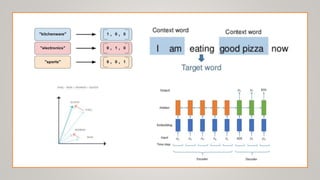
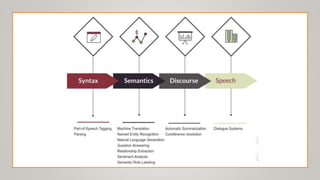
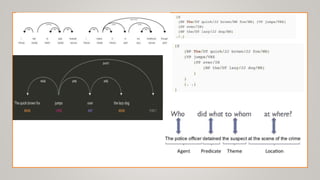
The document surveys advancements in natural language processing (NLP) through deep learning, detailing processes and models for tasks such as parsing, text classification, information extraction, sentiment analysis, machine translation, question answering, document summarization, and dialogue systems. It highlights state-of-the-art models and their respective accuracies, as well as the challenges posed by unstructured data and the computational demands of NLP tasks. The document serves as an extensive overview of methodologies and technologies shaping the current landscape of NLP.