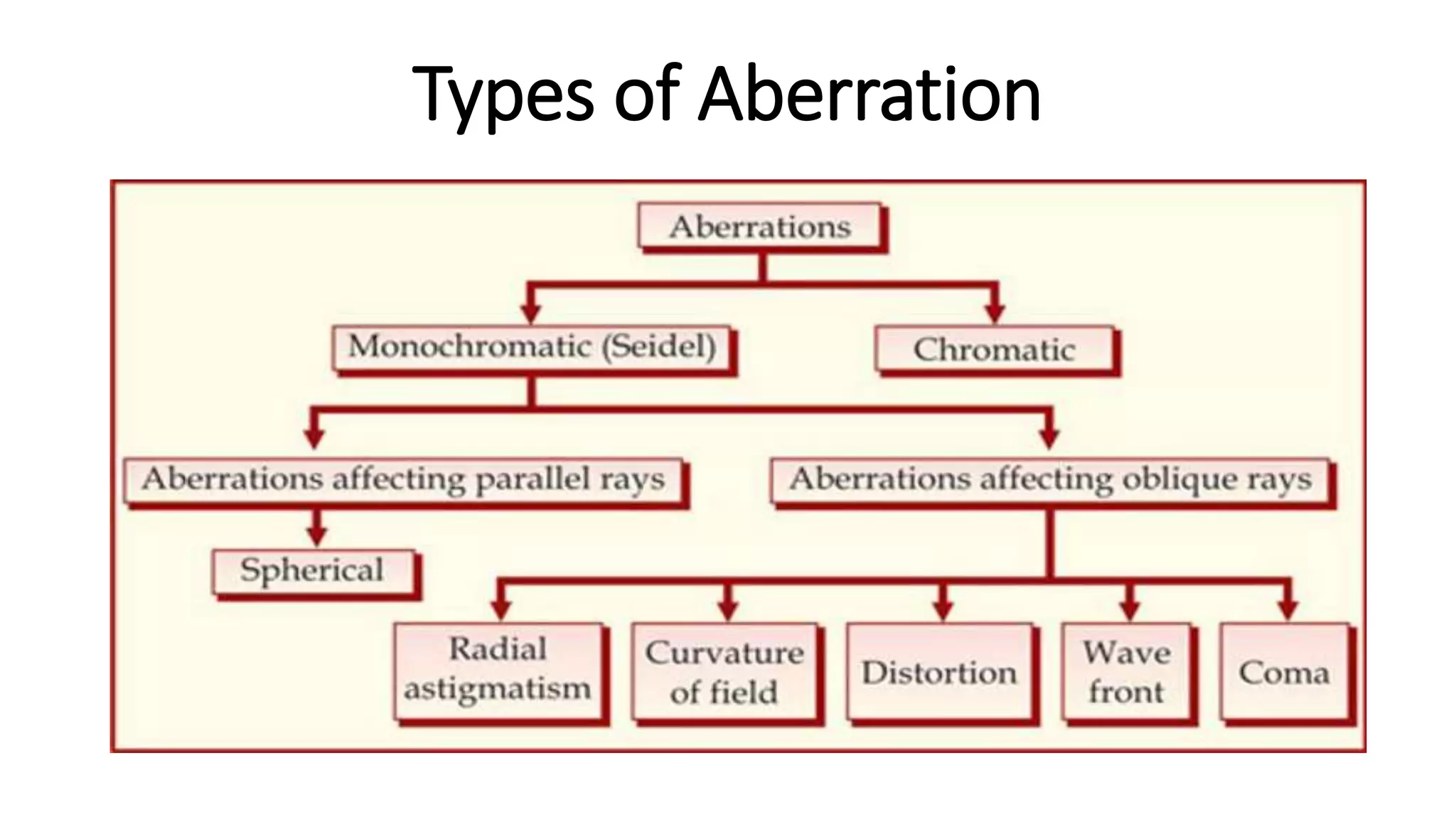
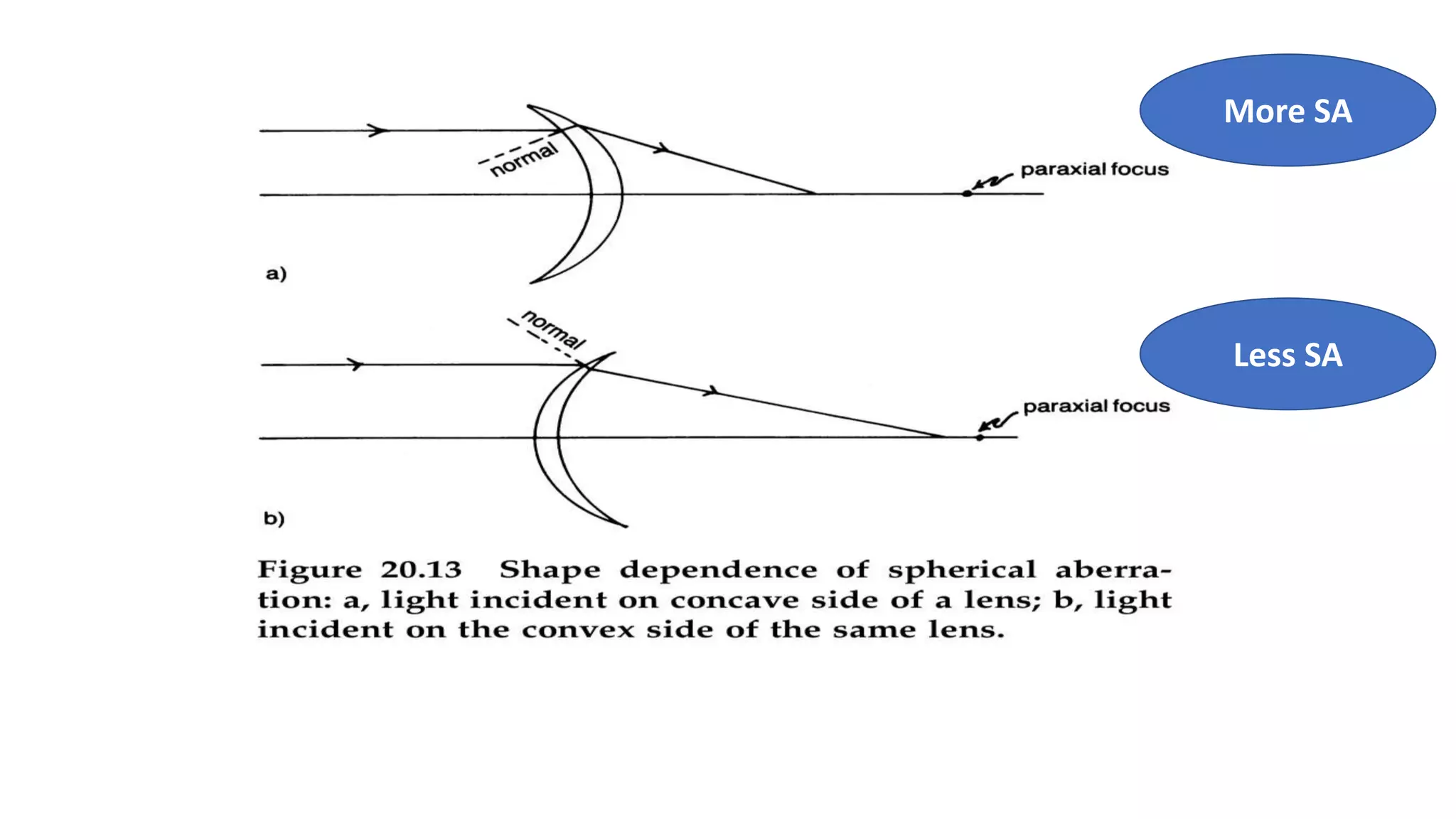
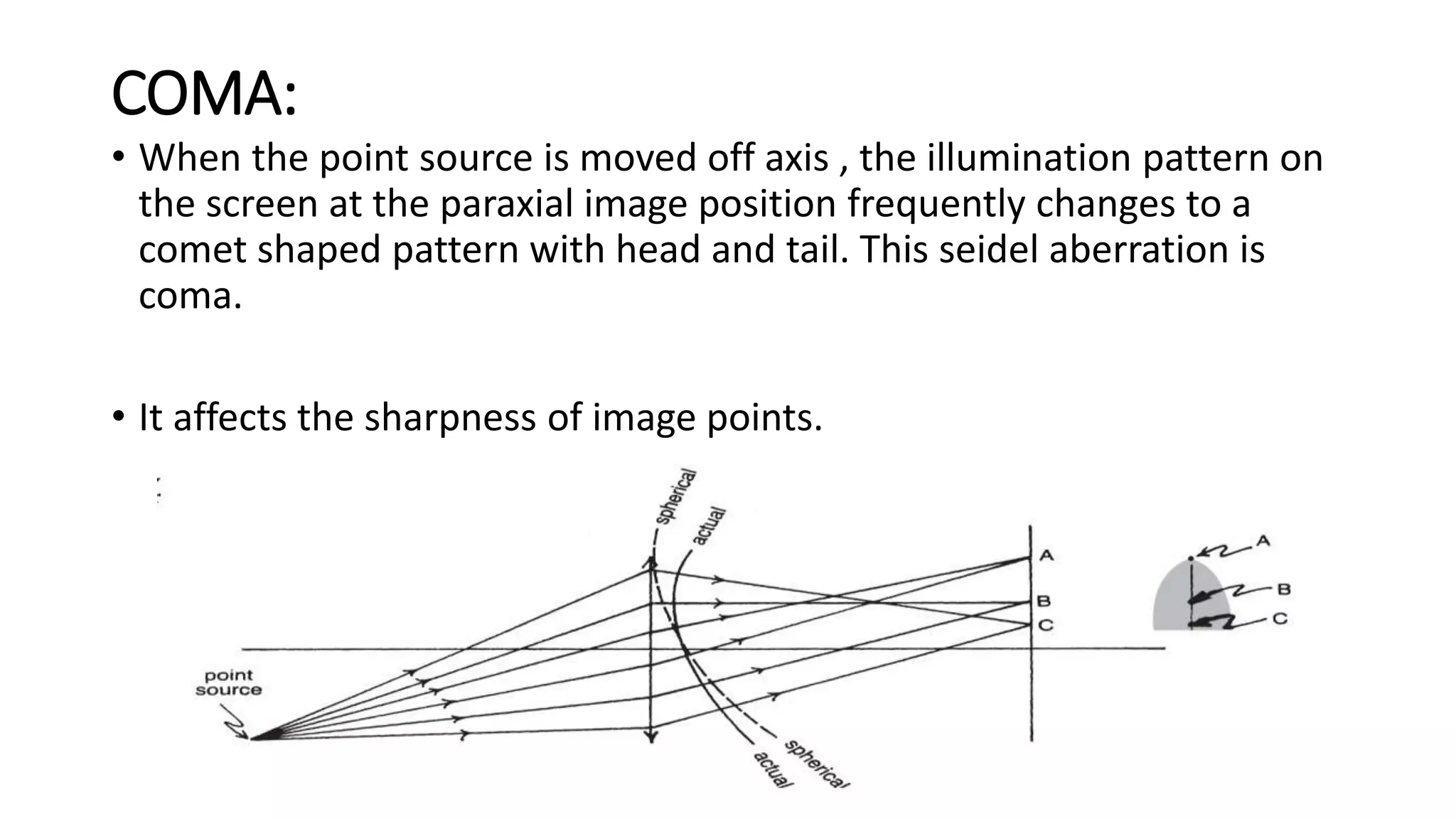
