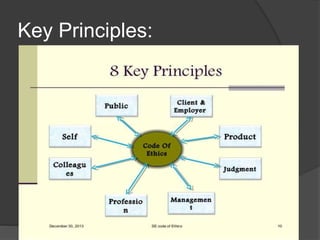
This document discusses computer ethics and the IEEE code of ethics for software engineers. It provides background on the history of computer ethics as a field emerging in the 1970s. It then discusses the IEEE as a professional organization and outlines the key principles of its code of ethics for software engineers, including their responsibilities to the public, clients/employers, products, maintaining integrity and independence in judgment, management duties, the profession, colleagues, and self-improvement.