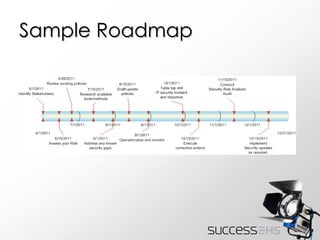
The document discusses the importance of IT security best practices for healthcare organizations. It outlines why IT security is important, how to get started with a security program, and provides information on specific best practices. These include recommendations for securing remote users' access to protected health information, implementing system log management, and meeting meaningful use security criteria. The document aims to help healthcare organizations develop an IT security roadmap.