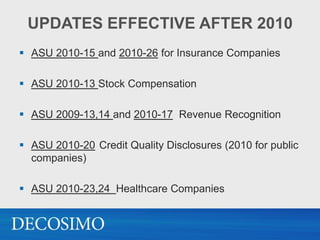
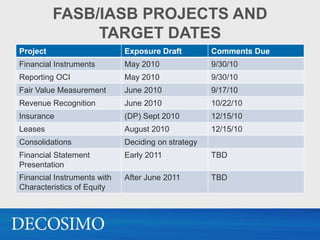
The document summarizes recent updates in accounting standards and the ongoing convergence projects between the FASB and IASB. Several standards were codified in 2009 without changing GAAP. New standards in 2010 related to consolidation of variable interest entities, fair value disclosures, and revenue recognition. Ongoing convergence projects address financial instruments, revenue recognition, leases, and consolidations. The SEC will decide in 2011 whether and when to require US companies to adopt IFRS. Private companies may adopt IFRS, IFRS for SMEs, or continue with US GAAP.