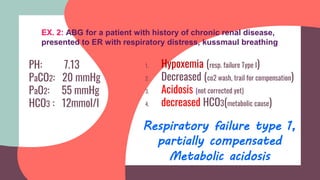
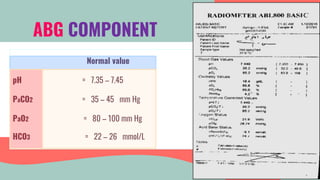
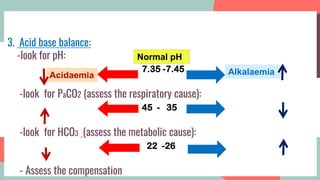
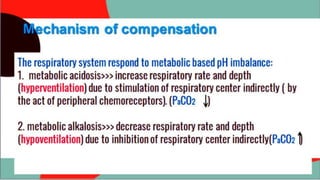
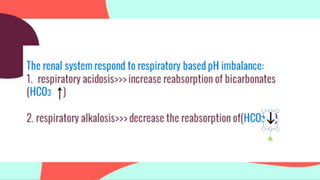
This document provides information about arterial blood gas (ABG) testing, including how to perform the test, interpret results, and assess acid-base balance and respiratory function. ABG testing measures pH, partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide, and bicarbonate levels in arterial blood to help diagnose conditions affecting ventilation, oxygenation, and acid-base balance. The radial artery is most commonly used for sampling. Results are analyzed to determine if a patient has hypoxemia, respiratory acidosis or alkalosis, or a metabolic imbalance. Compensation by the respiratory or renal systems in response to acid-base disturbances is also assessed.
















![PH 7.36
PaCO2 60 mmHg
PaO2 50 mmHg
HCO3 30 mmol/l
Respiratory failure type
2,fully compensated
Respiratory acidosis
1. Decreased PaO2 [hypoxemia]
2. Increased(hypercapnea i.e respiratory cause)
3. Normal pH (corrected)
4. increased HCO3 (compensation)
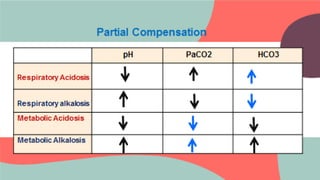
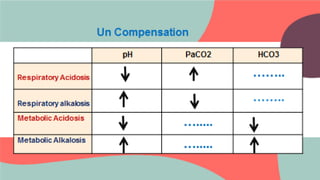
INTERPRETATION OF ABG RESULTS:
Exp.1 : ABG sample for a patient in ER diagnosed as acute
exacerbation COPD :
N.B. Even if pH was normal
look for PaCO2 and HCO3
to exclude compensated
acid base imbalance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abglast-210326222819/85/ABG-test-26-320.jpg)