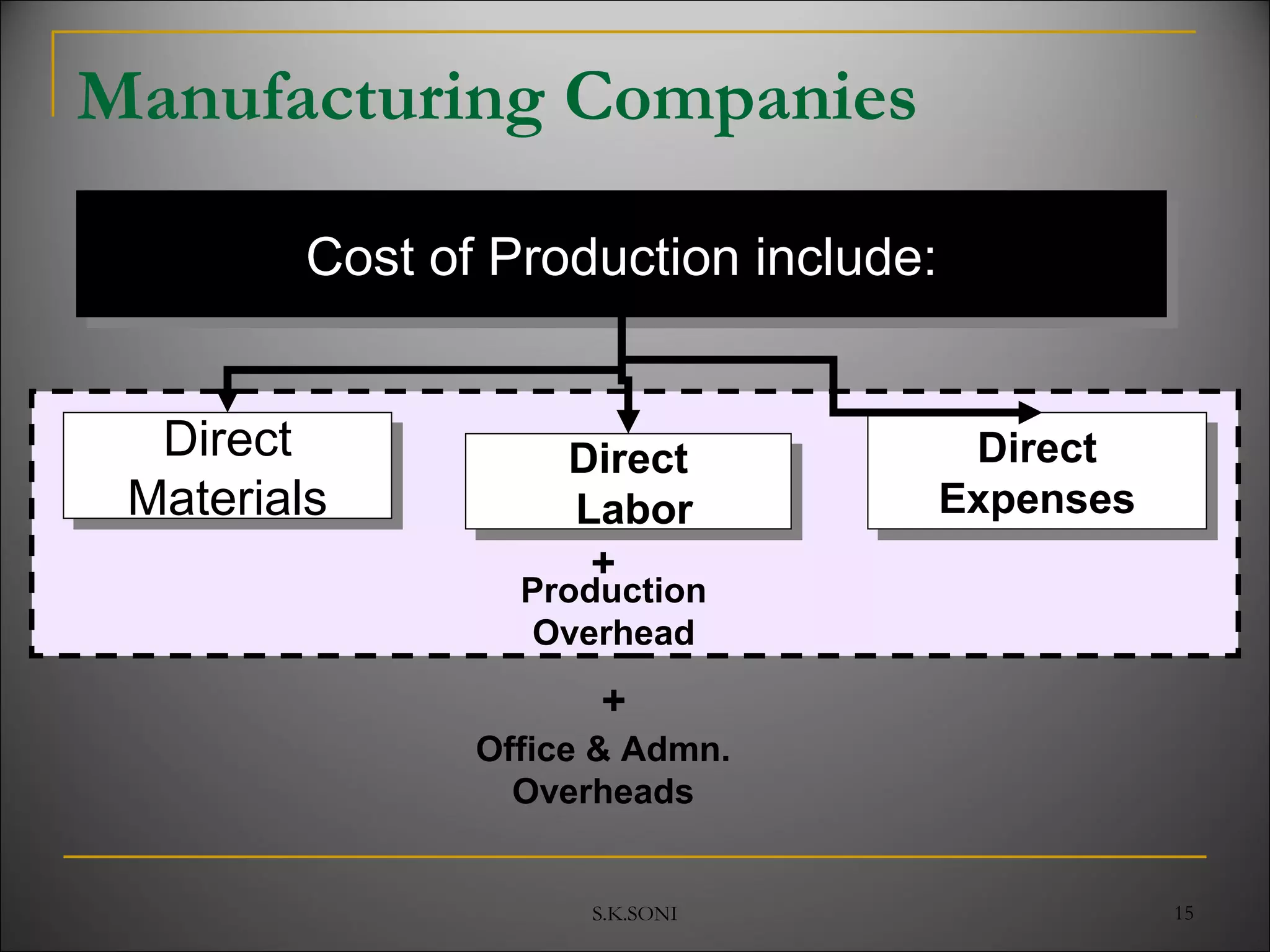
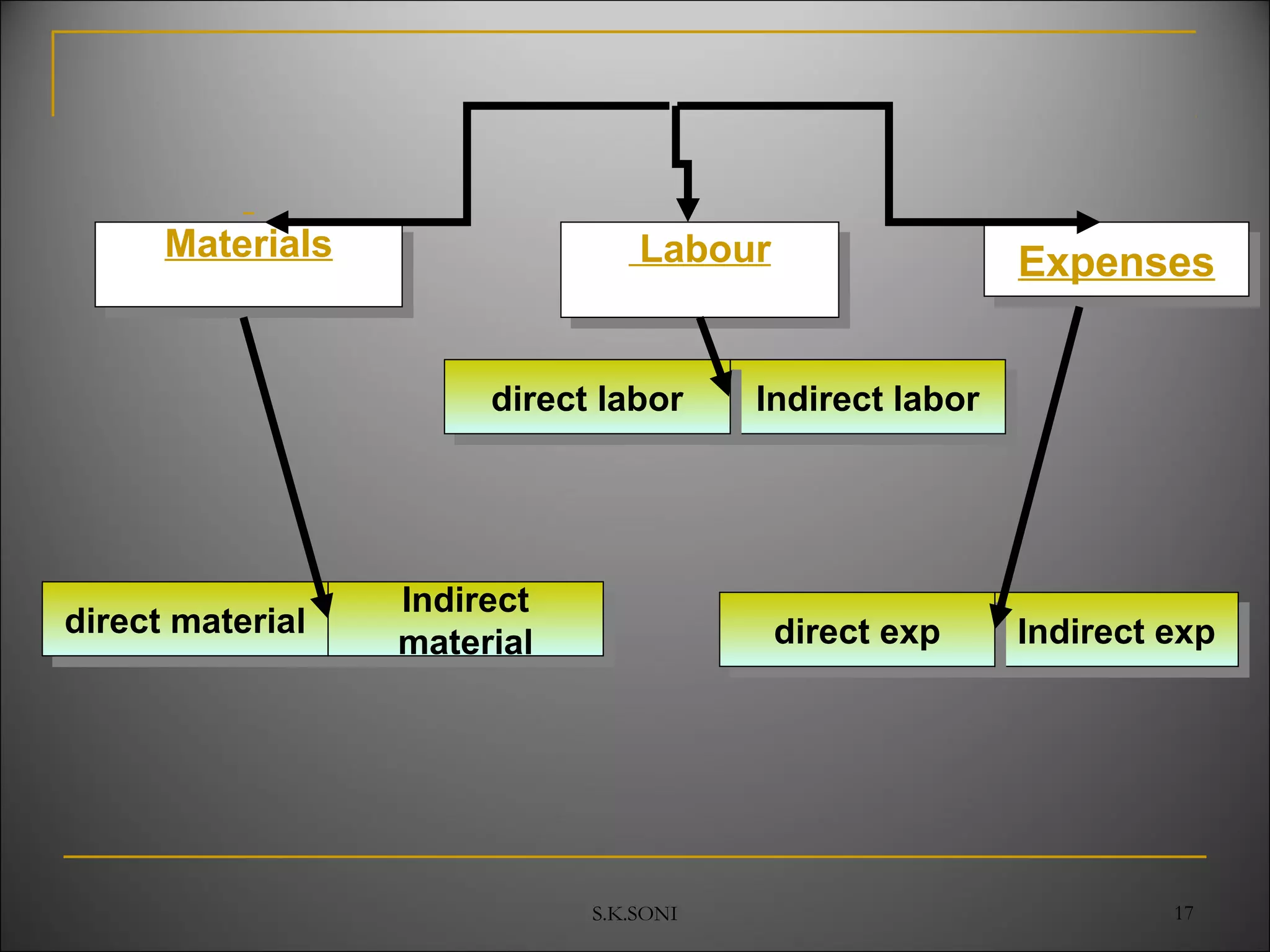
This document defines key cost accounting terms and concepts. It discusses that cost is the monetary value of all resources sacrificed to achieve an objective. There are three major elements of cost: materials, labor, and expenses. Costs are further broken down into direct and indirect costs. Direct costs can be traced to a specific cost object, while indirect costs cannot. The document also outlines different levels of costs including prime cost, factory cost, cost of production, and cost of sales. It provides manufacturing companies as an example, detailing the various costs that make up each level.