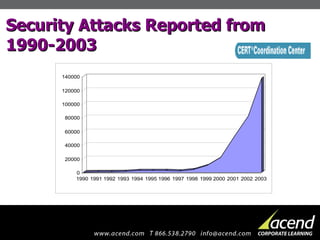
The document discusses the importance of information security for businesses, highlighting risks such as data breaches and their financial implications. It identifies common types of attacks like viruses and insider abuse, providing security strategies and top tips for mitigating risks. Lastly, it promotes Acend's customized corporate learning solutions to enhance employee training in security practices.