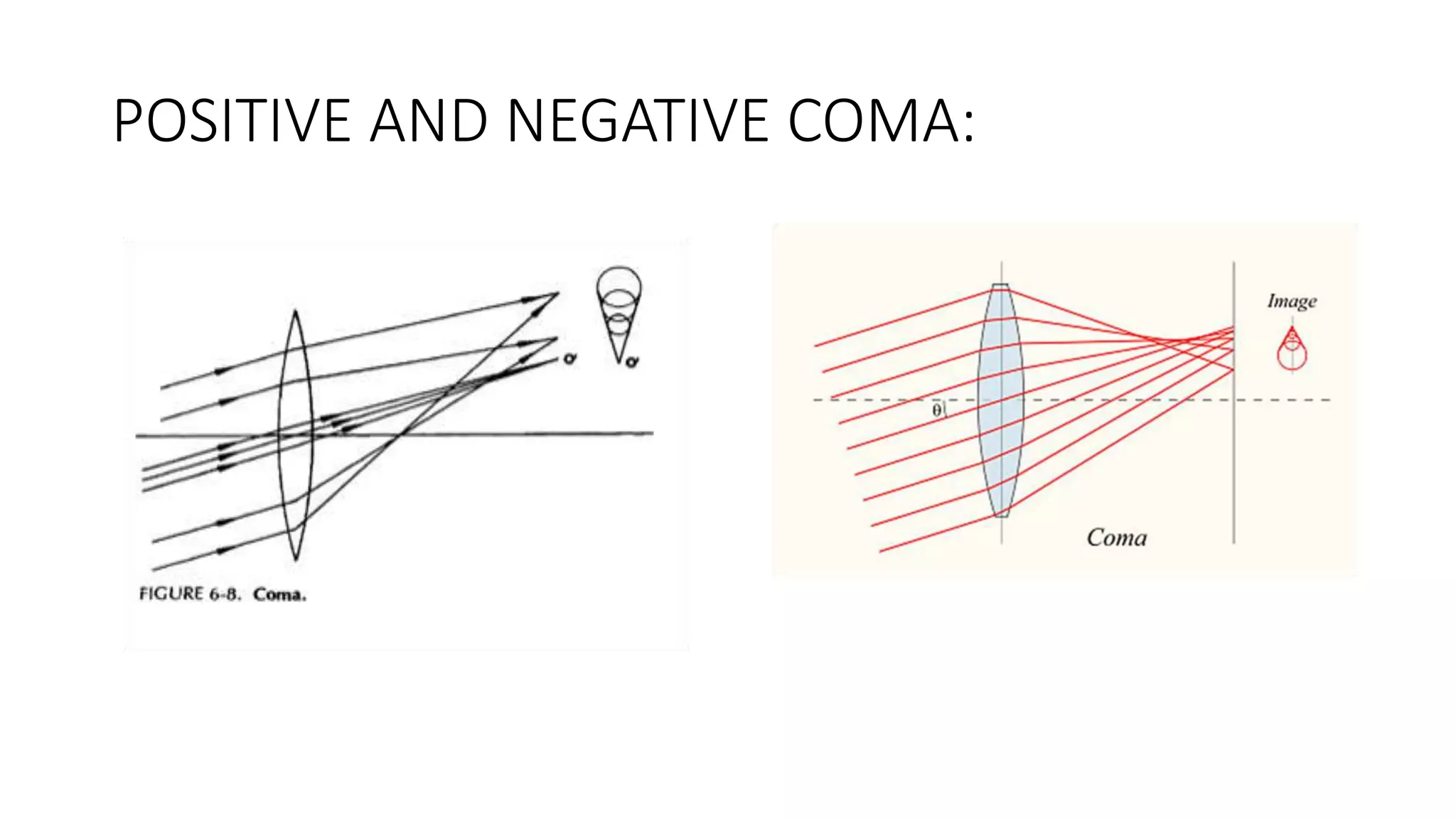
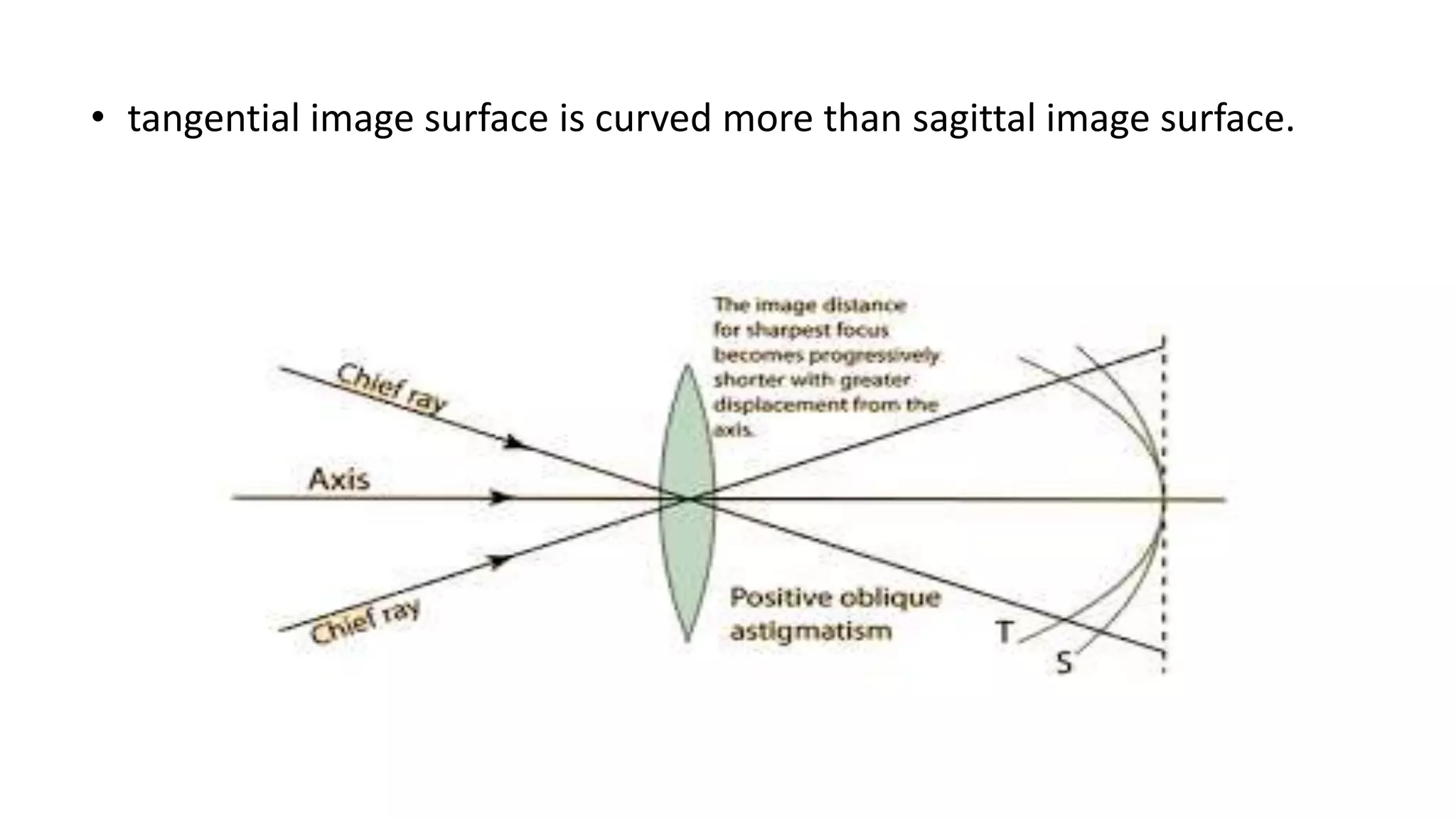
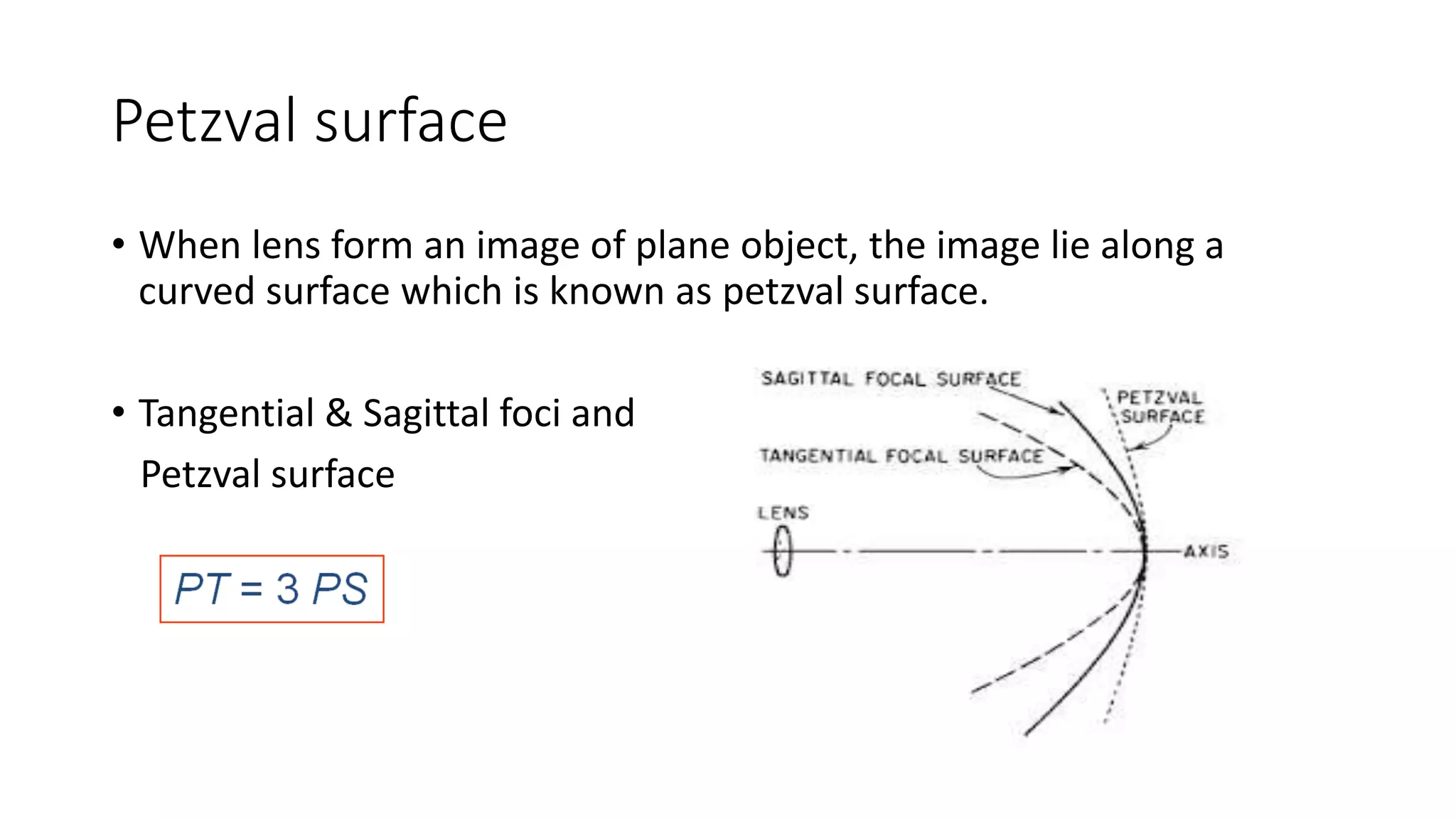
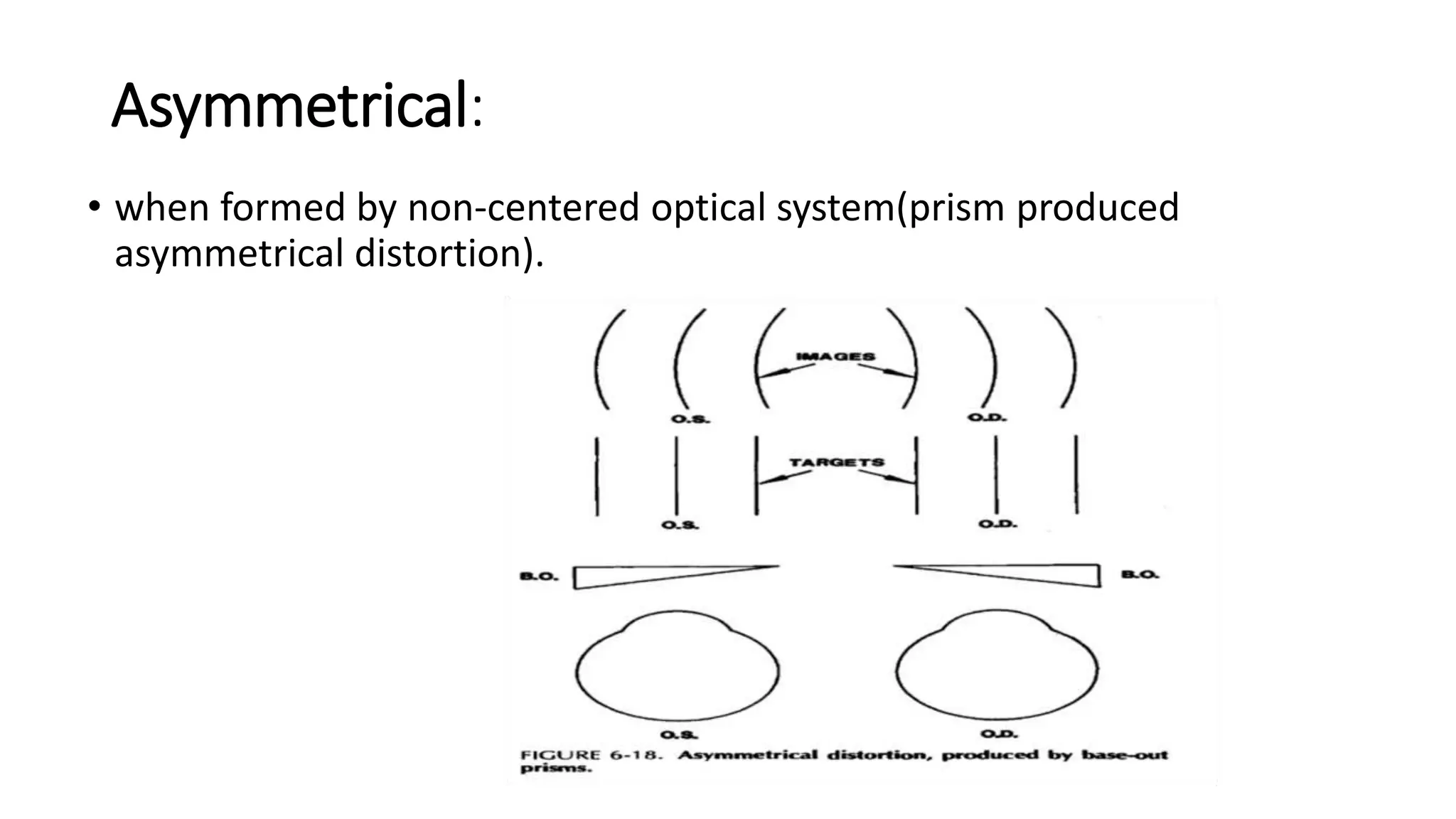
Aberrations are defects in an optical system that prevent light from being brought to a single focus. There are two main types: chromatic aberration, caused by the wavelength-dependent refractive index of materials, and monochromatic aberration, caused by flaws in the lens design. Five primary monochromatic aberrations were described by Seidel: spherical aberration, coma, astigmatism, field curvature, and distortion. Spherical aberration occurs when peripheral rays converge at a different point than paraxial rays, degrading image focus. Coma and astigmatism affect image sharpness for off-axis points. Field curvature results in a curved image plane rather than a flat one. Distortion al